Licensing controls the legal permissions granted to individuals or businesses for using intellectual property, products, or services. It defines the scope, duration, and conditions under which your rights can be exercised, ensuring protection and avoiding infringement risks. Explore the full article to understand how licensing can safeguard your interests and optimize your opportunities.
Table of Comparison
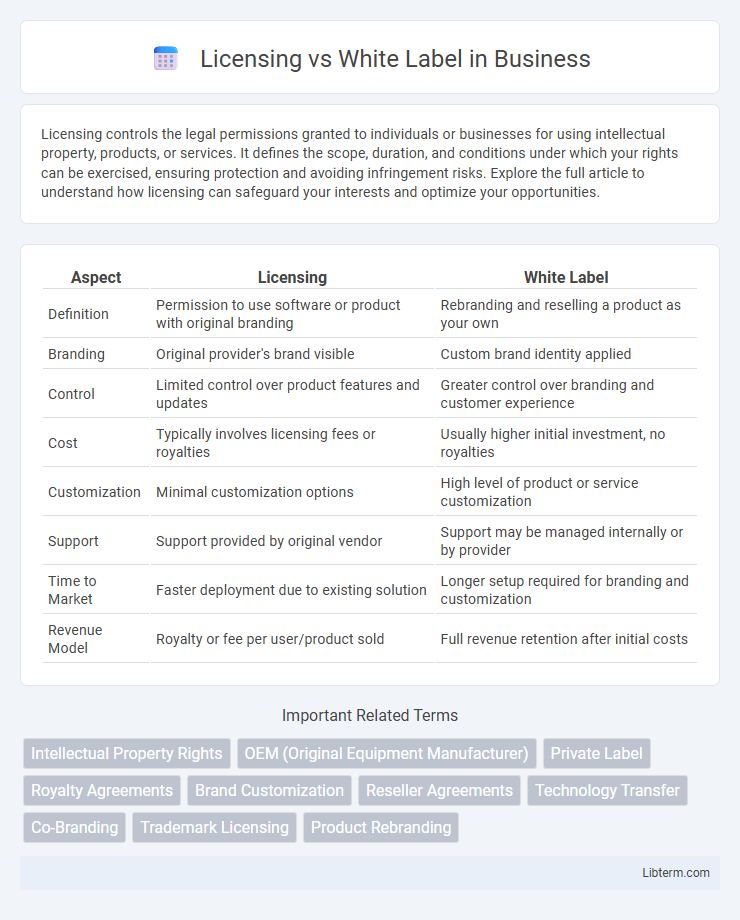
| Aspect | Licensing | White Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Permission to use software or product with original branding | Rebranding and reselling a product as your own |
| Branding | Original provider's brand visible | Custom brand identity applied |
| Control | Limited control over product features and updates | Greater control over branding and customer experience |
| Cost | Typically involves licensing fees or royalties | Usually higher initial investment, no royalties |
| Customization | Minimal customization options | High level of product or service customization |
| Support | Support provided by original vendor | Support may be managed internally or by provider |
| Time to Market | Faster deployment due to existing solution | Longer setup required for branding and customization |
| Revenue Model | Royalty or fee per user/product sold | Full revenue retention after initial costs |
Understanding Licensing vs White Label
Licensing grants permission to use intellectual property, such as trademarks or software, while retaining ownership rights, enabling businesses to leverage established brands or technologies without full control. White labeling involves rebranding a product or service produced by one company to appear as if it is created by another, allowing companies to offer market-ready solutions under their own brand identity. Understanding the distinctions between licensing and white label strategies helps businesses choose between leveraging existing products with limited control or fully customizing offerings to fit their brand.
Key Differences Between Licensing and White Label
Licensing grants permission to use intellectual property or technology while maintaining the original brand identity, whereas white label involves rebranding a generic product or service to appear as the purchaser's own. Licensing typically restricts modifications and requires royalty payments, contrasting with white label solutions which allow full customization and often operate under a fixed fee. Key differences include control over branding, customization options, and the nature of ownership rights.
Advantages of Licensing
Licensing offers the advantage of maintaining full brand ownership while enabling access to established intellectual property, reducing time-to-market and development costs. It allows businesses to customize products or services under their own brand, ensuring quality control and brand consistency. Furthermore, licensing facilitates scalable expansion by providing legal rights to use patented technology or proprietary content without the complexities of full business acquisition.
Benefits of White Label Solutions
White label solutions provide businesses with the ability to quickly enter the market using pre-developed products that can be customized under their own brand, significantly reducing development time and costs. These solutions offer scalability and flexibility, allowing companies to focus on marketing and customer acquisition rather than product creation. By leveraging white label products, businesses gain access to proven technology and support infrastructure while maintaining control over brand identity and user experience.
Common Use Cases for Licensing
Licensing is commonly used in software development, allowing companies to integrate third-party technology or content into their own products while retaining control over branding and distribution. It is prevalent in industries such as media streaming, where platforms license content libraries to offer exclusive shows and movies. Licensing also supports hardware manufacturers who embed patented technology into devices without losing rights over the core intellectual property.
Popular Applications of White Labeling
White labeling finds popular applications in software as a service (SaaS) platforms, where companies rebrand cloud-based tools like CRM systems and email marketing software to offer customized solutions. E-commerce businesses also utilize white label products to create unique online storefronts without developing inventory or technology from scratch. Financial services leverage white label banking platforms to provide personalized, branded customer experiences while relying on established backend infrastructures.
Cost Considerations: Licensing vs White Label
Licensing typically involves lower upfront costs but includes ongoing royalty or usage fees, making it suitable for businesses seeking minimal initial investment. White label solutions require higher initial expenditures for customization and branding, yet they offer long-term cost benefits through full ownership and control over the product. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including development, maintenance, and scalability, is crucial when deciding between licensing and white label options.
Intellectual Property Implications
Licensing grants a company the right to use another entity's intellectual property (IP) while ownership remains with the licensor, limiting control but reducing risk. White label agreements transfer brand ownership to the reseller, allowing full branding rights but requiring careful management of IP rights to avoid infringement. Both models necessitate clear contracts to delineate IP use, protection, and liability for infringement to safeguard business interests.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing between licensing and white label models involves evaluating your business goals and control preferences; licensing grants permission to use intellectual property while maintaining brand identity, whereas white labeling allows rebranding a product entirely as your own. Licensing suits businesses seeking to leverage established IP without product development, while white label is ideal for companies aiming to offer customized solutions with minimal R&D investment. Analyzing factors like brand control, market strategy, and long-term scalability ensures selecting the optimal model aligned with your business objectives.
Future Trends in Licensing and White Label
Future trends in licensing emphasize increased adoption of AI-powered customization tools, enabling licensors to offer more flexible and scalable solutions. White label services are evolving towards deeper integration with blockchain for enhanced transparency and security, fostering trust between brands and consumers. Both models are projected to leverage data analytics for personalized customer experiences, driving more efficient market penetration and innovation.
Licensing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com