Green bonds are financial instruments designed to fund projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and sustainable water management. These bonds attract investors seeking to support eco-friendly initiatives while earning competitive returns, aligning financial goals with environmental responsibility. Discover how green bonds can enhance your investment strategy and contribute to a sustainable future by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
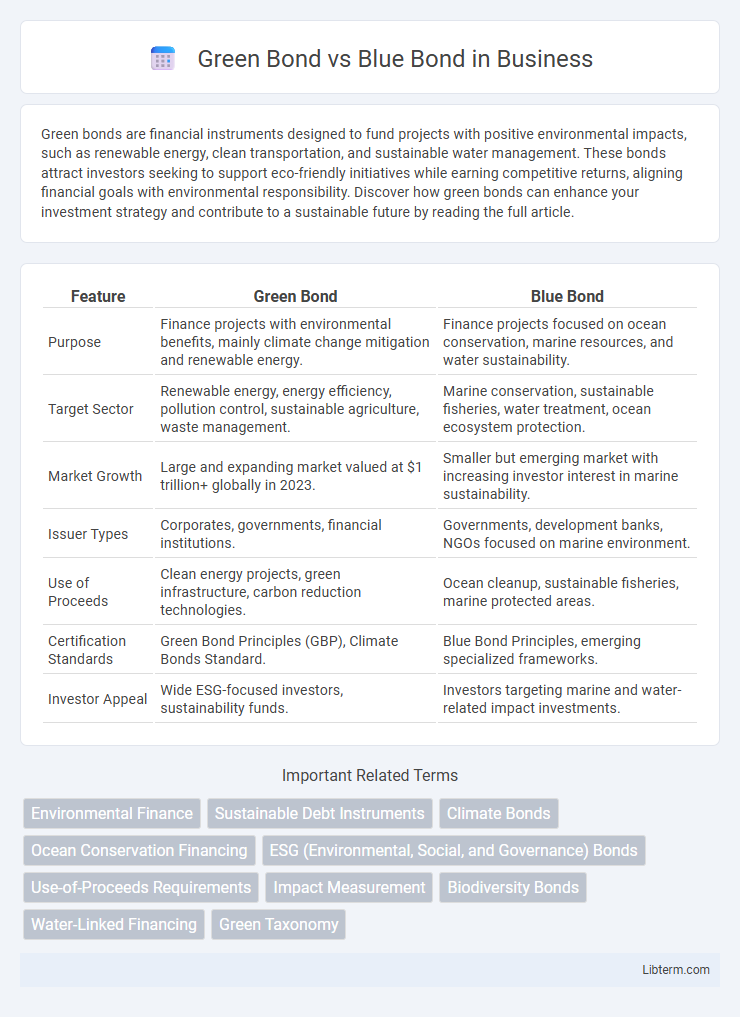
| Feature | Green Bond | Blue Bond |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Finance projects with environmental benefits, mainly climate change mitigation and renewable energy. | Finance projects focused on ocean conservation, marine resources, and water sustainability. |
| Target Sector | Renewable energy, energy efficiency, pollution control, sustainable agriculture, waste management. | Marine conservation, sustainable fisheries, water treatment, ocean ecosystem protection. |
| Market Growth | Large and expanding market valued at $1 trillion+ globally in 2023. | Smaller but emerging market with increasing investor interest in marine sustainability. |
| Issuer Types | Corporates, governments, financial institutions. | Governments, development banks, NGOs focused on marine environment. |
| Use of Proceeds | Clean energy projects, green infrastructure, carbon reduction technologies. | Ocean cleanup, sustainable fisheries, marine protected areas. |
| Certification Standards | Green Bond Principles (GBP), Climate Bonds Standard. | Blue Bond Principles, emerging specialized frameworks. |
| Investor Appeal | Wide ESG-focused investors, sustainability funds. | Investors targeting marine and water-related impact investments. |
Understanding Green Bonds and Blue Bonds
Green bonds finance projects that produce positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution prevention initiatives. Blue bonds specifically target marine and water-related projects, including ocean conservation, sustainable fisheries, and water quality improvement. Both bond types support sustainable development by directing capital toward environmentally responsible ventures with measurable impact.
Key Differences Between Green Bonds and Blue Bonds
Green Bonds primarily finance projects with general environmental benefits like renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction, while Blue Bonds focus specifically on ocean-related conservation and sustainable marine resource management. The key difference lies in their targeted use of proceeds: Green Bonds support a broad range of ecological initiatives, whereas Blue Bonds are dedicated to addressing challenges such as ocean pollution, overfishing, and habitat degradation. Issuers of Blue Bonds often include governments and organizations committed to marine sustainability, reflecting an emerging niche within the broader green finance market.
Environmental Impact: Green vs Blue Bonds
Green Bonds primarily finance projects that promote renewable energy, energy efficiency, and pollution reduction, contributing broadly to climate change mitigation and ecological sustainability. Blue Bonds specifically target marine and water-related environmental projects, such as ocean conservation, sustainable fisheries, and water resource management, addressing critical challenges like ocean pollution and habitat preservation. Both bonds play crucial roles in environmental finance, with Green Bonds offering widespread ecological benefits and Blue Bonds providing focused support for aquatic ecosystems and marine biodiversity.
Eligible Projects for Green and Blue Bonds
Green bonds finance projects that promote environmental sustainability, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, pollution prevention, sustainable agriculture, and climate change mitigation. Blue bonds specifically target marine and ocean-related projects such as coastal restoration, sustainable fisheries, marine pollution control, and protection of ocean biodiversity. Both bond types attract investors focused on environmental impact but differ in project scope, with green bonds having a broader ecological focus and blue bonds concentrating on water and marine ecosystem preservation.
Market Growth and Trends: Green vs Blue Bonds
Green bonds have experienced significant market growth, with global issuance surpassing $500 billion in 2023, driven by increased investor demand for environmentally sustainable projects. Blue bonds, focused on ocean and water-related conservation efforts, remain a niche yet rapidly expanding segment, with issuance reaching approximately $3 billion as governments and corporations prioritize marine ecosystem preservation. Market trends indicate that while green bonds dominate due to their broader scope, blue bonds are gaining traction for targeted climate resilience and biodiversity goals, suggesting diversified growth in sustainable finance.
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
Green Bonds and Blue Bonds are subject to distinct regulatory frameworks reflecting their environmental objectives. Green Bonds primarily adhere to the Green Bond Principles (GBP) established by the International Capital Market Association (ICMA), ensuring transparency, use of proceeds for climate-friendly projects, and regular impact reporting. Blue Bonds, while often following the GBP, incorporate additional criteria specific to marine and water-related projects, with frameworks like the Blue Bond Guidelines by the Climate Bonds Initiative (CBI) emphasizing sustainable ocean economy standards and marine ecosystem protection.
Investor Profiles in Green and Blue Bonds
Investors in green bonds typically include institutional investors such as pension funds, insurance companies, and asset managers seeking sustainable investments with environmental impact. Blue bond investors often comprise development banks, impact investors, and governments focused on marine conservation and sustainable ocean economies. Both investor profiles prioritize ESG criteria, but blue bond investors place stronger emphasis on ocean health and coastal community resilience.
Challenges and Risks for Green and Blue Bonds
Green bonds face challenges including project verification complexities, regulatory uncertainties, and risks of greenwashing that can undermine investor confidence. Blue bonds encounter additional risks such as the difficulty of measuring marine ecosystem impacts, limited market liquidity, and regulatory barriers specific to ocean-related projects. Both bond types require robust frameworks to ensure transparency, credible impact assessment, and alignment with environmental goals to mitigate financial and reputational risks.
Case Studies: Successful Green and Blue Bond Initiatives
The European Investment Bank's Climate Awareness Bonds showcase a successful green bond initiative, financing renewable energy and energy efficiency projects across the EU, reducing carbon emissions by millions of tons annually. The Seychelles blue bond, the first sovereign blue bond globally, raised $15 million to support sustainable marine and fisheries projects, enhancing ocean health and economic resilience. Both case studies highlight effective mobilization of private capital for environmental sustainability through tailored bond frameworks.
Future Outlook for Green and Blue Bonds
Green bonds are projected to maintain strong growth driven by global climate initiatives and increasing investor demand for sustainable assets, with market size expected to surpass $1 trillion in the next few years. Blue bonds, targeting ocean and water conservation projects, are gaining momentum as governments and private sectors recognize the urgent need to finance marine ecosystem protection, potentially becoming a significant niche within the sustainable finance market. Innovations in impact measurement and regulatory support will likely accelerate the adoption and diversification of both green and blue bonds, enhancing their roles in achieving net-zero and biodiversity goals.
Green Bond Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com