C2B, or Consumer-to-Business, is a business model where individuals offer products or services to companies, reversing the traditional B2C dynamic. This approach empowers consumers by allowing them to monetize their skills, data, or ideas directly to businesses, enhancing market efficiency and innovation. Explore how C2B models can transform your interactions with companies and unlock new opportunities in the digital economy.
Table of Comparison
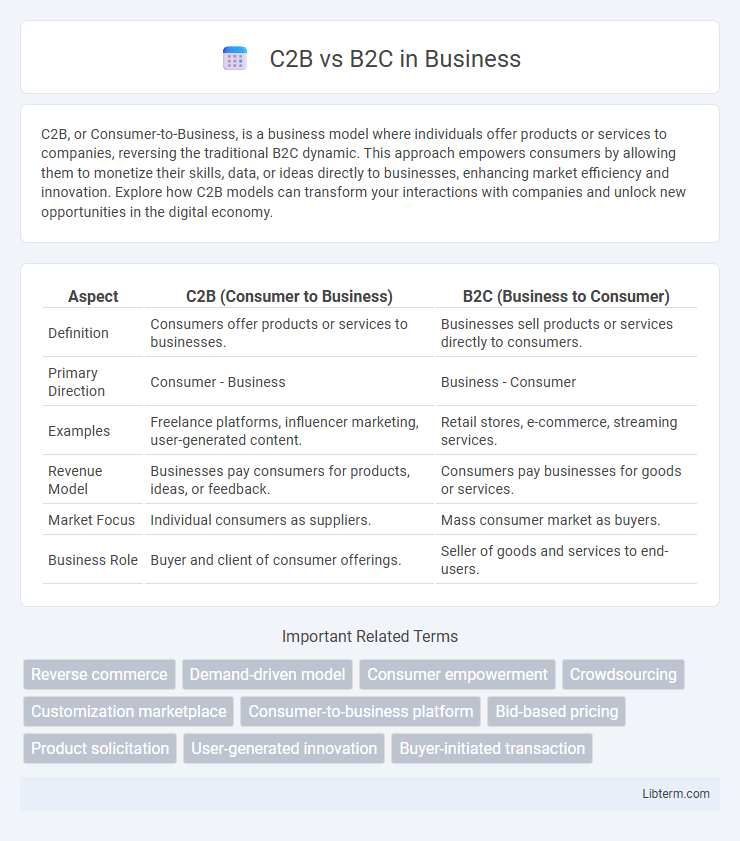
| Aspect | C2B (Consumer to Business) | B2C (Business to Consumer) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consumers offer products or services to businesses. | Businesses sell products or services directly to consumers. |
| Primary Direction | Consumer - Business | Business - Consumer |
| Examples | Freelance platforms, influencer marketing, user-generated content. | Retail stores, e-commerce, streaming services. |
| Revenue Model | Businesses pay consumers for products, ideas, or feedback. | Consumers pay businesses for goods or services. |
| Market Focus | Individual consumers as suppliers. | Mass consumer market as buyers. |
| Business Role | Buyer and client of consumer offerings. | Seller of goods and services to end-users. |
Understanding C2B and B2C Business Models
C2B (Consumer-to-Business) and B2C (Business-to-Consumer) are distinct business models where C2B involves consumers creating value for businesses, such as through user-generated content, freelance services, or product reviews, while B2C centers on organizations selling products or services directly to individual consumers. C2B models leverage consumer influence and data to enhance business offerings, often seen in influencer marketing and crowdsourcing platforms, whereas B2C prioritizes seamless customer experiences and brand loyalty to drive sales. Understanding these models highlights the shift in power dynamics and the importance of personalized engagement in contemporary commerce.
Key Differences Between C2B and B2C
C2B (Consumer-to-Business) involves individuals offering products or services to businesses, while B2C (Business-to-Consumer) features companies selling directly to end consumers. In C2B, consumers are content creators, influencers, or freelancers providing value, whereas B2C focuses on businesses targeting large consumer markets with goods or services. Pricing flexibility and personalized interactions define C2B, contrasting with standardized product offerings and mass marketing typical in B2C transactions.
How C2B Works: Process and Examples
The C2B (Consumer-to-Business) model operates when individuals offer products or services to companies, reversing the traditional B2C flow. Consumers might provide content, freelance services, or data through platforms where businesses bid or purchase directly, such as influencer marketing or stock photo websites. Examples include affiliate marketers promoting brand products or users selling personal data insights to corporations for targeted advertising.
How B2C Works: Process and Examples
B2C (Business-to-Consumer) operates by businesses selling products or services directly to individual consumers through digital platforms, retail stores, or subscription models. The process typically involves product discovery via marketing, purchasing through e-commerce websites or physical outlets, and seamless payment and delivery systems. Examples of B2C include Amazon, Netflix, and Zara, where user-friendly interfaces and personalized customer experiences drive sales and brand loyalty.
Advantages of C2B for Businesses and Consumers
C2B models empower businesses with direct access to consumer-generated ideas, reducing market research costs and enhancing product innovation through real-time feedback. Consumers benefit from monetizing their content or data, gaining personalized offers and greater influence over business decisions. This two-way interaction fosters stronger brand loyalty and drives customized marketing strategies, creating a win-win ecosystem for both parties.
Benefits of B2C for Businesses and Shoppers
B2C (Business-to-Consumer) models offer businesses direct access to a large consumer market, enabling stronger brand recognition and increased sales volume. For shoppers, B2C platforms provide convenience through easy product comparison, personalized offers, and fast delivery options. Enhanced customer data analytics in B2C help businesses tailor marketing strategies and improve customer satisfaction.
Major Challenges in C2B and B2C Models
C2B models face challenges in establishing trust and ensuring fair compensation for consumer-generated content or services, while handling complex payment processing and verifying authenticity. B2C models struggle with maintaining customer engagement, managing high competition, and optimizing personalized marketing strategies for diverse consumer segments. Both models require advanced data security measures and efficient technology integration to enhance user experience and operational efficiency.
Real-World Examples of Successful C2B Companies
C2B (Consumer-to-Business) models feature platforms like Fiverr and Upwork, where freelancers provide services directly to businesses, exemplifying the growing trend of consumers driving value in the marketplace. Companies like Airbnb leverage C2B by enabling individuals to rent out personal properties to travelers, creating significant revenue streams from consumer assets. These examples highlight how C2B models empower individuals to monetize skills or resources while offering businesses flexible, scalable options compared to traditional B2C frameworks.
Real-World Examples of Successful B2C Companies
Amazon revolutionizes the B2C landscape by offering millions of products directly to consumers with fast delivery and personalized recommendations, driving massive ecommerce growth. Netflix exemplifies B2C success through its subscription-based streaming service that capitalizes on consumer demand for on-demand entertainment worldwide. Apple's retail strategy effectively targets individual customers with innovative devices and seamless user experiences, solidifying its dominance in the B2C market.
Future Trends: The Evolution of C2B vs B2C
Future trends indicate a significant shift in the digital economy where C2B models are gaining traction through influencer marketing, user-generated content, and personalized consumer insights, driving businesses to adopt more collaborative and responsive strategies. Advanced AI and big data analytics enhance C2B interactions by enabling companies to tailor products and services based on direct consumer feedback, surpassing traditional B2C one-way communication. This evolution fosters a more dynamic marketplace where consumer empowerment and active participation shape product development, marketing campaigns, and overall business growth.
C2B Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com