Licensing grants you the legal authority to use, distribute, or modify intellectual property while protecting the rights of the original creator. Understanding different types of licenses, such as open-source, commercial, or proprietary, can help you navigate compliance and avoid potential legal issues. Discover how licensing impacts your projects and business by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
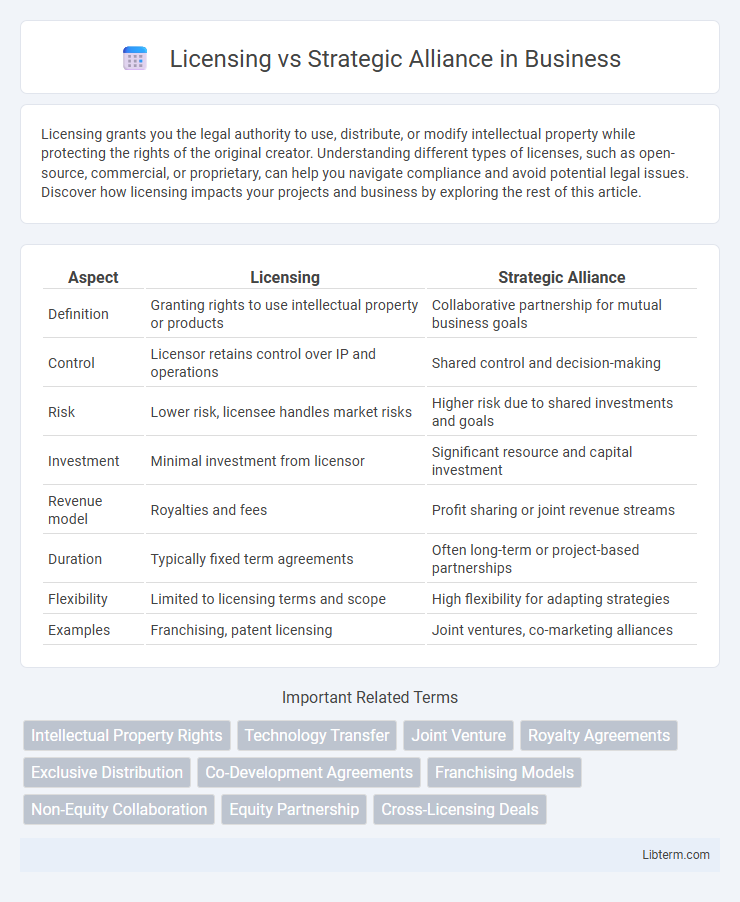
| Aspect | Licensing | Strategic Alliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Granting rights to use intellectual property or products | Collaborative partnership for mutual business goals |
| Control | Licensor retains control over IP and operations | Shared control and decision-making |
| Risk | Lower risk, licensee handles market risks | Higher risk due to shared investments and goals |
| Investment | Minimal investment from licensor | Significant resource and capital investment |
| Revenue model | Royalties and fees | Profit sharing or joint revenue streams |
| Duration | Typically fixed term agreements | Often long-term or project-based partnerships |
| Flexibility | Limited to licensing terms and scope | High flexibility for adapting strategies |
| Examples | Franchising, patent licensing | Joint ventures, co-marketing alliances |
Introduction to Licensing and Strategic Alliances
Licensing involves granting permission to another company to use intellectual property, technology, or brand rights in exchange for royalties or fees, enabling market expansion with lower investment risk. Strategic alliances are collaborative agreements between businesses to share resources, knowledge, and capabilities to achieve common objectives while remaining independent entities. Both approaches facilitate growth and market entry but differ in control, commitment, and resource sharing.
Defining Licensing: Key Characteristics
Licensing involves a legal agreement where one company permits another to use its intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, or technology, under specific conditions without transferring ownership. Key characteristics include low resource commitment, controlled market expansion, and a revenue model based on royalties or fees. This contrasts with strategic alliances, which are collaborative partnerships focused on shared goals and resource pooling without granting IP rights.
Understanding Strategic Alliances: Essential Elements
Strategic alliances involve collaboration between two or more companies to achieve mutual goals while maintaining independence, often sharing resources, knowledge, and capabilities. Key elements include aligned objectives, complementary strengths, trust, clear communication, and effective governance structures to manage the partnership. Unlike licensing, which transfers rights or technology for royalties, strategic alliances focus on joint efforts to enhance competitive advantage without full mergers or acquisitions.
Advantages of Licensing Agreements
Licensing agreements offer businesses the advantage of rapid market entry with lower capital investment and reduced risks compared to full-scale expansion. They enable licensors to generate steady revenue streams through royalties while retaining control over intellectual property rights. Moreover, licensing facilitates access to established distribution networks and local market expertise, enhancing product reach and brand recognition.
Benefits of Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances enable companies to share resources, expertise, and market access, fostering innovation and competitive advantage without the heavy investment required in licensing agreements. These partnerships facilitate rapid entry into new markets and enhance flexibility in responding to changing business environments. Collaborating firms benefit from shared risks and combined strengths, leading to improved product development and operational efficiency.
Risks and Challenges in Licensing
Licensing involves granting permission to use intellectual property, which exposes licensors to risks such as loss of control over how the technology or brand is utilized and potential misuse. Challenges also include enforcing compliance with licensing agreements across different jurisdictions, leading to legal complexities and increased monitoring costs. Furthermore, licensors face risks of creating future competitors by transferring critical knowledge and capabilities to licensees.
Pitfalls and Risks of Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances present risks such as misaligned goals, cultural clashes, and unequal resource contributions that can lead to conflicts and operational inefficiencies. Unlike licensing agreements that provide defined control and revenue streams, alliances often involve shared decision-making, increasing complexity in governance and accountability. Failure to establish clear communication and conflict resolution mechanisms may result in loss of proprietary information, damaged brand reputation, and financial losses.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Licensing and Strategic Alliances
When choosing between licensing and strategic alliances, evaluate control over intellectual property, the level of resource commitment, and market entry speed as key factors. Licensing offers lower risk and faster market access but limits control and long-term profits, while strategic alliances require deeper collaboration, shared risks, and greater integration of resources. Consider the company's strategic goals, core competencies, and the need for flexibility when selecting the optimal partnership model.
Real-World Examples: Licensing vs Strategic Alliance
Nike's licensing agreement with Converse allows Nike to manufacture and distribute products under the Converse brand, leveraging Converse's established market presence without full acquisition. In contrast, the strategic alliance between Starbucks and PepsiCo enables both companies to co-develop and distribute ready-to-drink coffee beverages, combining Starbucks' brand strength with PepsiCo's extensive distribution network. Licensing offers brand extension with lower risk, while strategic alliances foster collaborative innovation and market penetration.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Expansion Strategy
Licensing provides a cost-effective and low-risk entry into new markets by allowing companies to leverage established local partners' resources and expertise. Strategic alliances, however, enable deeper collaboration, sharing of technology, and mutual market development, often leading to stronger competitive advantages. Choosing the optimal expansion strategy depends on factors such as desired control level, resource commitment, market conditions, and long-term business goals.
Licensing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com