Building a strong partnership involves trust, clear communication, and shared goals that align with your vision for success. Effective collaboration maximizes resources, fosters innovation, and drives sustainable growth in any business venture. Discover how to cultivate lasting partnerships that elevate your opportunities by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
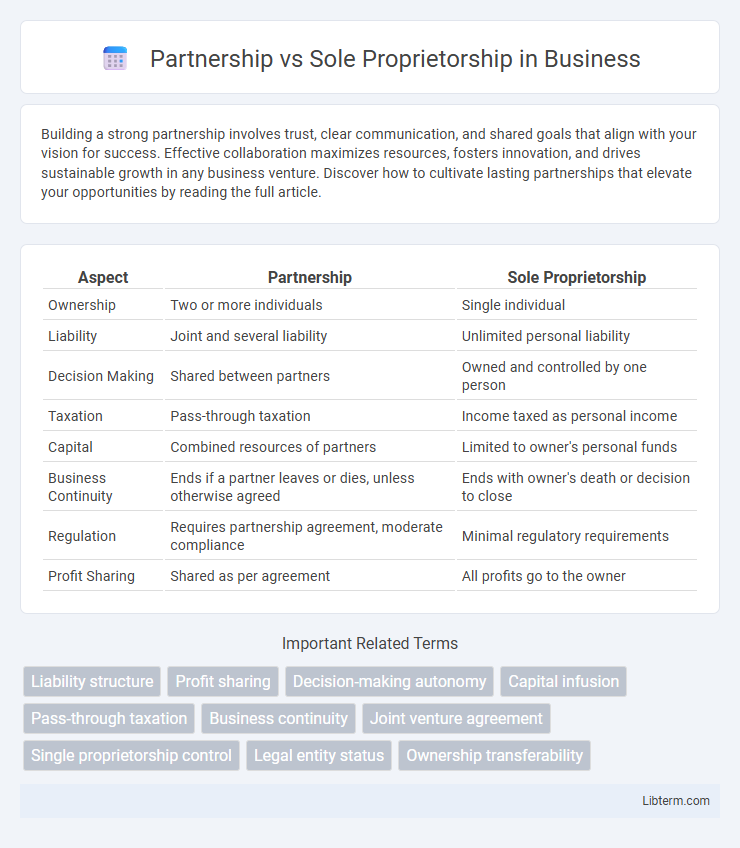
| Aspect | Partnership | Sole Proprietorship |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Two or more individuals | Single individual |
| Liability | Joint and several liability | Unlimited personal liability |
| Decision Making | Shared between partners | Owned and controlled by one person |
| Taxation | Pass-through taxation | Income taxed as personal income |
| Capital | Combined resources of partners | Limited to owner's personal funds |
| Business Continuity | Ends if a partner leaves or dies, unless otherwise agreed | Ends with owner's death or decision to close |
| Regulation | Requires partnership agreement, moderate compliance | Minimal regulatory requirements |
| Profit Sharing | Shared as per agreement | All profits go to the owner |
Introduction to Business Structures
Partnerships involve two or more individuals who share ownership, profits, and liabilities, offering more combined resources and skills compared to sole proprietorships. Sole proprietorships are owned and operated by a single person, providing complete control but bearing unlimited personal liability for business debts. Business structures impact taxation, management flexibility, and legal responsibilities, making the choice crucial for new entrepreneurs.
What is a Sole Proprietorship?
A sole proprietorship is a business structure owned and operated by one individual, offering complete control over decision-making and profits. This entity type features unlimited personal liability, meaning the owner is personally responsible for all business debts and obligations. It is the simplest and most common form of business, often ideal for small-scale entrepreneurs due to minimal regulatory requirements and straightforward tax filing.
What is a Partnership?
A partnership is a business structure where two or more individuals share ownership, responsibilities, profits, and liabilities. Unlike a sole proprietorship, partnerships allow for shared decision-making and resource pooling, which can enhance business growth and operational flexibility. Legal agreements such as partnerships agreements define roles, profit distribution, and conflict resolution among partners.
Key Differences Between Sole Proprietorship and Partnership
Sole proprietorship is owned and managed by a single individual who bears full liability and enjoys complete control, while a partnership involves two or more persons sharing ownership, responsibilities, profits, and liabilities based on an agreement. In sole proprietorship, financial decisions and losses solely impact the owner, whereas partnerships distribute profits and risks among partners according to their contributions outlined in the partnership deed. Taxation also differs, with sole proprietorship income taxed directly to the owner and partnerships potentially taxed either at the entity level or pass-through depending on jurisdiction and partnership type.
Legal and Tax Implications
Partnerships involve multiple owners sharing liability and profits, with each partner personally responsible for business debts, while sole proprietorships have a single owner bearing unlimited personal liability. For tax purposes, partnerships file an informational return and profits pass through to partners' individual tax returns, avoiding corporate tax, whereas sole proprietors report income and expenses directly on their personal tax return using Schedule C. Legal complexities and tax filing requirements are generally higher for partnerships due to joint liability and profit sharing, compared to the simpler structure and tax reporting of sole proprietorships.
Decision-Making and Management Control
In a partnership, decision-making is shared among partners, allowing for diverse perspectives but requiring consensus or majority agreement, which can slow down processes. Sole proprietorships offer complete management control to the owner, enabling fast decisions and unified strategic direction without needing approval from others. The choice between these structures depends on the owner's preference for collaborative input versus autonomous control in business operations.
Profit Sharing and Liabilities
In a partnership, profits are shared among partners according to the agreed ratio, while liabilities are jointly and severally borne, meaning each partner is personally responsible for the business's debts. In contrast, a sole proprietorship vests all profits directly with the owner, who also holds unlimited personal liability for all obligations and debts of the business. Understanding the distribution of profits and exposure to liabilities is crucial when choosing between a partnership and sole proprietorship structure.
Ease of Formation and Registration
Sole proprietorships offer the simplest ease of formation with minimal registration requirements, often needing only a local business license and minimal paperwork. Partnerships require a formal agreement between partners and may involve more complex registration procedures, including filing a partnership agreement and obtaining applicable permits. The streamlined process of sole proprietorships makes them ideal for quick startups, while partnerships benefit from collaborative ownership despite slightly longer setup times.
Pros and Cons of Each Business Structure
Partnerships offer shared responsibility and combined skills, enhancing resource availability and decision-making, but carry the risk of joint liability and potential conflicts among partners. Sole proprietorships allow full control and simple tax filing, providing flexibility and easier management, yet expose the owner to unlimited personal liability and challenges in raising capital. Choosing between these structures depends on factors like risk tolerance, desired control, and business growth plans.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Business
Choosing the right business structure greatly impacts liabilities, tax obligations, and management control. A partnership allows for shared responsibilities and combined resources but involves joint liability, whereas a sole proprietorship offers complete control and simplicity with the owner bearing all risks. Evaluating factors like business goals, financial investment, and legal protection helps determine whether a partnership or sole proprietorship aligns best with your entrepreneurial vision.
Partnership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com