Mass production streamlines manufacturing processes by producing large quantities of standardized products efficiently, reducing costs and increasing consistency. Techniques such as assembly lines and automation play a crucial role in meeting high consumer demand while maintaining quality. Explore the rest of the article to understand how mass production can transform your business operations.
Table of Comparison
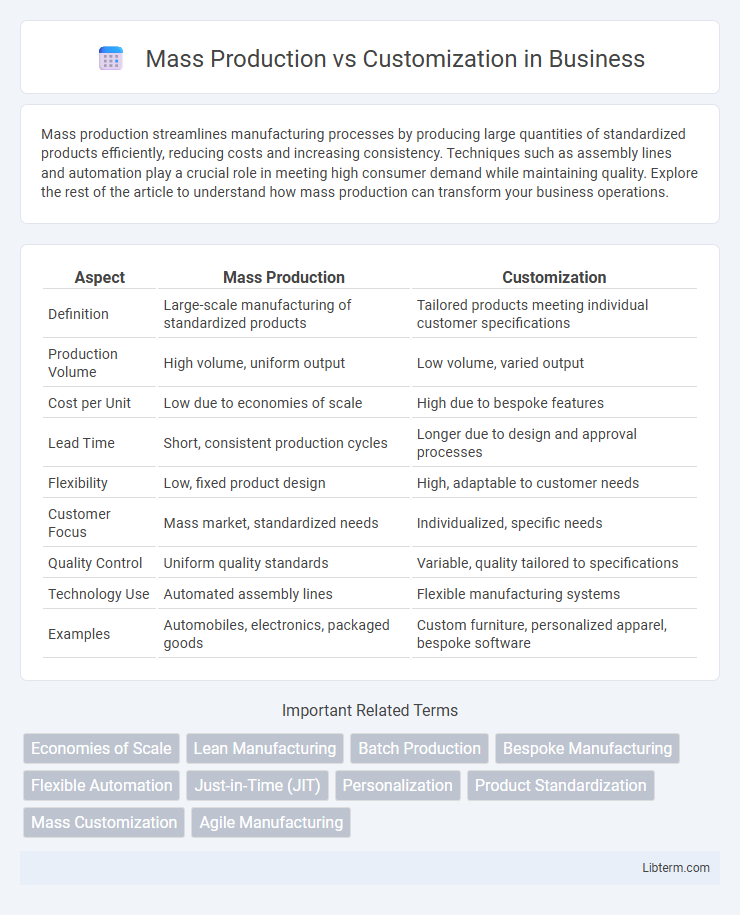
| Aspect | Mass Production | Customization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large-scale manufacturing of standardized products | Tailored products meeting individual customer specifications |
| Production Volume | High volume, uniform output | Low volume, varied output |
| Cost per Unit | Low due to economies of scale | High due to bespoke features |
| Lead Time | Short, consistent production cycles | Longer due to design and approval processes |
| Flexibility | Low, fixed product design | High, adaptable to customer needs |
| Customer Focus | Mass market, standardized needs | Individualized, specific needs |
| Quality Control | Uniform quality standards | Variable, quality tailored to specifications |
| Technology Use | Automated assembly lines | Flexible manufacturing systems |
| Examples | Automobiles, electronics, packaged goods | Custom furniture, personalized apparel, bespoke software |
Understanding Mass Production and Customization
Mass production involves manufacturing large quantities of standardized products using assembly line techniques, which maximizes efficiency and reduces costs per unit. Customization tailors products to individual customer preferences, offering unique features or specifications that cater to specific needs. Understanding the balance between mass production's scalability and customization's personalization is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize supply chain management and meet diverse market demands.
Historical Overview of Manufacturing Approaches
Mass production revolutionized manufacturing in the early 20th century with Henry Ford's assembly line, enabling large-scale output and affordability through standardized parts and processes. Customization has roots in artisanal crafts and bespoke production, emphasizing uniqueness and individual customer specifications, which maintained prominence before industrialization. Recent manufacturing trends blend these approaches, leveraging flexible technologies like CNC machining and 3D printing to meet varied consumer demands without sacrificing efficiency.
Key Differences Between Mass Production and Customization
Mass production emphasizes high-volume output with standardized products to maximize efficiency and reduce costs, while customization tailors products to individual customer preferences, resulting in lower volume but higher uniqueness. Mass production relies heavily on automation and assembly lines, whereas customization often involves manual adjustments or flexible manufacturing systems. The primary difference lies in the balance between economies of scale in mass production and the personalized value delivered through customization.
Advantages of Mass Production
Mass production enables businesses to achieve economies of scale, significantly reducing the cost per unit and increasing overall efficiency. The standardized processes ensure consistent product quality and faster output rates, meeting high market demand effectively. This approach supports widespread availability and affordability of products, benefiting both manufacturers and consumers.
Benefits of Customization
Customization offers enhanced customer satisfaction by delivering products tailored to individual preferences and specific needs. It improves product differentiation and brand loyalty, allowing businesses to stand out in competitive markets. Personalized products often justify premium pricing, increasing profitability and fostering long-term customer relationships.
Challenges in Implementing Each Approach
Mass production faces challenges such as high initial capital investment, inflexible manufacturing processes, and difficulties in meeting diverse customer preferences. Customization struggles with increased production complexity, longer lead times, and higher costs due to tailored designs and smaller batch sizes. Balancing efficiency and personalization requires advanced supply chain management and adaptive production technologies.
Impact on Product Quality and Innovation
Mass production streamlined manufacturing processes, ensuring consistent product quality through standardized methods but often limiting innovation due to uniform designs. Customization drives product innovation by enabling tailored solutions that meet specific customer needs, though it can introduce variability in quality due to less standardized production. The balance between mass production and customization influences a company's ability to maintain high quality while fostering continuous innovation.
Cost Implications: Mass Production vs Customization
Mass production significantly reduces cost per unit through economies of scale, enabling manufacturers to produce large quantities at lower prices. Customization often increases production costs due to the need for specialized materials, labor, and processes tailored to individual customer requirements. Businesses must weigh fixed cost savings in mass production against variable cost increases in customization to optimize overall profitability.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor customization as demand for personalized products rises, driven by desires for unique experiences and tailored solutions. Market trends show a shift from traditional mass production models towards flexible manufacturing systems that accommodate smaller, varied production runs efficiently. This evolution highlights the growing importance of agility in supply chains to meet diverse consumer needs and sustain competitive advantage.
Future Outlook: Balancing Efficiency and Personalization
Mass production is evolving through advanced automation and AI integration to boost efficiency while reducing costs. Customization leverages digital manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing and flexible supply chains, enabling tailored products at scale. The future outlook emphasizes a hybrid manufacturing model that balances mass production's cost-effectiveness with the growing consumer demand for personalized goods.
Mass Production Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com