The P/B ratio measures a company's market value relative to its book value, providing insight into whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued. Investors use this ratio to assess the financial stability and intrinsic worth of a company compared to its market price. Explore the full article to understand how the P/B ratio can enhance your investment decisions.
Table of Comparison
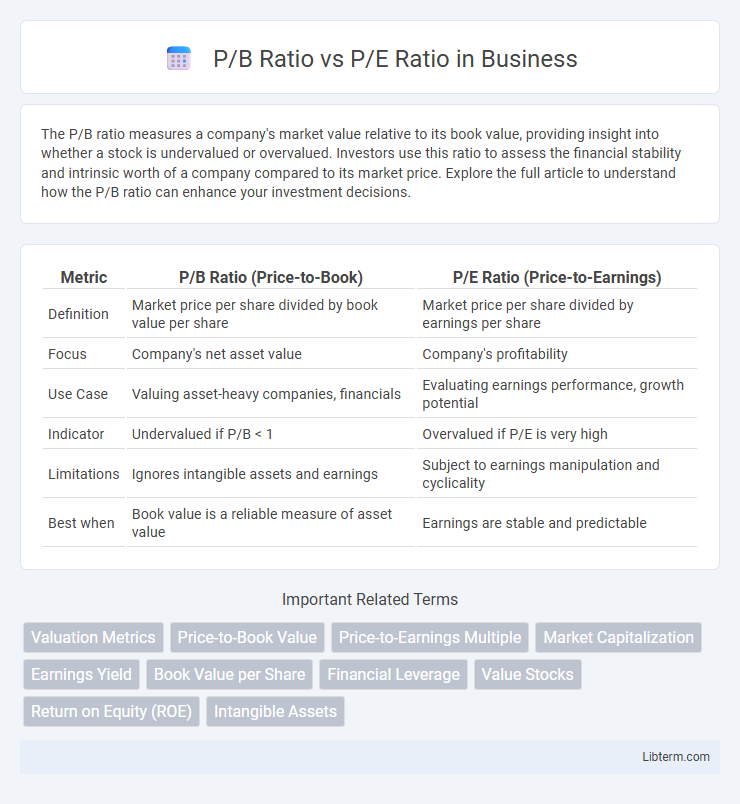
| Metric | P/B Ratio (Price-to-Book) | P/E Ratio (Price-to-Earnings) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market price per share divided by book value per share | Market price per share divided by earnings per share |
| Focus | Company's net asset value | Company's profitability |
| Use Case | Valuing asset-heavy companies, financials | Evaluating earnings performance, growth potential |
| Indicator | Undervalued if P/B < 1 | Overvalued if P/E is very high |
| Limitations | Ignores intangible assets and earnings | Subject to earnings manipulation and cyclicality |
| Best when | Book value is a reliable measure of asset value | Earnings are stable and predictable |
Introduction to Valuation Ratios
The Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio measures a company's market value relative to its book value, providing insight into how investors value the firm's net assets. The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio compares the current share price to the company's earnings per share, indicating market expectations of future profitability. Both P/B and P/E ratios serve as fundamental valuation metrics for analyzing stock investment potential across different industries.
What is the P/B Ratio?
The P/B Ratio, or Price-to-Book Ratio, measures a company's current market price relative to its book value per share, offering insight into how the market values the firm's net assets. This ratio is calculated by dividing the stock price by the book value per share, making it a key indicator for assessing whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued compared to its actual net asset value. Investors often use the P/B Ratio alongside the P/E Ratio to evaluate a company's valuation from both asset and earnings perspectives.
What is the P/E Ratio?
The P/E Ratio, or Price-to-Earnings Ratio, measures a company's current share price relative to its earnings per share (EPS). It indicates how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings, helping assess stock valuation and growth expectations. Unlike the P/B Ratio, which compares stock price to book value, the P/E Ratio focuses on profitability and future earnings potential.
Key Differences Between P/B and P/E Ratios
The P/B ratio compares a company's market value to its book value, emphasizing asset valuation, while the P/E ratio measures market price relative to earnings, focusing on profitability. P/B is often used for companies with significant tangible assets, whereas P/E is preferred for evaluating earnings performance and growth potential. Investors rely on P/B for asset-heavy industries like finance and manufacturing, while P/E aids in assessing companies across sectors with varying income consistency.
When to Use P/B Ratio
The P/B ratio is most useful when analyzing companies with significant tangible assets, such as banks and manufacturing firms, providing insight into how the market values a company's net asset base relative to its book value. Investors rely on the P/B ratio during financial distress or liquidation scenarios to assess if the stock is undervalued based on its asset liquidation value rather than earnings, which can be volatile. Unlike the P/E ratio, the P/B ratio is more effective when earnings are negative or inconsistent, offering a clearer picture of intrinsic value.
When to Use P/E Ratio
The P/E ratio is best used when evaluating companies with consistent earnings and stable profit margins, as it reflects market expectations of future earnings growth. Investors should rely on the P/E ratio for firms in sectors like technology or consumer goods, where earnings are a key indicator of performance. Unlike the P/B ratio, which emphasizes asset values, the P/E ratio provides insight into profitability and growth potential.
Pros and Cons of P/B Ratio
The Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio offers insight into a company's market value relative to its book value, making it particularly useful for asset-heavy industries like finance and real estate. It tends to provide a more stable valuation metric during earnings volatility or accounting fluctuations, unlike the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio which is sensitive to profit swings and can be distorted by non-recurring items. However, the P/B ratio may undervalue companies with significant intangible assets such as intellectual property or brand equity, limiting its effectiveness for technology or service-oriented firms.
Pros and Cons of P/E Ratio
The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio offers a straightforward measure of company valuation by comparing current share price to earnings per share, making it useful for assessing profitability relative to market price. It can be misleading during periods of earnings volatility or in companies with inconsistent profits, leading to distorted valuations. P/E ratio's reliance on accounting earnings also makes it less effective for comparing firms in different industries or with varying accounting policies.
Industry Applications of P/B and P/E Ratios
P/B ratio is widely used in capital-intensive industries like banking, insurance, and manufacturing where asset values play a critical role in valuation. P/E ratio is more relevant in sectors such as technology, consumer goods, and services that emphasize earnings performance and growth potential. Investors analyze P/B ratios to assess book value relative to market price, while P/E ratios help evaluate profitability and market expectations across different industries.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Ratio
Selecting the appropriate financial metric depends on industry context and company specifics; the Price-to-Book (P/B) ratio suits asset-heavy sectors while the Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio better evaluates profitability and earnings potential. Analysts should consider P/B ratio for companies with significant tangible assets or during liquidation scenarios, whereas P/E ratio offers insights into earnings performance and future growth prospects. Combining both ratios with other financial indicators enhances investment decision accuracy and risk assessment.
P/B Ratio Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com