Lean process streamlines operations by eliminating waste and optimizing workflows to enhance efficiency and productivity. This approach focuses on delivering maximum value to customers while minimizing resources and time. Explore this article to discover how your business can implement lean processes for sustained growth and success.
Table of Comparison
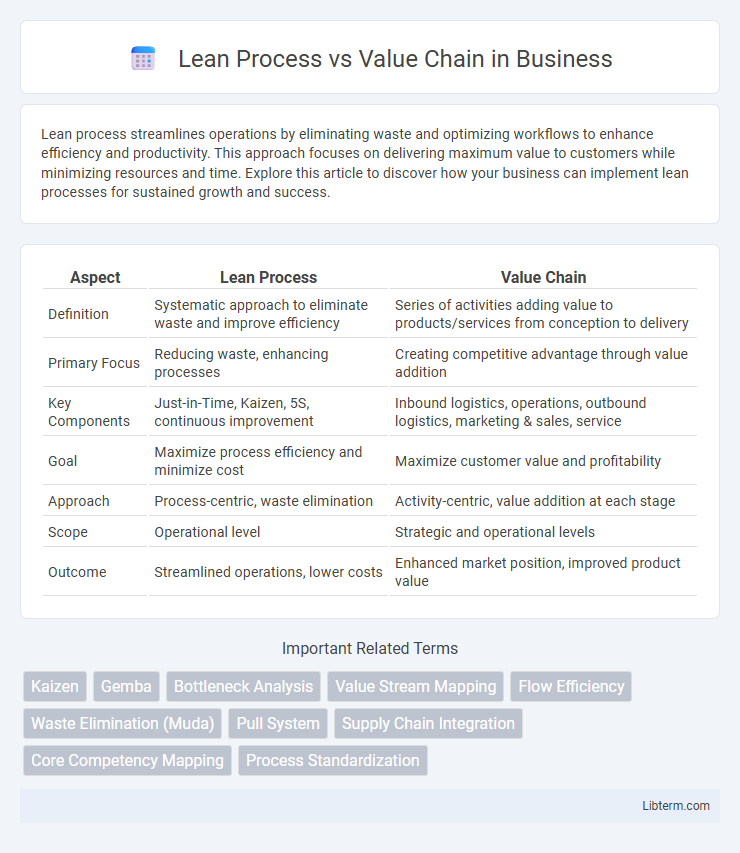
| Aspect | Lean Process | Value Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic approach to eliminate waste and improve efficiency | Series of activities adding value to products/services from conception to delivery |
| Primary Focus | Reducing waste, enhancing processes | Creating competitive advantage through value addition |
| Key Components | Just-in-Time, Kaizen, 5S, continuous improvement | Inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing & sales, service |
| Goal | Maximize process efficiency and minimize cost | Maximize customer value and profitability |
| Approach | Process-centric, waste elimination | Activity-centric, value addition at each stage |
| Scope | Operational level | Strategic and operational levels |
| Outcome | Streamlined operations, lower costs | Enhanced market position, improved product value |
Introduction to Lean Process and Value Chain
Lean Process emphasizes eliminating waste and optimizing workflows to enhance efficiency and reduce costs, prioritizing continuous improvement and customer value creation. The Value Chain framework identifies primary and support activities within an organization that add value to products or services, enabling firms to analyze processes for competitive advantage. Integrating Lean principles within the Value Chain strengthens operational effectiveness by streamlining value-adding activities and minimizing non-value-adding tasks.
Key Principles of Lean Process
The Lean Process emphasizes eliminating waste, continuous improvement (Kaizen), and maximizing customer value by streamlining workflows and reducing non-value-added activities. Core principles include defining value from the customer's perspective, mapping the value stream to identify inefficiencies, and creating flow by organizing work processes that prevent delays and bottlenecks. Implementing pull systems and striving for perfection through iterative refinement ensures lean operations consistently deliver quality and efficiency throughout the value chain.
Core Components of Value Chain
The core components of a value chain include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, each contributing to value creation through different stages. Lean process principles emphasize waste reduction across these components by streamlining workflows, eliminating non-value-added activities, and enhancing efficiency. Integrating lean methodologies within the value chain optimizes resource utilization and maximizes customer value by improving quality and reducing lead times.
Lean Process vs Value Chain: Fundamental Differences
Lean Process focuses on eliminating waste and improving efficiency within specific operational workflows, targeting process-level optimization. In contrast, the Value Chain encompasses a broader scope, analyzing all activities from product conception to delivery to maximize value creation across the entire business ecosystem. The fundamental difference lies in Lean Process's micro-level focus on waste reduction versus the Value Chain's macro-level approach to strategic value enhancement.
Efficiency in Lean Process vs Value Creation in Value Chain
Lean Process emphasizes efficiency by minimizing waste, streamlining workflows, and optimizing resource utilization to deliver products faster and at lower costs. In contrast, the Value Chain focuses on value creation by enhancing each activity's contribution to customer satisfaction, driving innovation, and differentiating products or services in the market. While Lean prioritizes operational efficiency, the Value Chain integrates activities to maximize overall value and competitive advantage.
Impact on Cost Reduction and Profitability
Lean Process methodology streamlines operations by eliminating waste, reducing cycle times, and optimizing resource use, directly lowering operational costs. The Value Chain framework identifies primary and support activities that add value to products or services, enabling strategic cost management and enhancing profit margins. Integrating Lean Process improvements within the Value Chain maximizes cost reduction and drives profitability by improving efficiency across all value-creating activities.
Application in Various Industries
Lean Process enhances operational efficiency by identifying and eliminating waste in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, leading to reduced lead times and improved quality. Value Chain analysis applies across industries such as retail, technology, and automotive by mapping key activities that create value, enabling strategic optimization of procurement, production, and distribution. Both frameworks drive competitive advantage through process improvement and value maximization tailored to industry-specific demands.
Challenges in Implementing Lean and Value Chain Strategies
Implementing Lean processes often faces challenges such as employee resistance to change, lack of management commitment, and difficulties in sustaining continuous improvement initiatives. Value Chain strategies encounter obstacles including complex supplier coordination, inadequate integration of technology, and misalignment between value-adding activities and customer expectations. Both approaches require robust communication, clear performance metrics, and a culture of collaboration to successfully overcome implementation barriers.
Integration of Lean Process with Value Chain Analysis
Integrating Lean Process with Value Chain Analysis enhances operational efficiency by identifying and eliminating waste across each activity within the value chain. This synergy allows organizations to streamline processes from inbound logistics to after-sales service, resulting in reduced costs and improved customer value. Leveraging data from value chain mapping enables targeted lean interventions that optimize workflow, inventory management, and quality control throughout the entire production and delivery system.
Future Trends in Lean Process and Value Chain Management
Future trends in Lean Process emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and machine learning to enhance real-time data analytics and automate waste reduction across production cycles. Value Chain Management is increasingly adopting digital platforms and blockchain to improve transparency, traceability, and collaboration among global suppliers and customers. Both approaches are converging towards sustainable practices and agile frameworks, promoting resilience and efficiency in rapidly changing market environments.
Lean Process Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com