The Dodd-Frank Act established comprehensive financial regulations aimed at reducing risks in the U.S. financial system and protecting consumers from predatory lending practices. It introduced measures like increased transparency, stricter oversight of financial institutions, and the creation of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau to safeguard Your interests. Explore the rest of this article to understand how the Dodd-Frank Act may impact your financial security and investment decisions.
Table of Comparison
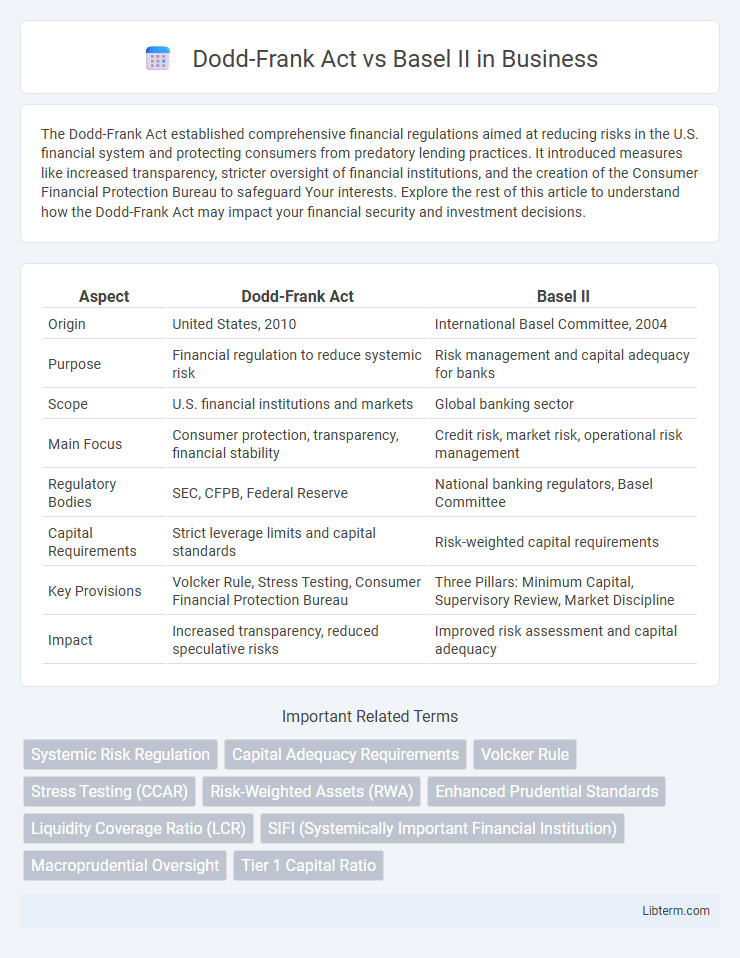
| Aspect | Dodd-Frank Act | Basel II |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | United States, 2010 | International Basel Committee, 2004 |
| Purpose | Financial regulation to reduce systemic risk | Risk management and capital adequacy for banks |
| Scope | U.S. financial institutions and markets | Global banking sector |
| Main Focus | Consumer protection, transparency, financial stability | Credit risk, market risk, operational risk management |
| Regulatory Bodies | SEC, CFPB, Federal Reserve | National banking regulators, Basel Committee |
| Capital Requirements | Strict leverage limits and capital standards | Risk-weighted capital requirements |
| Key Provisions | Volcker Rule, Stress Testing, Consumer Financial Protection Bureau | Three Pillars: Minimum Capital, Supervisory Review, Market Discipline |
| Impact | Increased transparency, reduced speculative risks | Improved risk assessment and capital adequacy |
Introduction to Financial Regulations
The Dodd-Frank Act and Basel II represent two pivotal frameworks in financial regulation, with Dodd-Frank emphasizing enhanced transparency and systemic risk reduction post-2008 financial crisis primarily in the United States, while Basel II, developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, focuses on international banking standards for capital adequacy, stress testing, and market discipline. Dodd-Frank introduced rigorous oversight mechanisms including the creation of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, whereas Basel II established a three-pillar approach enhancing risk management practices globally. Both frameworks aim to strengthen financial stability but differ in scope and regulatory emphasis, reflecting domestic versus global regulatory priorities.
Overview of the Dodd-Frank Act
The Dodd-Frank Act, enacted in 2010, is a comprehensive U.S. financial reform law aimed at reducing systemic risk and increasing transparency in the financial system following the 2008 crisis. It establishes the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) to safeguard consumers and imposes stricter regulations on banks, including stress testing and capital requirements under the Volcker Rule. Unlike Basel II, which primarily sets international banking standards for capital adequacy and risk management, the Dodd-Frank Act focuses on regulatory oversight, consumer protection, and addressing too-big-to-fail institutions within the United States.
Key Principles of Basel II
Basel II centers on three key principles: minimum capital requirements, supervisory review, and market discipline, aiming to enhance banking sector stability by aligning regulatory capital with underlying risks. The framework improves risk sensitivity through standardized approaches and internal ratings-based models for credit, market, and operational risk assessments. Unlike the Dodd-Frank Act's broader focus on systemic financial reform and consumer protection, Basel II specifically targets international banking regulation and risk management consistency.
Objectives: Dodd-Frank Act vs Basel II
The Dodd-Frank Act aims to enhance financial stability, increase transparency, and protect consumers by imposing stricter regulations on banks and financial institutions in response to the 2008 financial crisis. Basel II focuses on establishing international banking standards that address risk management, capital adequacy, and supervisory review to ensure the resilience of individual banks and the banking system globally. While Dodd-Frank primarily targets U.S. domestic financial reform, Basel II provides a global framework for banks to manage credit, market, and operational risks through standardized risk-weighted capital requirements.
Regulatory Scope and Coverage
The Dodd-Frank Act primarily targets the regulation of U.S. financial institutions with a focus on consumer protection and systemic risk reduction, covering banks, investment firms, and derivatives markets. Basel II, developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, provides an international regulatory framework emphasizing risk-sensitive capital requirements for banks worldwide. While Dodd-Frank enforces comprehensive oversight including mortgage lending and executive compensation, Basel II centers on minimum capital adequacy, supervisory review, and market discipline across global banks.
Risk Management Approaches
The Dodd-Frank Act emphasizes comprehensive regulatory oversight, enhancing transparency and consumer protection to mitigate systemic risk in the U.S. financial system. Basel II focuses on internationally standardized risk management, particularly credit, operational, and market risks, through capital adequacy requirements based on internal ratings and advanced measurement approaches. Both frameworks aim to strengthen financial stability but differ in scope, with Dodd-Frank targeting regulatory reforms and Basel II providing risk-sensitive capital standards.
Capital Requirements: A Comparative Analysis
The Dodd-Frank Act and Basel II both emphasize capital requirements but differ fundamentally in scope and approach; Dodd-Frank mandates stricter capital buffers for U.S. financial institutions to enhance stability and protect consumers, while Basel II employs a risk-sensitive framework standardized across international banks. Basel II's minimum capital ratios focus on credit, market, and operational risks calculated through internal models, enabling banks to adjust capital based on their unique risk profiles. The Dodd-Frank Act, by contrast, imposes higher capital floors and stress testing requirements, reinforcing resilience against systemic risks specific to the U.S. banking sector.
Impact on Financial Institutions
The Dodd-Frank Act introduced stringent regulatory standards to enhance transparency and reduce systemic risk in U.S. financial institutions, emphasizing consumer protection and limiting risky proprietary trading through the Volcker Rule. Basel II, implemented internationally, focuses on risk-based capital requirements, encouraging financial institutions to improve risk management practices by aligning capital reserves with credit, market, and operational risks. The Dodd-Frank framework primarily targets the stability of large, complex institutions in the domestic market, while Basel II fosters a global regulatory baseline promoting resilience and prudent risk assessment across diverse financial entities.
Implementation Challenges and Criticisms
The Dodd-Frank Act faced significant implementation challenges due to its complexity and the extensive regulatory requirements imposed on financial institutions, often leading to increased compliance costs and operational burdens. Basel II struggled with criticisms related to its reliance on internal risk models, which sometimes resulted in inconsistent risk assessments and inadequate capital buffers during financial crises. Both frameworks have been criticized for insufficiently addressing systemic risks and for the difficulties financial firms encountered in adapting to evolving regulatory standards.
Conclusion: Dodd-Frank Act vs Basel II
The Dodd-Frank Act emphasizes comprehensive regulatory oversight and consumer protection within the U.S. financial system, targeting systemic risk and enhancing transparency. Basel II focuses on international banking standards, risk-sensitive capital requirements, and supervisory review mechanisms to promote global financial stability. Both frameworks prioritize risk management but differ in approach, with Dodd-Frank centered on regulatory reform and Basel II on standardized risk measurement.
Dodd-Frank Act Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com