Private placement offers a strategic way for companies to raise capital by selling securities directly to a select group of investors, bypassing public markets. This approach ensures faster funding with potentially lower regulatory requirements and greater confidentiality. Explore the rest of the article to understand how private placement can benefit your investment strategy.
Table of Comparison
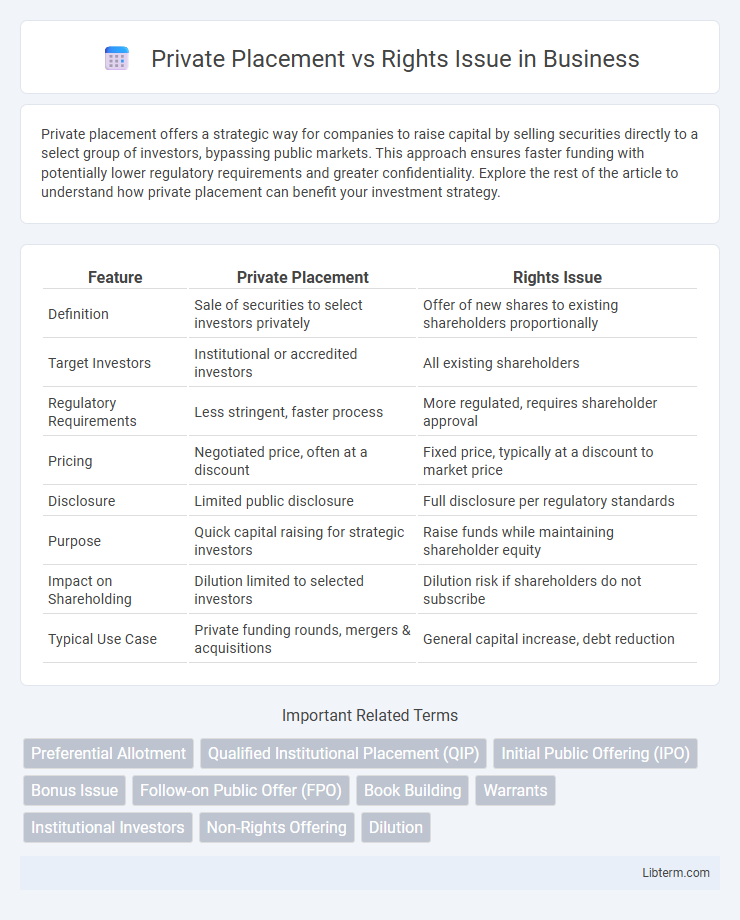
| Feature | Private Placement | Rights Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sale of securities to select investors privately | Offer of new shares to existing shareholders proportionally |
| Target Investors | Institutional or accredited investors | All existing shareholders |
| Regulatory Requirements | Less stringent, faster process | More regulated, requires shareholder approval |
| Pricing | Negotiated price, often at a discount | Fixed price, typically at a discount to market price |
| Disclosure | Limited public disclosure | Full disclosure per regulatory standards |
| Purpose | Quick capital raising for strategic investors | Raise funds while maintaining shareholder equity |
| Impact on Shareholding | Dilution limited to selected investors | Dilution risk if shareholders do not subscribe |
| Typical Use Case | Private funding rounds, mergers & acquisitions | General capital increase, debt reduction |
Introduction to Private Placement and Rights Issue
Private placement involves raising capital by selling securities directly to a select group of investors, such as institutional buyers or accredited individuals, allowing for quicker access to funds without public offering requirements. Rights issue grants existing shareholders the option to purchase additional shares at a discounted price, maintaining their proportional ownership and preventing dilution. Both methods serve as efficient strategies for companies to raise equity capital while catering to different investor bases and regulatory frameworks.
Key Differences Between Private Placement and Rights Issue
Private placement involves the sale of securities directly to a select group of investors, often institutional or accredited, bypassing the public market, whereas a rights issue offers existing shareholders the opportunity to purchase additional shares proportionate to their holdings, maintaining their ownership stake. Private placements provide faster capital access with less regulatory scrutiny but may result in ownership dilution for non-participating shareholders, while rights issues are more transparent and equitable but can be time-consuming due to shareholder approval requirements. The key differences lie in the target audience, regulatory framework, pricing mechanisms, and impact on shareholder equity.
Purpose and Objectives of Private Placement
Private placement is primarily aimed at raising capital quickly from a select group of investors, often institutional or accredited, to fund expansion, acquisitions, or improve liquidity without the lengthy regulatory requirements of a public offering. The objective of private placement is to provide flexibility in terms, speed up the fundraising process, and maintain confidentiality by avoiding public disclosure. Compared to rights issues, which target existing shareholders to maintain their ownership proportion, private placements focus on bringing new strategic investors to strengthen the company's financial position and support long-term growth.
Purpose and Objectives of Rights Issue
Rights issues primarily aim to raise capital from existing shareholders, offering them the opportunity to purchase additional shares at a discounted price, which helps maintain their proportional ownership and control in the company. This method ensures a fair and equitable capital increase while supporting the company's strategic objectives such as debt reduction, funding expansion projects, or improving working capital. In contrast, private placements target select investors to quickly raise funds without the need for shareholder approval, often resulting in diluted ownership for existing shareholders.
Advantages of Private Placement
Private placement offers companies quicker access to capital by bypassing lengthy regulatory procedures associated with public offerings. It enables targeted fundraising from institutional investors or high-net-worth individuals, ensuring confidentiality and reduced public scrutiny. This method also allows issuers to negotiate terms directly, potentially resulting in more favorable financing conditions and streamlined dilution of equity.
Advantages of Rights Issue
Rights issues offer existing shareholders the advantage of purchasing additional shares at a discounted price, preserving their proportional ownership and preventing dilution. This method raises capital while maintaining shareholder loyalty and promoting fairness by giving current investors priority access. The process also tends to be quicker and involves lower underwriting fees compared to private placements, enhancing cost efficiency for companies.
Disadvantages of Private Placement
Private placement can limit market liquidity due to restrictions on resale and a narrower pool of investors, which may lead to undervaluation of shares. It often results in less transparency compared to public offerings, causing potential distrust among existing shareholders and impacting the company's reputation. Furthermore, private placements may dilute existing shareholders' control if preferential terms are granted to new investors.
Disadvantages of Rights Issue
Rights issues can dilute existing shareholders' ownership and often require shareholders to invest additional capital, which may not be feasible for all investors. The process can be time-consuming and costly due to regulatory compliance and underwriting fees. Market perception of a rights issue may signal financial distress, potentially leading to a decline in share price.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Private placements operate under regulatory frameworks that often provide exemptions from full public disclosure, subject to limits on the number and type of investors, typically accredited or institutional. Rights issues must comply with stringent disclosure obligations as they involve offering securities to existing shareholders, ensuring transparency and fairness in accordance with securities laws and stock exchange rules. Both methods require adherence to compliance standards, but rights issues generally entail more rigorous investor communication and regulatory filings to protect shareholder interests.
Choosing Between Private Placement and Rights Issue
Choosing between private placement and rights issue depends on the company's need for speed and target investor base. Private placement offers faster capital raising through selective investors, often at negotiated terms, ideal for companies seeking discreet funding without broad shareholder involvement. Rights issues involve existing shareholders in proportion to their holdings, providing a fair opportunity to maintain ownership but requiring regulatory compliance and longer timelines.
Private Placement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com