Organizational adaptability enables businesses to respond swiftly to market changes and evolving customer demands, ensuring long-term sustainability and competitive advantage. Embracing flexible structures and fostering a culture of continuous learning empower your team to innovate and overcome unforeseen challenges. Dive into the rest of this article to discover practical strategies for enhancing your organization's adaptability.
Table of Comparison
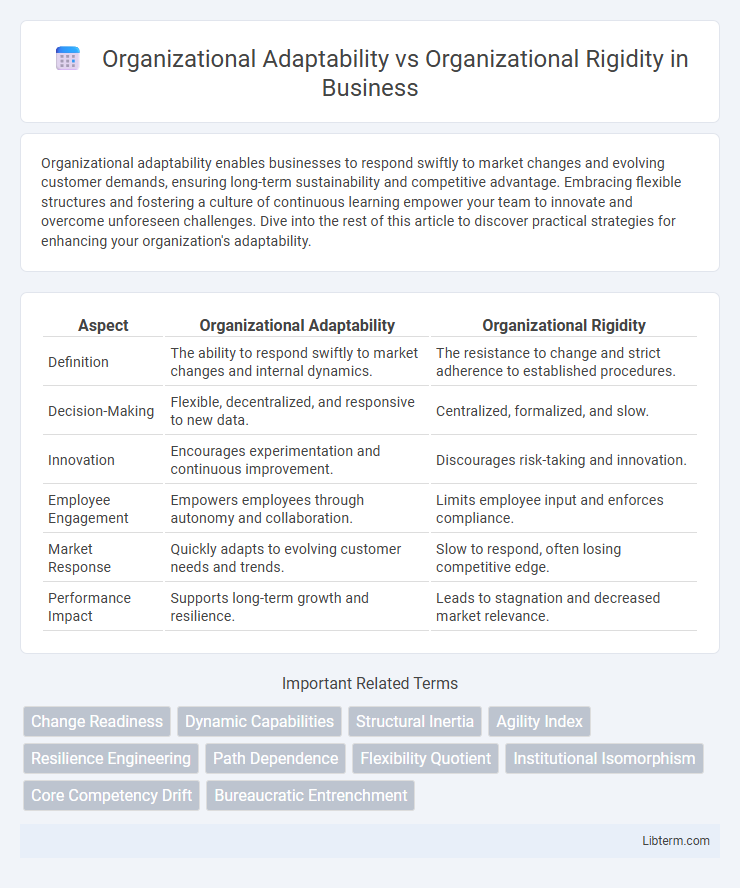
| Aspect | Organizational Adaptability | Organizational Rigidity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to respond swiftly to market changes and internal dynamics. | The resistance to change and strict adherence to established procedures. |
| Decision-Making | Flexible, decentralized, and responsive to new data. | Centralized, formalized, and slow. |
| Innovation | Encourages experimentation and continuous improvement. | Discourages risk-taking and innovation. |
| Employee Engagement | Empowers employees through autonomy and collaboration. | Limits employee input and enforces compliance. |
| Market Response | Quickly adapts to evolving customer needs and trends. | Slow to respond, often losing competitive edge. |
| Performance Impact | Supports long-term growth and resilience. | Leads to stagnation and decreased market relevance. |
Introduction to Organizational Adaptability and Rigidity
Organizational adaptability refers to a company's ability to rapidly respond and adjust to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and evolving customer demands. In contrast, organizational rigidity characterizes a resistance to change, often resulting in stagnation and reduced competitive advantage. Key factors influencing adaptability include flexible leadership, open communication, and a culture that embraces continuous learning and innovation.
Defining Organizational Adaptability
Organizational adaptability refers to a company's ability to swiftly respond to market changes, technological advancements, and evolving customer demands through flexible structures and innovative processes. It enables continuous learning, agile decision-making, and dynamic resource allocation, which drive competitive advantage and long-term sustainability. Companies exhibiting high adaptability outperform those with organizational rigidity, which often struggle with resistance to change and stagnation in dynamic business environments.
Understanding Organizational Rigidity
Organizational rigidity refers to a company's resistance to change, characterized by fixed processes, hierarchical decision-making, and inflexible structures that inhibit innovation. This rigidity limits the organization's ability to respond to dynamic market conditions, technological advancements, and evolving customer demands. Understanding organizational rigidity involves analyzing internal barriers such as entrenched corporate culture, outdated policies, and limited employee empowerment that prevent agile adaptation.
Key Drivers of Adaptability in Organizations
Key drivers of organizational adaptability include a culture of continuous learning, agile leadership, and effective communication channels that foster innovation and rapid decision-making. Embracing technological advancements and encouraging employee empowerment also enhance flexibility in responding to market changes. Organizations investing in these drivers outperform rigid counterparts when navigating uncertainty and complex environments.
Root Causes of Organizational Rigidity
Organizational rigidity often stems from deeply ingrained hierarchical structures, resistance to change due to fear of uncertainty, and rigid policies that limit flexibility and innovation. Lack of open communication channels reinforces this rigidity, as employee feedback and creative ideas are suppressed or ignored. Furthermore, an overemphasis on short-term performance metrics discourages risk-taking and adaptability, making organizations less responsive to dynamic market conditions.
Impacts on Performance: Adaptable vs Rigid Organizations
Adaptable organizations demonstrate enhanced performance by swiftly responding to market changes, fostering innovation, and maintaining competitive advantage, while rigid organizations often suffer from decreased efficiency and slowed decision-making processes due to inflexible structures. Performance metrics in adaptable firms typically show higher employee engagement, increased customer satisfaction, and sustained revenue growth compared to rigid counterparts. The ability to realign resources and strategies quickly correlates strongly with improved organizational resilience and long-term success.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Case studies reveal that organizations demonstrating adaptability, such as IBM's pivot to cloud computing, often achieve sustained growth and innovation, while companies like Blockbuster illustrate failures linked to rigidity and resistance to market shifts. Adaptable firms leverage continuous learning and flexible strategies to respond effectively to technological and consumer changes, ensuring resilience in dynamic environments. Conversely, rigid organizations frequently suffer stagnation and decline due to inflexible structures and failure to anticipate industry disruption.
Building a Culture of Adaptability
Building a culture of adaptability requires fostering continuous learning, encouraging open communication, and empowering employees to embrace change. Organizations with adaptive cultures prioritize innovation, flexibility, and resilience, enabling them to respond effectively to market shifts and disruptions. In contrast, organizational rigidity often stems from hierarchical structures and fixed processes that hinder responsiveness and limit growth opportunities.
Overcoming Barriers to Change
Organizational adaptability enhances resilience by fostering continuous learning and flexible processes that quickly respond to market shifts, while organizational rigidity creates barriers through entrenched hierarchies and resistance to innovation. Overcoming these barriers involves implementing change management strategies, promoting open communication, and empowering employees to participate in decision-making. Leveraging adaptive technologies and cultivating a culture that rewards experimentation can mitigate resistance and accelerate successful transformation.
Future Trends in Organizational Agility
Future trends in organizational agility emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance adaptive decision-making processes. Organizations exhibiting high adaptability leverage real-time data analytics to predict market shifts and rapidly reconfigure their strategies, surpassing rigid structures that hinder responsiveness. Embracing flexible work environments and continuous learning cultures further positions agile organizations to thrive amid increasing volatility and digital transformation.
Organizational Adaptability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com