Horizontal integration enhances a company's market share by acquiring or merging with competitors within the same industry, leading to increased operational efficiencies and reduced competition. This strategy often results in improved economies of scale, stronger customer base, and greater control over pricing. Discover how horizontal integration can transform Your business landscape by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
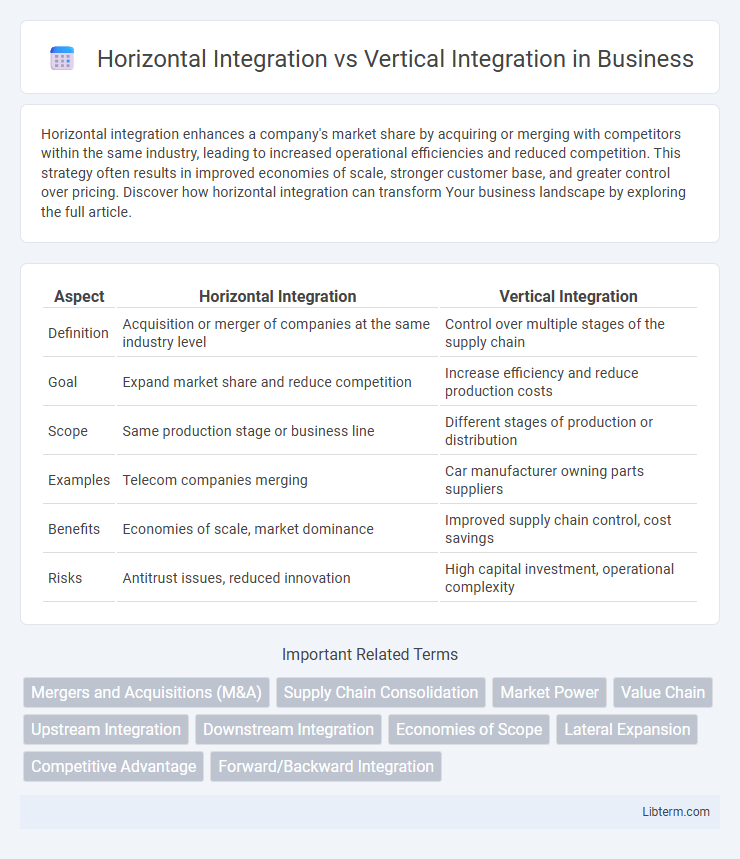
| Aspect | Horizontal Integration | Vertical Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquisition or merger of companies at the same industry level | Control over multiple stages of the supply chain |
| Goal | Expand market share and reduce competition | Increase efficiency and reduce production costs |
| Scope | Same production stage or business line | Different stages of production or distribution |
| Examples | Telecom companies merging | Car manufacturer owning parts suppliers |
| Benefits | Economies of scale, market dominance | Improved supply chain control, cost savings |
| Risks | Antitrust issues, reduced innovation | High capital investment, operational complexity |
Understanding Horizontal and Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration involves a company expanding its operations at the same level of the supply chain by acquiring or merging with competitors to increase market share and reduce competition. Vertical integration refers to a company controlling multiple stages of production or distribution within its industry, such as owning suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers, to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Understanding the differences between horizontal and vertical integration helps businesses decide whether to strengthen their market position or optimize their supply chain management.
Key Differences Between Horizontal and Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration involves acquiring or merging with companies operating at the same stage of the supply chain, expanding market share and reducing competition within the same industry. Vertical integration refers to the acquisition or control of companies at different stages of production or distribution, enhancing supply chain efficiency and reducing dependency on suppliers or distributors. The key difference lies in their strategic focus: horizontal integration aims at market consolidation, while vertical integration focuses on controlling the value chain.
Pros and Cons of Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration allows companies to expand market share by acquiring or merging with competitors, leading to economies of scale and reduced competition. However, this strategy may result in antitrust issues, reduced innovation due to less competition, and challenges in managing a larger, more complex organization. While horizontal integration can enhance bargaining power with suppliers and customers, it risks market monopolization and vulnerability to sector-specific downturns.
Pros and Cons of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration enhances control over supply chains and reduces dependency on external suppliers, leading to cost savings and improved product quality. However, it requires significant capital investment and can reduce flexibility in adapting to market changes or innovations. Firms may also face increased operational complexity and potential antitrust scrutiny due to reduced competition.
Examples of Successful Horizontal Integration
Horizontal integration occurs when a company acquires or merges with competitors at the same stage of the supply chain to increase market share and reduce competition. A prime example is Facebook's acquisition of Instagram and WhatsApp, which expanded its user base and strengthened its dominance in social media. Another successful case is the merger of Disney with 21st Century Fox, enabling Disney to broaden its media content portfolio and scale its entertainment offerings globally.
Examples of Successful Vertical Integration
Tesla exemplifies successful vertical integration by controlling its supply chain from battery production to vehicle assembly, enhancing efficiency and reducing dependency on suppliers. Apple also demonstrates vertical integration through its control over hardware design, software development, and retail distribution, creating a seamless product experience. These companies achieve competitive advantages by owning multiple stages of production and distribution, driving innovation and cost savings.
Impact on Market Competition
Horizontal integration reduces market competition by increasing market share through acquiring or merging with competitors, often leading to monopolistic or oligopolistic market structures. Vertical integration impacts market competition by controlling supply chains, which can create barriers for new entrants and limit competitors' access to essential inputs or distribution channels. Both strategies significantly influence competitive dynamics by altering market power and entry barriers within industries.
Strategic Considerations for Businesses
Horizontal integration allows businesses to expand market share by acquiring or merging with competitors within the same industry, enhancing economies of scale and reducing competition. Vertical integration involves controlling multiple stages of the supply chain, improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and increasing control over product quality and distribution. Strategic considerations include market power, cost reduction opportunities, diversification of risks, and potential regulatory challenges impacting mergers and acquisitions.
Risks and Challenges in Integration Strategies
Horizontal integration risks include regulatory scrutiny due to antitrust concerns and potential cultural clashes when merging similar companies. Vertical integration challenges involve significant capital investment, complex supply chain coordination, and reduced flexibility to switch suppliers. Both strategies face integration issues such as operational disruptions, misaligned corporate cultures, and difficulties in achieving anticipated synergies.
Choosing the Right Integration Approach
Choosing the right integration approach depends on a company's strategic goals, market position, and resource capabilities. Horizontal integration focuses on acquiring or merging with competitors to increase market share and reduce competition, while vertical integration involves controlling multiple stages of the supply chain to improve efficiency and control over production. Careful analysis of industry dynamics, cost structures, and long-term objectives guides the decision between horizontal and vertical integration to maximize competitive advantage.
Horizontal Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com