Private equity-backed companies often benefit from strategic guidance, operational improvements, and access to capital that drives growth and innovation. These investments can transform businesses by enhancing efficiency and expanding market reach. Discover how private equity backing can impact your company's success by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
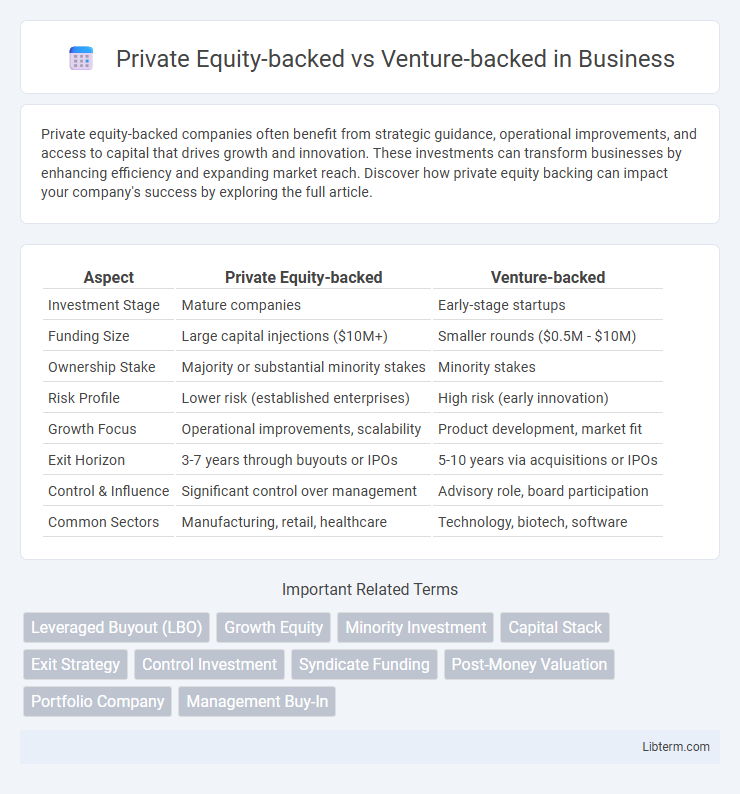
| Aspect | Private Equity-backed | Venture-backed |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Stage | Mature companies | Early-stage startups |
| Funding Size | Large capital injections ($10M+) | Smaller rounds ($0.5M - $10M) |
| Ownership Stake | Majority or substantial minority stakes | Minority stakes |
| Risk Profile | Lower risk (established enterprises) | High risk (early innovation) |
| Growth Focus | Operational improvements, scalability | Product development, market fit |
| Exit Horizon | 3-7 years through buyouts or IPOs | 5-10 years via acquisitions or IPOs |
| Control & Influence | Significant control over management | Advisory role, board participation |
| Common Sectors | Manufacturing, retail, healthcare | Technology, biotech, software |
Introduction: Defining Private Equity-backed and Venture-backed
Private Equity-backed companies receive investment from private equity firms that typically acquire significant ownership stakes to drive operational improvements and long-term value creation. Venture-backed companies obtain funding from venture capitalists who invest primarily in early-stage startups with high growth potential in exchange for equity. These two funding approaches differ in investment stages, risk tolerance, and strategic objectives, shaping distinct paths for company development.
Key Differences in Investment Stages
Private equity-backed companies typically invest in mature businesses during later stages, focusing on restructuring or expanding established operations, whereas venture-backed firms target early-stage startups with high growth potential. Private equity involves larger capital deployment with emphasis on stable cash flows and long-term value creation, while venture capital prioritizes innovation and disruptive technologies with higher risk tolerance. The investment horizon for private equity is generally 4-7 years, contrasting with venture capital's 5-10 year timeframe aimed at scaling startups rapidly.
Funding Size and Structuring
Private equity-backed companies typically raise larger funding rounds compared to venture-backed startups, often exceeding hundreds of millions of dollars due to mature business models and stable cash flows. The structuring in private equity involves majority equity stakes and leveraged buyouts, aiming for control and value extraction through operational improvements. Venture-backed firms usually receive smaller, phased investments aligned with growth milestones, structured as preferred equity to balance risk and promote scalability in early-stage innovation.
Ownership and Control Considerations
Private equity-backed companies typically involve significant ownership stakes held by a few institutional investors, granting them substantial control over strategic decisions and board composition. Venture-backed firms often feature more dispersed ownership among multiple early-stage investors, with founders retaining considerable influence while investors guide growth and exit strategies. The balance of ownership and control in private equity usually emphasizes value creation through operational involvement, whereas venture capital prioritizes rapid scaling and innovation.
Growth Objectives and Time Horizons
Private equity-backed companies typically pursue aggressive growth objectives aimed at scaling established operations and improving profitability within a 3 to 7-year timeframe. Venture-backed firms prioritize rapid innovation and market expansion, often targeting high-growth sectors with a shorter investment horizon of 5 to 10 years. The difference in time horizons reflects private equity's focus on operational efficiency and stable returns, contrasting with venture capital's emphasis on disruptive growth and exit through IPO or acquisition.
Risk Tolerance and Target Returns
Private Equity-backed firms typically demonstrate lower risk tolerance, targeting steady returns between 15% and 20% through mature companies and operational improvements. Venture-backed startups accept higher risk levels, often seeking exponential growth with target returns exceeding 30% to compensate for early-stage uncertainties. The contrasting risk-return profiles influence investment horizons, portfolio diversification, and exit strategies within private equity and venture capital domains.
Role in Company Governance and Decision-making
Private equity-backed firms typically have experienced investors who play an active role in company governance, often securing board seats and influencing strategic decisions to drive operational improvements and financial performance. Venture-backed companies usually experience more founder involvement in decision-making, with investors providing guidance and oversight while focusing on growth and innovation. The governance structure in private equity tends to be more control-oriented, whereas venture capital prioritizes collaborative support to scale the business.
Typical Industries and Business Models Funded
Private equity-backed firms often target established industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and consumer goods, focusing on mature businesses with stable cash flows and potential for operational improvements. Venture-backed companies primarily invest in technology, biotechnology, and fintech sectors, supporting early-stage startups with scalable business models driven by innovation and rapid growth potential. Both funding types emphasize value creation, yet private equity prefers leveraged buyouts and operational efficiency, while venture capital prioritizes high-growth, disruptive solutions.
Exit Strategies and Liquidity Events
Private equity-backed companies typically pursue exit strategies through leveraged buyouts, secondary buyouts, or mergers and acquisitions, aiming for liquidity events within 3 to 7 years by selling to strategic buyers or other financial sponsors. Venture-backed firms often focus on initial public offerings (IPOs) and high-profile acquisitions as primary exit routes, with exits usually occurring during the early-growth or late-stage expansion phases. Both private equity and venture capital prioritize maximizing returns, but private equity tends to target more mature companies with stable cash flows, while venture capital invests in higher-growth startups with greater exit volatility.
Choosing Between Private Equity or Venture Capital
Choosing between private equity and venture capital depends on your company's stage and funding needs. Private equity targets mature businesses seeking growth capital or restructuring, offering larger investments with control stakes, whereas venture capital focuses on early-stage startups with high growth potential, providing smaller funding rounds and strategic guidance. Assess your business maturity, growth trajectory, and desired investor involvement to determine the optimal funding source.
Private Equity-backed Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com