An advisory board offers valuable expert guidance to help your business navigate complex challenges and seize growth opportunities. Leveraging diverse industry experience, advisory boards can provide strategic insights that enhance decision-making and drive innovation. Explore the rest of the article to discover how forming an effective advisory board can transform your company's future.
Table of Comparison
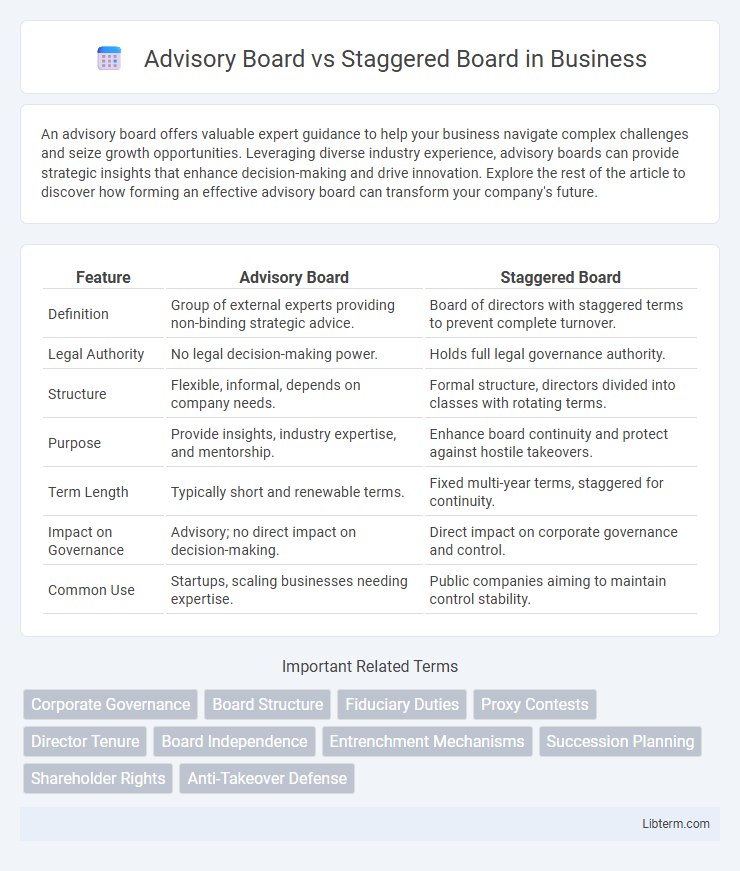
| Feature | Advisory Board | Staggered Board |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group of external experts providing non-binding strategic advice. | Board of directors with staggered terms to prevent complete turnover. |
| Legal Authority | No legal decision-making power. | Holds full legal governance authority. |
| Structure | Flexible, informal, depends on company needs. | Formal structure, directors divided into classes with rotating terms. |
| Purpose | Provide insights, industry expertise, and mentorship. | Enhance board continuity and protect against hostile takeovers. |
| Term Length | Typically short and renewable terms. | Fixed multi-year terms, staggered for continuity. |
| Impact on Governance | Advisory; no direct impact on decision-making. | Direct impact on corporate governance and control. |
| Common Use | Startups, scaling businesses needing expertise. | Public companies aiming to maintain control stability. |
Introduction to Board Structures
An Advisory Board provides non-binding strategic advice and expertise without formal decision-making authority, often enhancing a company's industry knowledge and networks. A Staggered Board, also known as a classified board, divides directors into separate classes with terms expiring in different years to promote continuity and reduce the risk of hostile takeovers. Understanding these distinct board structures is crucial for corporate governance, influencing control, accountability, and long-term stability in organizations.
What Is an Advisory Board?
An advisory board is a group of experts who provide non-binding strategic advice to a company's management, enhancing decision-making with specialized knowledge without the legal responsibilities of a board of directors. Unlike a staggered board, which consists of directors elected in different cycles to provide continuity and prevent hostile takeovers, an advisory board offers flexibility and diverse expertise without formal governance authority. Companies leverage advisory boards to gain insights, industry connections, and mentorship, improving operational effectiveness without altering corporate control.
Defining a Staggered Board
A staggered board is a corporate governance structure where directors are divided into different classes, with only a fraction elected each year, promoting continuity and stability within the board. This setup contrasts with an advisory board, which is an informal group providing strategic advice without voting power or direct oversight responsibilities. Companies adopt staggered boards to deter hostile takeovers and maintain long-term strategic direction by ensuring not all directors face re-election simultaneously.
Key Differences: Advisory vs Staggered Boards
Advisory boards provide non-binding strategic advice and expertise without formal governance power, supporting executive decisions with diverse insights. Staggered boards are structured so that only a fraction of directors are elected each year, enhancing board continuity and making hostile takeovers more difficult. Key differences include advisory boards' consultative role versus staggered boards' formal governance and defensive mechanism.
Roles and Responsibilities
An Advisory Board provides non-binding strategic advice and expertise without formal governance authority, primarily supporting company leadership with industry insights and recommendations. In contrast, a Staggered Board consists of directors elected in overlapping terms to ensure continuity and stability in decision-making, holding formal fiduciary responsibilities such as oversight, risk management, and corporate governance. Advisory Boards often focus on guidance and innovation, while Staggered Boards enforce accountability and protect against sudden shifts in control.
Strategic Impact on Corporate Governance
An Advisory Board offers non-binding strategic advice, enhancing corporate governance by providing diverse industry insights without formal decision-making power. A Staggered Board structures board member elections over multiple terms, impacting governance by limiting hostile takeovers and ensuring continuity in strategic oversight. Together, these board types influence corporate governance through improved strategic guidance and stability in leadership succession.
Pros and Cons of Advisory Boards
Advisory boards provide external expertise and strategic guidance without the formal responsibilities and liabilities of a staggered board, offering flexibility to startups and rapidly growing companies. They foster innovation and networking opportunities but lack decision-making authority, which can limit influence on critical corporate governance matters. The absence of legal accountability and potential for conflicting advice are notable drawbacks compared to the structured oversight and continuity ensured by staggered boards.
Pros and Cons of Staggered Boards
Staggered boards enhance corporate stability by preventing hostile takeovers through limited simultaneous director turnover, promoting long-term strategic planning. However, this structure can entrench management, reducing shareholder influence and delaying board refreshment. Critics argue staggered boards may lower firm valuation by decreasing accountability and responsiveness to shareholder concerns.
Choosing the Right Board Structure
Choosing the right board structure depends on your company's goals and governance needs, with advisory boards offering flexible, non-binding expertise and staggered boards providing continuity and defense against hostile takeovers. Advisory boards bring specialized knowledge without voting power, ideal for startups seeking mentorship and strategic advice without formal obligations. Staggered boards, by rotating director terms, enhance stability and protect long-term company vision but may reduce shareholder influence over board composition.
Conclusion: Making the Best Decision
Selecting between an advisory board and a staggered board hinges on a company's governance needs and strategic objectives. An advisory board offers flexible, expert guidance without formal voting power, ideal for startups seeking specialized advice. A staggered board enhances continuity and defense against hostile takeovers by rotating director elections, making it suitable for established firms prioritizing stability and control.
Advisory Board Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com