Acquisition plays a critical role in business growth by enabling companies to expand their market share, diversify product offerings, and gain competitive advantages. Understanding the strategic approaches and challenges involved in acquisition can empower your decision-making process. Explore the rest of the article to discover key insights that will enhance your acquisition strategy.
Table of Comparison
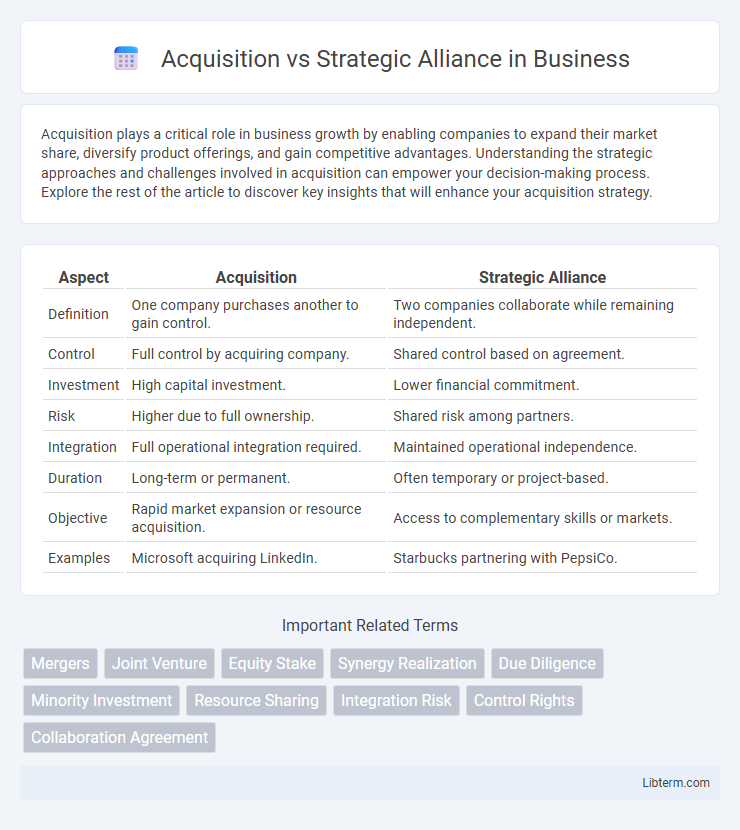
| Aspect | Acquisition | Strategic Alliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One company purchases another to gain control. | Two companies collaborate while remaining independent. |
| Control | Full control by acquiring company. | Shared control based on agreement. |
| Investment | High capital investment. | Lower financial commitment. |
| Risk | Higher due to full ownership. | Shared risk among partners. |
| Integration | Full operational integration required. | Maintained operational independence. |
| Duration | Long-term or permanent. | Often temporary or project-based. |
| Objective | Rapid market expansion or resource acquisition. | Access to complementary skills or markets. |
| Examples | Microsoft acquiring LinkedIn. | Starbucks partnering with PepsiCo. |
Understanding Acquisitions and Strategic Alliances
Acquisitions involve one company purchasing another to gain full control, often leading to immediate integration of resources and market expansion. Strategic alliances are collaborative agreements between companies to share resources and expertise while remaining independent, facilitating flexibility and joint innovation. Understanding the differences in control, risk, and long-term goals is essential for selecting the appropriate growth strategy.
Key Differences Between Acquisition and Strategic Alliance
Acquisition involves one company purchasing another to gain full control over its assets, operations, and decision-making, often resulting in complete ownership and integration. A strategic alliance, by contrast, is a collaborative agreement where companies retain independence while sharing resources, knowledge, or capabilities to achieve mutual goals without ownership transfer. Key differences include the level of control, financial investment, risk assumption, and the permanence of the relationship, with acquisitions requiring higher capital outlay and deeper integration versus the flexible, often temporary nature of strategic alliances.
Advantages of Acquisitions
Acquisitions offer companies complete control over the acquired entity's assets, resources, and operations, enabling faster integration and unified strategic direction. They provide access to established customer bases and proprietary technologies, reducing market entry risks and accelerating growth opportunities. Financial benefits include potential tax advantages and economies of scale, which enhance overall competitive positioning.
Benefits of Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances offer companies the advantage of shared resources and expertise without the complexities and financial burdens associated with acquisitions. These partnerships enable faster market entry and innovation by combining complementary strengths while maintaining organizational independence. Collaborative risk-sharing and flexibility allow firms to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and leverage new opportunities efficiently.
Risks and Challenges in Acquisitions
Acquisitions involve significant risks such as cultural integration difficulties, high financial costs, and potential regulatory hurdles that can delay or block the deal. The challenge of aligning operational processes and management styles often leads to employee turnover and loss of key talent. Financial risks also include overvaluation of the target company and unforeseen liabilities that can erode expected synergies and undermine long-term profitability.
Potential Drawbacks of Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances can face challenges such as misaligned objectives, which lead to conflicts and inefficiencies between partners. Differences in corporate culture and management styles often create communication barriers, hindering collaboration and decision-making. Furthermore, the lack of full control over key operations may expose companies to risks related to intellectual property and competitive advantage erosion.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Acquisition and Alliance
Evaluating financial resources, control requirements, and time to market is crucial when choosing between acquisition and strategic alliance. Acquisitions demand significant capital investment and provide full control but involve longer integration periods, while strategic alliances offer flexibility, lower upfront costs, and faster market entry with shared control risks. Assessing cultural compatibility, strategic objectives, and regulatory impact further guides the decision toward the optimal growth mechanism.
Case Studies: Successful Acquisitions vs Strategic Alliances
Amazon's acquisition of Whole Foods in 2017 demonstrated the power of acquisitions to rapidly expand market reach and integrate supply chains, boosting Amazon's presence in the grocery sector. In contrast, the strategic alliance between Starbucks and PepsiCo enabled the global distribution of Starbucks' ready-to-drink coffee products without the complexities of ownership transfer. These case studies highlight how acquisitions offer full control and resource integration, while strategic alliances provide flexibility and access to complementary capabilities.
Impact on Organizational Culture and Integration
Acquisitions typically lead to a significant cultural shift as the acquiring company imposes its values and practices, often resulting in integration challenges and employee resistance. Strategic alliances maintain separate organizational identities, fostering collaboration while preserving distinct cultures and minimizing disruption. The success of either approach depends on effective communication, mutual respect, and alignment of cultural values to ensure smooth integration or partnership synergy.
Choosing the Right Growth Strategy for Your Business
Choosing the right growth strategy for your business involves evaluating acquisition and strategic alliance options based on control, resource allocation, and long-term goals. Acquisitions provide complete ownership and integration, accelerating market entry and operational synergy but require significant capital investment. Strategic alliances offer flexibility, shared risks, and access to complementary strengths without full ownership, making them ideal for businesses seeking collaboration and innovation with less financial burden.
Acquisition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com