Book value represents a company's net asset value calculated by subtracting liabilities from total assets, reflecting its intrinsic worth on the balance sheet. It is a critical metric for investors to assess whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued relative to its market price. Discover how understanding book value can enhance your financial decisions by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
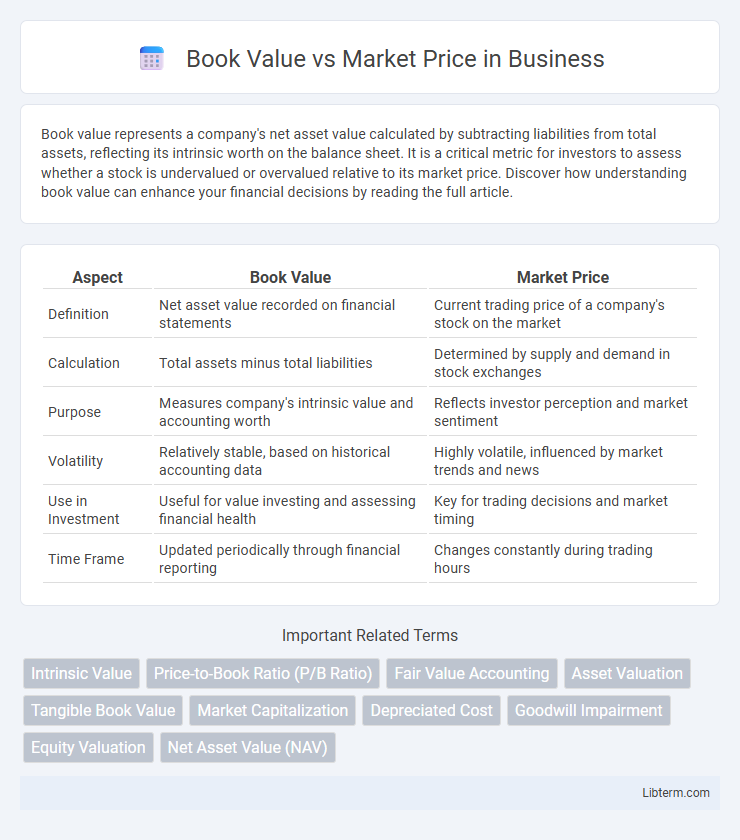
| Aspect | Book Value | Market Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Net asset value recorded on financial statements | Current trading price of a company's stock on the market |
| Calculation | Total assets minus total liabilities | Determined by supply and demand in stock exchanges |
| Purpose | Measures company's intrinsic value and accounting worth | Reflects investor perception and market sentiment |
| Volatility | Relatively stable, based on historical accounting data | Highly volatile, influenced by market trends and news |
| Use in Investment | Useful for value investing and assessing financial health | Key for trading decisions and market timing |
| Time Frame | Updated periodically through financial reporting | Changes constantly during trading hours |
Understanding Book Value
Book value represents a company's net asset value calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets, reflecting the accounting value recorded on the balance sheet. It provides investors with a baseline measure of a company's intrinsic worth based on historical costs rather than current market conditions. Understanding book value helps in assessing whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued compared to its market price.
Defining Market Price
Market price is the current price at which an asset or security can be bought or sold in the open market, reflecting real-time supply and demand dynamics. Unlike book value, which represents the accounting value of an asset based on historical costs minus depreciation, market price fluctuates continuously due to investor sentiment, market conditions, and economic factors. This price provides a snapshot of the asset's perceived worth among market participants at a given moment.
Key Differences Between Book Value and Market Price
Book value represents a company's net asset value calculated from its balance sheet by subtracting liabilities from total assets, reflecting the historical cost of assets. Market price is the current trading price of a company's stock on the stock exchange, influenced by investor perceptions, demand, and overall market conditions. Key differences include book value being an accounting measure based on recorded costs, while market price fluctuates in real time and often exceeds book value due to growth potential and market sentiment.
Importance of Book Value in Financial Analysis
Book value represents a company's net asset value, calculated as total assets minus total liabilities, providing a fundamental baseline for assessing intrinsic worth. Its importance in financial analysis lies in offering investors a tangible metric to evaluate whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued compared to its current market price. Analysts use book value to identify investment opportunities by comparing it with market price, aiding in risk assessment and long-term value estimation.
Factors Influencing Market Price
Market price is influenced by factors such as investor sentiment, supply and demand dynamics, and company performance indicators including earnings reports and future growth prospects. Macroeconomic conditions, interest rates, and industry trends also play a critical role in fluctuating stock prices. Market price often diverges from book value due to intangible assets, market speculation, and expectations of future profitability.
Book Value and Market Price in Stock Valuation
Book value represents a company's net asset value calculated as total assets minus liabilities, providing a fundamental measure of a stock's intrinsic worth. Market price reflects the current trading price of a stock on the stock exchange, influenced by investor sentiment, market conditions, and future growth expectations. Comparing book value to market price helps investors identify undervalued or overvalued stocks, which is essential for effective stock valuation and informed investment decisions.
Reasons for Discrepancies Between Book Value and Market Price
Discrepancies between book value and market price arise due to factors such as investor sentiment, future growth potential, and market conditions not reflected in accounting records. Book value represents historical costs and tangible assets, while market price incorporates intangible assets, brand value, and expectations of future earnings. Changes in industry trends, economic outlook, and company performance forecasts also contribute to the divergence between these two financial metrics.
Limitations of Book Value
Book value often underrepresents a company's true worth because it relies on historical cost accounting rather than current market conditions, ignoring intangible assets like brand value and intellectual property. It fails to account for market fluctuations, future growth potential, or changing economic environments, leading to possible undervaluation or overvaluation. Investors should consider book value alongside market price and other financial metrics for a comprehensive assessment.
How Investors Use Book Value vs. Market Price
Investors use book value to assess a company's intrinsic worth based on its financial statements, providing a conservative estimate of equity value. Market price, reflecting real-time investor sentiment and market conditions, helps investors gauge the stock's current trading value and potential growth prospects. Comparing book value to market price enables investors to identify undervalued or overvalued stocks, guiding strategic buy or sell decisions.
Book Value vs Market Price: Which Metric Matters More?
Book value represents a company's net asset value based on its financial statements, while market price reflects investor sentiment and external factors influencing stock valuation. Investors often prioritize market price for assessing growth potential and trading opportunities, but book value provides a fundamental benchmark for evaluating intrinsic worth and financial stability. The relative importance of book value versus market price depends on investment strategy, with value investors favoring book value metrics and growth investors focusing on market price trends.
Book Value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com