Fixed price contracts provide predictable budgeting by setting a specific cost for a project or service, minimizing financial uncertainty. These agreements are ideal for clearly defined projects where scope and deliverables are well understood. Discover how fixed price models can benefit your next project by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
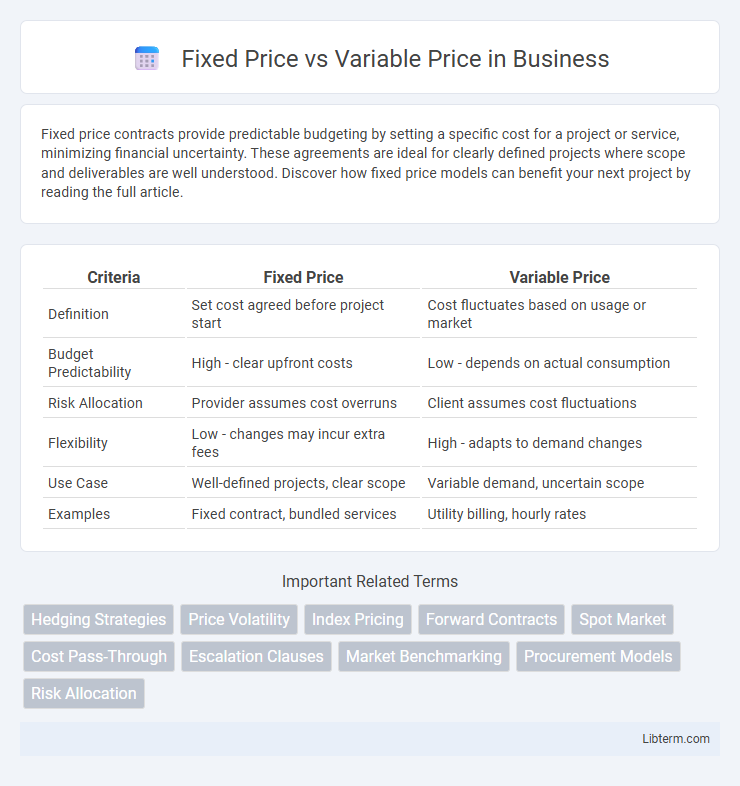
| Criteria | Fixed Price | Variable Price |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set cost agreed before project start | Cost fluctuates based on usage or market |
| Budget Predictability | High - clear upfront costs | Low - depends on actual consumption |
| Risk Allocation | Provider assumes cost overruns | Client assumes cost fluctuations |
| Flexibility | Low - changes may incur extra fees | High - adapts to demand changes |
| Use Case | Well-defined projects, clear scope | Variable demand, uncertain scope |
| Examples | Fixed contract, bundled services | Utility billing, hourly rates |
Understanding Fixed Price and Variable Price Models
Fixed price models involve setting a predetermined cost for a project or product, ensuring budget predictability and minimizing financial risk for buyers. Variable price models adjust costs based on usage, time, or scope changes, offering flexibility to accommodate fluctuating project requirements or market conditions. Choosing between these models depends on factors such as project scope clarity, risk tolerance, and the need for cost control versus adaptability.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Variable Pricing
Fixed price guarantees a set cost for goods or services, providing budget predictability and eliminating price fluctuations regardless of market changes. Variable price fluctuates based on factors like supply, demand, or production costs, potentially offering lower initial prices but increased financial risk. Understanding differences in cost stability, risk exposure, and market responsiveness is essential for selecting an optimal pricing strategy in project management and procurement.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Price Agreements
Fixed Price Agreements provide budget certainty by locking costs, which helps in controlling expenses and simplifies financial planning for projects. They minimize the risk of cost overruns but can lead to less flexibility in scope changes or unforeseen work, potentially requiring costly renegotiations. This pricing model benefits clients with well-defined project requirements but may cause challenges if project specifications evolve or uncertainties arise.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Variable Pricing
Variable pricing allows businesses to adjust prices based on demand, competition, and market conditions, enhancing revenue optimization and customer segmentation. This pricing strategy can increase sales during peak periods but may lead to customer dissatisfaction or confusion due to price fluctuations. Its disadvantages include potential damage to brand trust and the complexity of continuously monitoring and responding to market changes.
When to Choose Fixed Price Contracts
Fixed price contracts are ideal when project scope, specifications, and timelines are clearly defined and unlikely to change, providing budget certainty and reducing financial risk for clients. They are recommended for projects with well-understood requirements, such as construction or manufacturing, where deliverables and costs can be accurately estimated upfront. Choosing fixed price contracts helps ensure that the contractor is motivated to control costs and complete the project efficiently within the agreed budget.
Ideal Scenarios for Variable Price Contracts
Variable price contracts are ideal in projects where scope or market conditions frequently change, such as software development and construction with evolving requirements. These contracts allow flexibility to adjust costs based on actual resource usage or materials prices, reducing risk for both parties when estimations are uncertain. Businesses benefit from variable pricing in volatile markets or innovation-driven industries where adaptability to new information is critical for project success.
Risk Management in Pricing Models
Fixed price models offer predictable costs, minimizing financial risk by locking in prices regardless of market fluctuations. Variable price models expose businesses to pricing volatility, requiring robust risk management strategies such as hedging or dynamic pricing algorithms to mitigate potential losses. Effective risk management in pricing models balances cost certainty with market responsiveness to optimize profitability.
Budget Predictability: Fixed vs Variable Price
Fixed price contracts offer superior budget predictability by setting a specific cost for goods or services, reducing financial uncertainty and enabling precise budget allocation. Variable price contracts introduce cost fluctuations based on market conditions, resource usage, or performance metrics, posing risks to budget stability. Organizations prioritize fixed price agreements when maintaining strict budget control is critical for project success and financial planning.
Impact on Client-Vendor Relationships
Fixed price agreements provide clients with cost certainty, fostering trust and enabling precise budget planning, while vendors are incentivized to maintain efficiency and meet deadlines. Variable price contracts introduce financial flexibility, allowing adjustments based on project scope or market conditions, but can create uncertainty that challenges trust and requires transparent communication. The choice between fixed and variable pricing significantly influences collaboration dynamics, risk allocation, and long-term client-vendor partnership stability.
How to Decide: Fixed Price or Variable Price?
Choosing between fixed price and variable price depends on factors such as market volatility, risk tolerance, and budget predictability. Fixed price contracts offer stability and cost control, making them ideal for projects with well-defined scopes and low uncertainty. Variable price models provide flexibility and potential cost savings in fluctuating markets but require active monitoring and risk management.
Fixed Price Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com