Proprietary technology refers to unique innovations, software, or processes owned exclusively by a company, providing a competitive edge in the marketplace. This technology is protected through patents, copyrights, or trade secrets, ensuring that rivals cannot replicate or use it without permission. Discover how proprietary technology can transform Your business and why it plays a crucial role in industry leadership by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
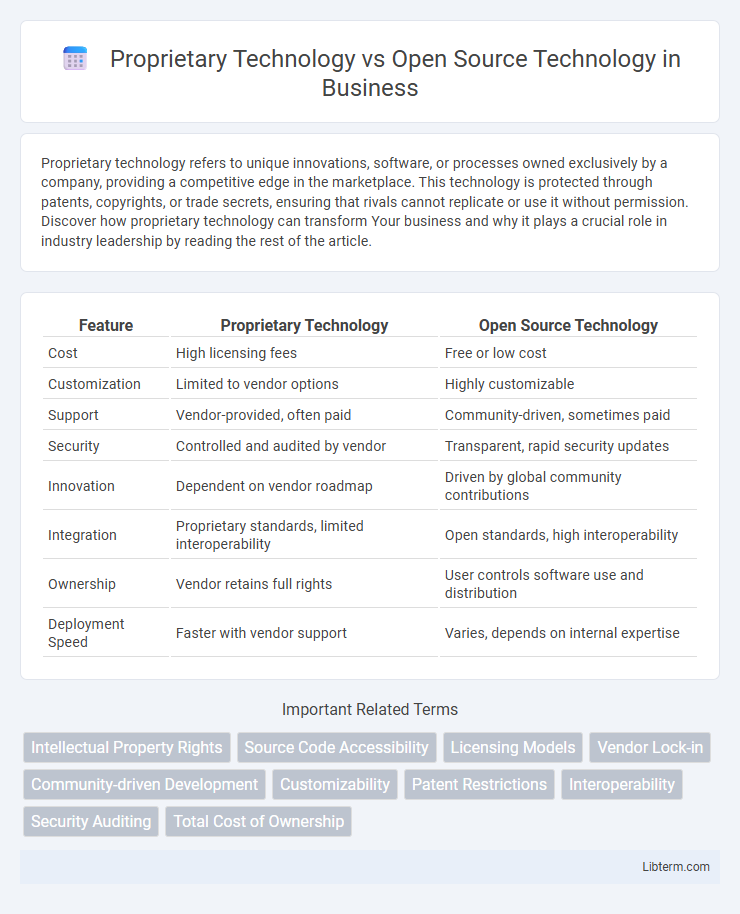
| Feature | Proprietary Technology | Open Source Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | High licensing fees | Free or low cost |
| Customization | Limited to vendor options | Highly customizable |
| Support | Vendor-provided, often paid | Community-driven, sometimes paid |
| Security | Controlled and audited by vendor | Transparent, rapid security updates |
| Innovation | Dependent on vendor roadmap | Driven by global community contributions |
| Integration | Proprietary standards, limited interoperability | Open standards, high interoperability |
| Ownership | Vendor retains full rights | User controls software use and distribution |
| Deployment Speed | Faster with vendor support | Varies, depends on internal expertise |
Introduction to Proprietary and Open Source Technologies
Proprietary technology refers to software or systems owned by a company or individual, with restrictions on usage, modification, and distribution, ensuring control over intellectual property and profit generation. Open source technology provides access to source code, allowing users to study, modify, and share software freely, fostering community collaboration and innovation. The fundamental difference lies in licensing models, where proprietary licenses impose limitations, while open source licenses promote transparency and collective development.
Definition and Core Principles
Proprietary technology is software or hardware owned by a company or individual, with usage rights restricted through licensing agreements, emphasizing control, exclusivity, and protection of intellectual property. Open source technology allows anyone to access, modify, and distribute the source code or design, promoting transparency, collaboration, and community-driven development. Core principles of proprietary technology include confidentiality and monetization, whereas open source technology prioritizes openness, interoperability, and shared innovation.
Key Differences Between Proprietary and Open Source
Proprietary technology is developed and maintained by a single organization, restricting access to its source code and requiring users to purchase licenses, while open source technology offers publicly available source code that anyone can modify and distribute. Security in proprietary systems depends on the vendor's updates, whereas open source benefits from community-driven scrutiny and faster vulnerability detection. Cost structures differ significantly, with proprietary software often involving high upfront or subscription fees, contrasting with the typically free or lower-cost model of open source solutions.
Cost Comparison: Licensing and Maintenance
Proprietary technology typically involves higher upfront costs due to licensing fees, which can include per-user or per-device charges, increasing overall expenses. Maintenance costs for proprietary solutions often require vendor-specific support contracts, leading to recurring fees and less flexibility in cost management. Open source technology usually offers lower initial costs by eliminating licensing fees, though organizations should consider internal support and customization expenses in ongoing maintenance budgets.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Proprietary technology often provides enhanced security through controlled access, rigorous testing, and regular updates managed by dedicated teams, ensuring vulnerabilities are promptly addressed. Open source technology allows for transparent code review by a global community, which can lead to quicker identification and patching of security flaws, but also requires active user vigilance to maintain privacy standards. Both approaches have unique security and privacy considerations, with proprietary solutions emphasizing centralized control and open source offering collaborative scrutiny.
Flexibility, Customization, and Scalability
Proprietary technology offers limited flexibility and customization due to controlled access to source code, restricting modifications to vendor-approved updates and features. Open source technology provides extensive flexibility and customization by allowing developers to modify and tailor the software to specific needs, promoting innovation and adaptability. Scalability in proprietary systems often depends on vendor capabilities and licensing, whereas open source solutions can be scaled more freely through community-driven enhancements and modular architectures.
Support, Updates, and Community Involvement
Proprietary technology offers structured support and regular updates directly from the vendor, ensuring consistent maintenance and security patches, while open source technology relies on community-driven support and frequent collaborative updates that can vary in quality and timeliness. Community involvement in open source projects fosters innovation and rapid problem-solving, leveraging a diverse user base to enhance features and fix bugs, whereas proprietary solutions benefit from dedicated in-house teams focused on stability and compliance. The balance between guaranteed vendor accountability in proprietary systems and the dynamic, transparent contributions in open source defines user preferences based on needs for reliability versus flexibility.
Case Studies: Industry Applications
Proprietary technology in industries such as healthcare and finance demonstrates enhanced security and tailored functionality through case studies like IBM Watson Health and SAP's ERP systems, showcasing controlled integration and compliance. Open source technology drives innovation and cost-efficiency in sectors like telecommunications and software development, with examples including the Linux operating system and Kubernetes container orchestration, enabling scalability and community-driven improvements. Both models highlight distinct advantages in real-world applications, guiding organizations in technology strategy decisions based on operational needs and ecosystem openness.
Pros and Cons of Proprietary vs Open Source
Proprietary technology offers controlled, secure environments with dedicated support but often comes with higher costs and limited customization. Open source technology provides flexibility, transparency, and community-driven innovation, though it may require more technical expertise and can have variable support quality. Organizations must weigh control and reliability against adaptability and cost-efficiency when choosing between proprietary and open source solutions.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Evaluating proprietary technology versus open source technology requires assessing factors such as cost, customization, security, and support tailored to your business needs. Proprietary solutions offer dedicated vendor support and enhanced security features, while open source provides flexibility and community-driven innovation that reduces expenses. Selecting the right technology aligns with your organization's long-term goals, scalability demands, and resource capabilities to maximize operational efficiency and competitive advantage.
Proprietary Technology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com