Accurate forecasting and estimation play a crucial role in project management, enabling teams to allocate resources efficiently and meet deadlines effectively. Employing data-driven techniques and historical insights enhances predictive accuracy and reduces risks associated with uncertainties. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical methods that can improve your forecasting and estimation skills.
Table of Comparison
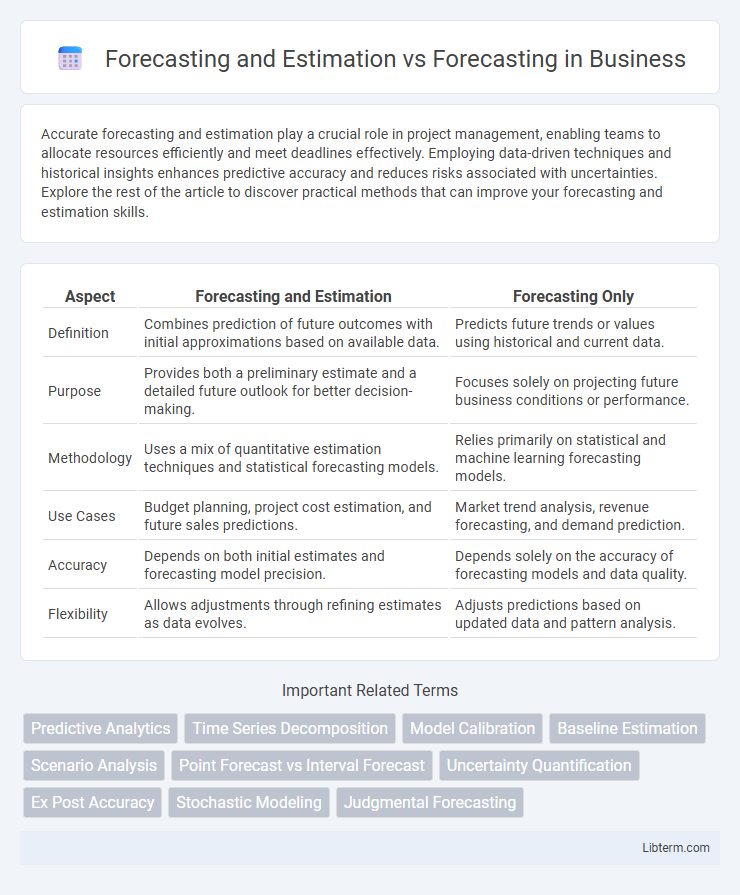
| Aspect | Forecasting and Estimation | Forecasting Only |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines prediction of future outcomes with initial approximations based on available data. | Predicts future trends or values using historical and current data. |
| Purpose | Provides both a preliminary estimate and a detailed future outlook for better decision-making. | Focuses solely on projecting future business conditions or performance. |
| Methodology | Uses a mix of quantitative estimation techniques and statistical forecasting models. | Relies primarily on statistical and machine learning forecasting models. |
| Use Cases | Budget planning, project cost estimation, and future sales predictions. | Market trend analysis, revenue forecasting, and demand prediction. |
| Accuracy | Depends on both initial estimates and forecasting model precision. | Depends solely on the accuracy of forecasting models and data quality. |
| Flexibility | Allows adjustments through refining estimates as data evolves. | Adjusts predictions based on updated data and pattern analysis. |
Understanding Forecasting and Estimation
Forecasting involves predicting future outcomes based on historical data and statistical models, focusing on identifying trends and patterns to make informed decisions. Estimation aims to approximate values or project results when exact data is unavailable, often relying on expert judgment and assumptions. Understanding the difference is crucial, as forecasting emphasizes data-driven projections, whereas estimation deals with educated guesses to handle uncertainty.
Key Differences Between Forecasting and Estimation
Forecasting involves predicting future values or trends based on historical data and statistical models, focusing on time horizons and uncertainty management, while estimation determines approximate values of parameters or quantities often using current or limited data. Forecasting emphasizes probabilistic outcomes and is used in planning and decision-making over time, whereas estimation typically provides a best guess or interval that serves as an input for further analysis or modeling. The key difference lies in forecasting's reliance on time-series data and predictive analytics compared to estimation's focus on point or interval calculation without explicit temporal forecasting.
The Role of Data in Forecasting and Estimation
Data plays a critical role in both forecasting and estimation by providing the empirical foundation necessary for accurate projections and informed decision-making. In forecasting, large datasets and historical trends are analyzed using statistical models and machine learning algorithms to predict future outcomes with a high degree of precision. Estimation relies on available data but often incorporates expert judgment and heuristics when data is incomplete or uncertain, emphasizing the importance of data quality and contextual understanding in both processes.
Methodologies Used in Forecasting
Forecasting methodologies primarily include qualitative techniques such as Delphi method and expert judgment, and quantitative methods like time series analysis, causal models, and machine learning algorithms. Estimation focuses more on approximating values based on available data and assumptions without extensive modeling, often used for project costs or resource needs. Forecasting leverages historical data and statistical tools to predict future trends, providing a structured approach to anticipate outcomes in business, finance, and supply chain management.
Techniques for Effective Estimation
Techniques for effective estimation in forecasting include expert judgment, analogy-based estimation, parametric modeling, and time series analysis, which enhance accuracy and reliability. Incorporating historical data and statistical methods such as regression analysis and Monte Carlo simulations improves forecasting precision by quantifying uncertainties. Leveraging machine learning algorithms enables adaptive estimation that refines predictions over time, addressing dynamic market conditions.
Impact of Uncertainty in Forecasting vs Estimation
Forecasting incorporates uncertainty by predicting future trends based on historical data, while estimation typically involves approximating values within a defined scope or dataset. The impact of uncertainty in forecasting is significant, as it affects accuracy and reliability through factors like market volatility, incomplete information, and unforeseeable events. Estimation faces less uncertainty since it relies on current or known variables, but it can still be influenced by measurement errors or subjective judgment.
Common Applications in Business and Industry
Forecasting and estimation play crucial roles in business decision-making, with forecasting typically used for predicting future trends based on historical data and statistical models, such as sales projections and demand planning in retail and manufacturing. Estimation helps approximate unknown values or costs when complete data is unavailable, commonly applied in budgeting, project management, and cost evaluation across construction and software development industries. Businesses leverage forecasting for inventory optimization and financial planning, while estimation aids in resource allocation and risk assessment during project execution.
Advantages and Limitations of Forecasting
Forecasting provides a data-driven approach to predict future trends by analyzing historical information, enabling businesses to prepare and allocate resources efficiently. Its advantages include improved decision-making, risk reduction, and enhanced strategic planning; however, its limitations stem from reliance on data quality, potential for inaccuracies due to unforeseen variables, and challenges in adapting to sudden market changes. Unlike simple estimation, forecasting integrates statistical models and algorithms to offer more precise and systematic insights into future outcomes.
Accuracy and Reliability: Forecasting vs Estimation
Forecasting uses historical data and statistical models to predict future outcomes with measurable accuracy and improved reliability over time. Estimation relies on judgment and limited data, often resulting in less precise and more subjective predictions. The enhanced accuracy and reliability of forecasting make it preferable for long-term strategic planning compared to the more immediate, approximate nature of estimation.
Best Practices for Choosing Between Forecasting and Estimation
Forecasting leverages historical data and statistical models to predict future trends with quantifiable confidence, making it ideal for projects with ample historical information. Estimation relies on expert judgment and analogous experiences, suited for new or unique projects lacking detailed data. Best practices recommend using forecasting when data availability and accuracy are high, while estimation is preferable for preliminary planning or when addressing uncertainties in innovative projects.
Forecasting and Estimation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com