Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across various asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, enhancing the stability of your portfolio. It allows you to capture growth opportunities while protecting against the volatility of any single market or sector. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective strategies for diversifying your investments successfully.
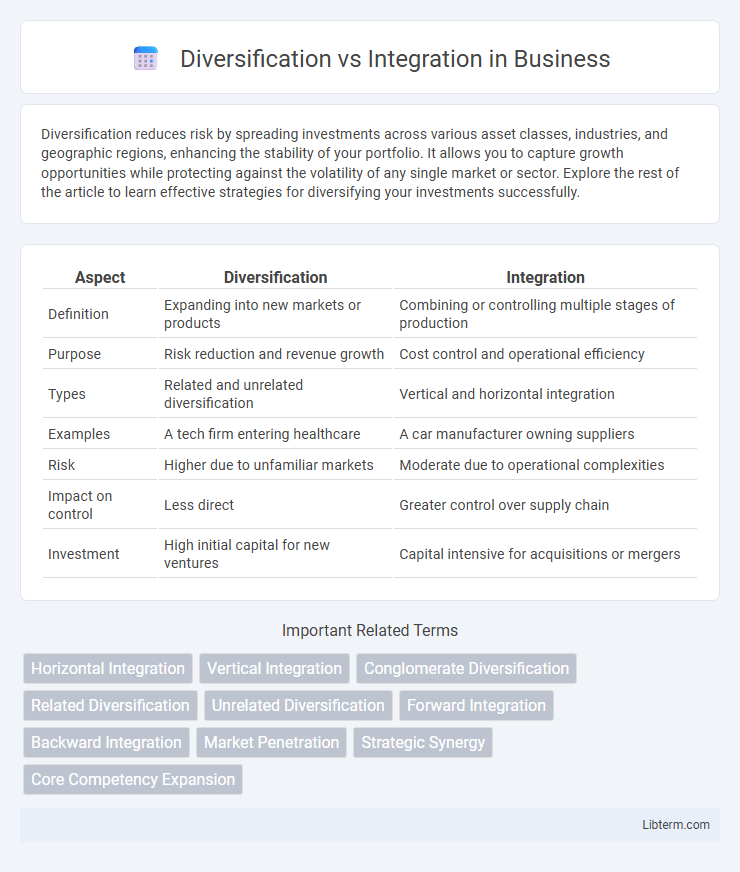
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Diversification | Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expanding into new markets or products | Combining or controlling multiple stages of production |
| Purpose | Risk reduction and revenue growth | Cost control and operational efficiency |
| Types | Related and unrelated diversification | Vertical and horizontal integration |
| Examples | A tech firm entering healthcare | A car manufacturer owning suppliers |
| Risk | Higher due to unfamiliar markets | Moderate due to operational complexities |
| Impact on control | Less direct | Greater control over supply chain |
| Investment | High initial capital for new ventures | Capital intensive for acquisitions or mergers |
Understanding Diversification and Integration
Diversification involves expanding a company's product lines or markets to reduce risk and capitalize on new growth opportunities, enhancing overall stability. Integration refers to the strategic alignment and coordination of internal processes or external entities, such as suppliers and distributors, to increase efficiency and control. Understanding the balance between diversification and integration helps businesses optimize resource allocation and competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Key Differences Between Diversification and Integration
Diversification involves expanding a company's operations into new markets or product lines to reduce risk, while integration focuses on combining different stages of production or business processes to improve efficiency and control. Diversification spreads business risk across various sectors, whereas integration enhances operational synergy by consolidating supply chains or distribution channels. Key differences include the strategic goal of risk reduction for diversification versus cost reduction and increased market power for integration.
Types of Diversification Strategies
Diversification strategies include related diversification, where a company expands into industries connected to its core business, leveraging existing capabilities and resources. Unrelated diversification involves entering entirely new markets or industries, minimizing risk through varied revenue streams. Geographic diversification targets new regions or countries to capitalize on different economic conditions and customer bases.
Forms of Integration: Vertical and Horizontal
Vertical integration involves a company expanding its operations into different stages of the supply chain, either upstream by controlling suppliers or downstream by managing distribution channels, enhancing control over production and reducing costs. Horizontal integration occurs when a company acquires or merges with competitors operating at the same stage of the supply chain, increasing market share and reducing competition. Both forms of integration can boost operational efficiency and market power, but vertical integration targets supply chain control while horizontal integration focuses on expanding market presence.
Benefits of Diversification in Business
Diversification in business minimizes risks by spreading investments across various industries and markets, reducing dependence on a single revenue stream. It enhances growth opportunities by tapping into new customer segments and innovating products or services. Companies with diverse portfolios often achieve greater financial stability and resilience during economic fluctuations.
Advantages of Integration Strategies
Integration strategies enhance operational efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing costs through tighter coordination across business units. They facilitate improved information flow and resource sharing, leading to stronger competitive advantages and faster decision-making. Moreover, integration fosters brand consistency and customer loyalty by delivering a unified market presence and seamless customer experience.
Risks and Challenges of Diversification
Diversification introduces risks such as increased complexity in managing diverse business units, potential dilution of core competencies, and higher operational costs due to varied market demands. Challenges include difficulties in maintaining consistent quality and brand identity across different sectors, along with the risk of overextending financial and managerial resources, which can lead to decreased overall performance. Market unfamiliarity and regulatory compliance issues in new industries further amplify the risks associated with diversification strategies.
Potential Drawbacks of Integration
Integration can lead to reduced flexibility as tightly connected systems or business units may struggle to adapt to market changes. High initial costs and complexity increase implementation risk, potentially disrupting operations and straining resources. Dependency on a single integrated system raises vulnerability to failures, impacting overall performance and continuity.
Choosing Between Diversification and Integration
Choosing between diversification and integration requires evaluating a company's core competencies, market conditions, and risk tolerance. Diversification spreads risk by entering new markets or products, enhancing growth potential but often demanding significant investment and management complexity. Integration, whether vertical or horizontal, strengthens control over supply chains or market presence, boosting efficiency and competitive advantage within existing sectors.
Case Studies: Successful Diversification and Integration
Apple's successful diversification into services like Apple Music and Apple TV+ complements its hardware business, generating substantial recurring revenue and enhancing customer loyalty. Amazon's integration of e-commerce with cloud computing via AWS demonstrates robust synergy, driving market dominance and exponential growth. Google's diversification into autonomous vehicles through Waymo and integration of AI across its platforms exemplify a strategic balance, fostering innovation and expanding market reach.
Diversification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com