A probation period allows employers to evaluate your skills, work habits, and fit within the company before confirming permanent employment. Understanding the terms of your probation can help you navigate expectations and improve your chances of success. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to make the most of your probation period.
Table of Comparison
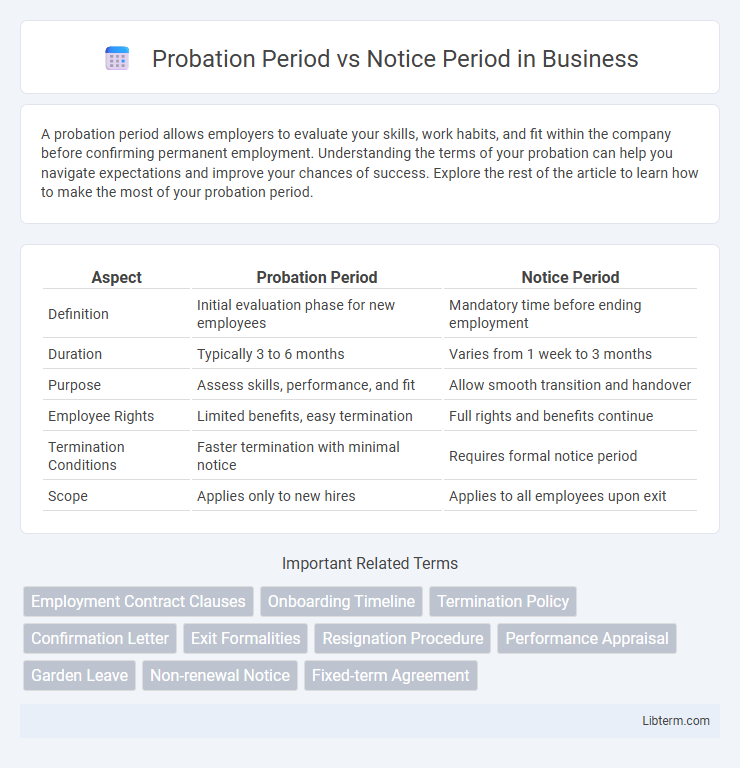
| Aspect | Probation Period | Notice Period |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Initial evaluation phase for new employees | Mandatory time before ending employment |
| Duration | Typically 3 to 6 months | Varies from 1 week to 3 months |
| Purpose | Assess skills, performance, and fit | Allow smooth transition and handover |
| Employee Rights | Limited benefits, easy termination | Full rights and benefits continue |
| Termination Conditions | Faster termination with minimal notice | Requires formal notice period |
| Scope | Applies only to new hires | Applies to all employees upon exit |
Understanding Probation Period: Definition and Purpose
The probation period is a defined timeframe at the beginning of employment during which an employer evaluates a new employee's performance, skills, and suitability for the role. Its primary purpose is to assess the compatibility between the employee and the company before confirming permanent employment status. This period allows both parties to terminate the contract with shorter notice or fewer penalties compared to the notice period after probation.
What is a Notice Period? Key Concepts
A notice period is the mandatory duration an employee or employer must provide before ending employment, ensuring a smooth transition and minimizing disruptions. It typically ranges from one week to three months, depending on contract terms and local labor laws. Notice periods allow both parties to prepare for the departure, such as finding a replacement or completing ongoing tasks.
Key Differences Between Probation Period and Notice Period
The probation period is a designated timeframe during which an employer assesses a new employee's performance, typically lasting from three to six months, whereas the notice period is the duration an employee or employer must provide before terminating employment, often ranging from one to three months. The probation period allows for evaluation and potential termination without formal notice, while the notice period ensures a structured transition following resignation or dismissal. Key differences include the purpose--assessment versus termination protocol--and the legal obligations tied to each period.
Legal Framework: Probation and Notice Periods in Employment Law
The legal framework governing probation and notice periods in employment law varies by jurisdiction but generally stipulates shorter notice requirements during probation to allow employers to assess suitability. Probation periods typically range from three to six months, providing a trial phase after which standard notice periods apply, commonly from one to three months depending on contract terms and local labor regulations. Employment laws often mandate clear communication of probation and notice period conditions in the employment contract to ensure compliance and protect both employer and employee rights.
Duration: How Long Do Probation and Notice Periods Last?
Probation periods typically last between three to six months, allowing employers to evaluate new employees' performance and fit within the company. Notice periods vary based on contract terms and local labor laws, generally ranging from one week to three months, depending on the employee's tenure and role. Understanding the specific durations for probation and notice periods is crucial for both employers and employees to manage expectations and legal compliance.
Rights and Responsibilities During Probation Period
During the probation period, employees have the right to receive clear communication regarding performance expectations and feedback, while employers hold the responsibility to provide adequate training and support. Both parties can terminate the employment with shorter notice or no notice, depending on the contract terms, reflecting a more flexible arrangement compared to the notice period after probation. Legal protections during probation vary by jurisdiction but generally include fair treatment and non-discrimination to safeguard employee rights.
Employee and Employer Obligations During Notice Period
During the notice period, employees are obligated to fulfill their job responsibilities diligently while adhering to company policies and providing formal resignation as required. Employers must ensure clear communication regarding the duration of the notice period, monitor employee performance, and complete any final settlements or documentation. Both parties should collaborate to facilitate a smooth transition, respecting the contractual terms outlined in the employment agreement.
Termination Procedures: Probation vs Notice Period
Termination during the probation period typically involves shorter notice requirements or immediate dismissal due to the provisional nature of employment and the employer's ongoing evaluation. In contrast, termination after the probation period mandates adherence to formal notice periods as stipulated in employment contracts or labor laws, ensuring job security and fair process. Employers must carefully follow these procedures to avoid legal disputes and ensure compliance with relevant labor regulations.
Impact on Employee Benefits and Entitlements
During the probation period, employees often have limited access to full benefits and entitlements, such as health insurance, paid leave, and retirement contributions, which typically commence after successful completion. Notice periods during or post-probation can directly affect severance pay eligibility and the continuation of employee benefits, with shorter notice potentially limiting compensation. Understanding the distinctions between probation and notice periods is critical for employees to safeguard their rights to benefits and negotiate appropriate terms.
Best Practices for Managing Probation and Notice Periods
Establish clear expectations and deliverables during the probation period to accurately assess employee performance and cultural fit, using regular feedback sessions for continuous improvement. Implement a structured notice period policy that balances adequate transition time with business needs, ensuring smooth handover and knowledge transfer. Maintain transparent communication throughout both periods to foster trust and minimize potential conflicts, enhancing overall workforce stability and productivity.
Probation Period Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com