Platform-based business models leverage digital ecosystems to connect users, developers, and service providers, optimizing value creation through network effects and scalability. These models drive innovation by enabling seamless interactions and efficient resource allocation across various industries. Discover how understanding platform-based strategies can transform your business in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
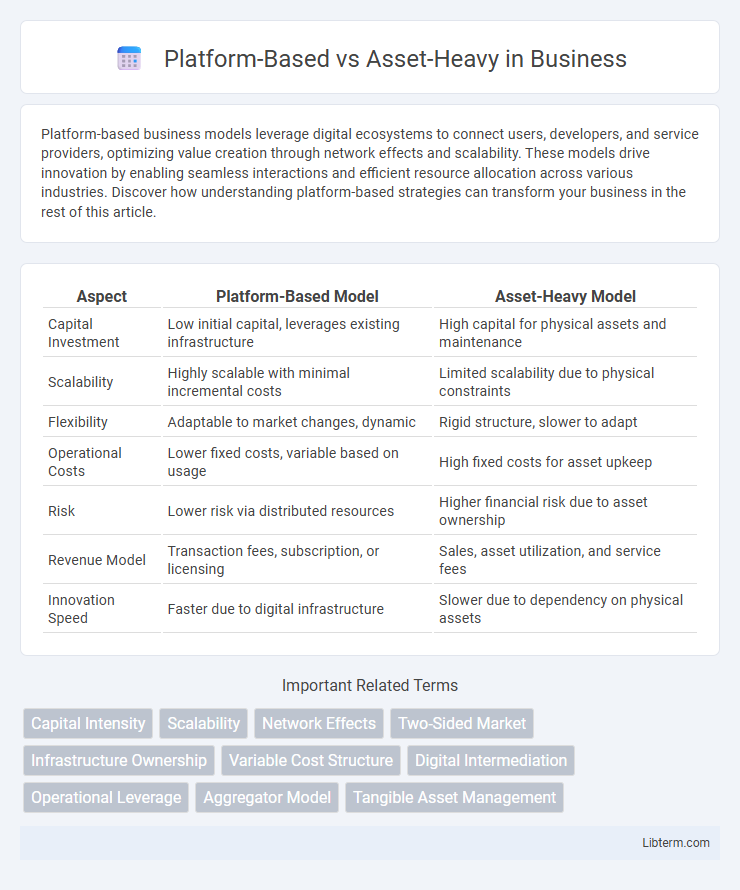
| Aspect | Platform-Based Model | Asset-Heavy Model |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Low initial capital, leverages existing infrastructure | High capital for physical assets and maintenance |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with minimal incremental costs | Limited scalability due to physical constraints |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to market changes, dynamic | Rigid structure, slower to adapt |
| Operational Costs | Lower fixed costs, variable based on usage | High fixed costs for asset upkeep |
| Risk | Lower risk via distributed resources | Higher financial risk due to asset ownership |
| Revenue Model | Transaction fees, subscription, or licensing | Sales, asset utilization, and service fees |
| Innovation Speed | Faster due to digital infrastructure | Slower due to dependency on physical assets |
Understanding Platform-Based and Asset-Heavy Models
Platform-based models leverage digital infrastructures to connect users, facilitate transactions, and enable ecosystem growth without owning physical assets, resulting in scalable and asset-light operations. Asset-heavy models require significant investment and ownership of physical resources, such as manufacturing plants or real estate, which leads to higher fixed costs but greater control over production and quality. Understanding the trade-offs between flexibility, scalability, and capital intensity is crucial for businesses when choosing between platform-based and asset-heavy strategies.
Key Characteristics of Platform-Based Businesses
Platform-based businesses leverage digital ecosystems to connect users, providers, and third parties, facilitating seamless interactions without owning physical assets. These models prioritize scalability, network effects, and data-driven insights to optimize user engagement and transaction efficiency. Key characteristics include multi-sided markets, low marginal costs, and reliance on algorithmic matching to enhance value creation.
Defining Features of Asset-Heavy Companies
Asset-heavy companies are characterized by significant ownership of physical assets such as factories, machinery, and real estate, which directly influence their production capacity and operational control. These firms require substantial capital investment and maintenance, leading to higher fixed costs but enabling greater control over quality and supply chain stability. The strategic focus on asset utilization and long-term depreciation impacts their financial structure and competitive positioning in industries like manufacturing, transportation, and energy.
Market Examples: Platform vs Asset-Heavy Leaders
Market leaders in platform-based business models like Airbnb and Uber maximize scalability by leveraging digital ecosystems without owning physical assets, enabling rapid user growth and market reach. In contrast, asset-heavy giants such as Walmart and ExxonMobil invest significantly in physical infrastructure and inventory, fostering control over supply chains and operational efficiency. Platform-based companies emphasize network effects and data-driven innovation, whereas asset-heavy leaders focus on capital-intensive resources to maintain competitive advantages.
Revenue Streams: How Each Model Generates Profit
Platform-based business models generate revenue primarily through transaction fees, subscription services, and advertising by facilitating connections between users and service providers without owning physical assets. Asset-heavy models rely on direct sales, leasing, or usage fees from owned assets such as manufacturing equipment, real estate, or vehicles to create consistent cash flow. The platform approach scales rapidly with lower operational costs, while the asset-heavy model demands significant capital investment but offers control over product quality and supply.
Scalability and Growth Potential Compared
Platform-based business models offer superior scalability by leveraging digital infrastructure and network effects, enabling rapid user base expansion with relatively low incremental costs. Asset-heavy models require substantial capital investment in physical resources, which can limit growth speed due to high fixed costs and slower asset utilization. Consequently, platform-based strategies typically provide greater flexibility and faster market penetration, driving higher growth potential compared to asset-heavy operations.
Risk Factors: Platform-Based versus Asset-Heavy
Platform-based business models face significant operational risks due to reliance on network effects, user trust, and data security, which can impact scalability and reputation. In contrast, asset-heavy models carry substantial financial risk from high capital investments, maintenance costs, and asset depreciation, affecting liquidity and profitability. Platform-based ventures must mitigate cyber threats and market volatility, while asset-heavy companies manage risks related to physical asset obsolescence and regulatory compliance.
Innovation Opportunities in Both Business Models
Platform-based business models offer innovation opportunities through scalable digital ecosystems that enable rapid integration of third-party services and customer-driven value creation, leveraging network effects for continuous growth. Asset-heavy models foster innovation by investing in physical infrastructure and proprietary technologies, providing control over production quality and enabling incremental improvements in manufacturing processes. Combining the agility of platform strategies with the reliability of asset-heavy operations creates a hybrid approach that maximizes innovation potential across supply chain optimization and customer experience enhancement.
Customer Experience and Engagement Differences
Platform-based business models prioritize seamless digital interfaces and real-time data analytics to enhance customer experience by offering personalized, flexible interactions and fostering community engagement. Asset-heavy models rely on physical infrastructure and direct customer service, which can lead to more consistent quality but often less agility in adapting to customer preferences and slower response times. The platform approach accelerates engagement through network effects and continuous feedback loops, while asset-heavy companies focus on tangible service delivery and face challenges scaling personalized interactions efficiently.
Choosing the Right Model: Strategic Considerations
Selecting the right business model requires evaluating key strategic factors such as capital investment, scalability, and operational flexibility. Platform-based models leverage digital infrastructure to connect users with minimal asset ownership, enabling rapid growth and lower fixed costs. Asset-heavy models demand substantial upfront investment in physical resources but provide greater control over quality and supply chain stability, influencing long-term profitability and risk management.
Platform-Based Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com