Commercial software offers robust features, reliable support, and regular updates tailored for business needs, ensuring enhanced productivity and security. Companies often prefer commercial solutions for their proven performance and compliance with industry standards. Explore this article to discover how commercial software can optimize your organization's workflow and decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
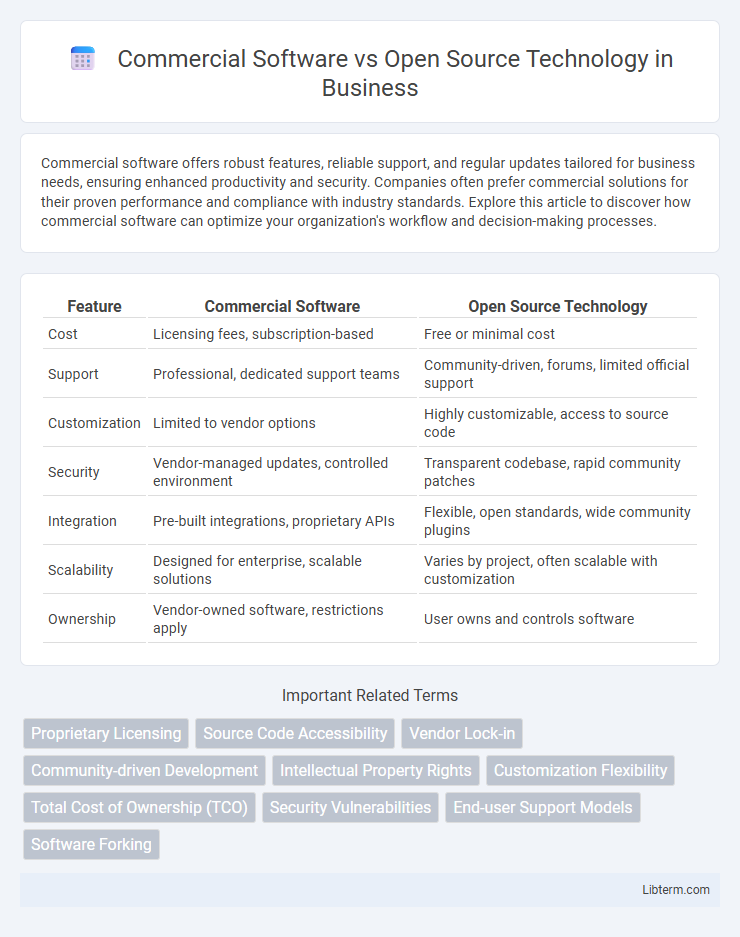
| Feature | Commercial Software | Open Source Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Licensing fees, subscription-based | Free or minimal cost |
| Support | Professional, dedicated support teams | Community-driven, forums, limited official support |
| Customization | Limited to vendor options | Highly customizable, access to source code |
| Security | Vendor-managed updates, controlled environment | Transparent codebase, rapid community patches |
| Integration | Pre-built integrations, proprietary APIs | Flexible, open standards, wide community plugins |
| Scalability | Designed for enterprise, scalable solutions | Varies by project, often scalable with customization |
| Ownership | Vendor-owned software, restrictions apply | User owns and controls software |
Introduction to Commercial Software and Open Source Technology
Commercial software refers to proprietary programs developed and sold by companies with exclusive rights, often requiring purchase or subscription fees for access and support. Open source technology involves software with publicly accessible source code, allowing users to freely view, modify, and distribute the software under various licenses like GPL or MIT. The distinction lies in control and collaboration, with commercial software prioritizing revenue and closed development, while open source emphasizes transparency, community involvement, and innovation.
Key Differences Between Commercial and Open Source Solutions
Commercial software typically involves licensing fees, proprietary code, and vendor support, ensuring regular updates and dedicated customer service. Open source technology offers free access to source code, promoting community-driven development and customization but may rely on user expertise for troubleshooting. Security in commercial solutions is managed by the vendor, while open source relies on transparency and community reviews to identify vulnerabilities.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Long-Term Expenses
Commercial software typically involves significant upfront licensing fees and ongoing subscription costs, impacting initial budget allocation and long-term financial planning. Open source technology offers minimal or no upfront purchase costs, but may incur expenses related to customization, support, and maintenance over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires analyzing both direct software expenses and indirect costs such as training, integration, and scalability.
Flexibility and Customization Capabilities
Commercial software often provides standardized features with limited customization, catering to broad user needs but restricting flexibility due to proprietary constraints. Open source technology allows extensive flexibility and customization since users can modify source code to tailor software precisely to their requirements. This adaptability makes open source ideal for businesses seeking specific functionality and control over their software environment.
Security Considerations and Vulnerability Management
Commercial software often benefits from dedicated security teams and regular patch management, ensuring timely vulnerability identification and resolution. Open source technology, while offering transparency and community-driven audits, may require proactive monitoring to address vulnerabilities promptly. Effective security considerations in both models depend on rigorous update practices and thorough vulnerability management frameworks.
Support, Maintenance, and Community Involvement
Commercial software offers dedicated support teams and regular maintenance updates, ensuring prompt issue resolution and system stability for enterprises. Open source technology relies heavily on community involvement, where collective contributions drive continuous improvements and provide diverse support channels such as forums and user groups. The choice impacts scalability and reliability, with commercial solutions offering structured support agreements, while open source depends on active, engaged communities for ongoing development and troubleshooting.
Licensing Models and Compliance Issues
Commercial software typically operates under proprietary licensing models that restrict usage, modification, and distribution, requiring organizations to adhere strictly to vendor agreements and incur licensing fees. Open source technology is governed by various licenses such as GPL, MIT, and Apache, which allow free use, modification, and distribution but impose specific compliance obligations like attribution, source code disclosure, or copyleft conditions. Organizations must carefully evaluate compliance requirements, risk of license violation, and legal implications to ensure adherence in mixed environments involving both commercial and open source components.
Scalability and Performance Factors
Commercial software often delivers robust scalability and optimized performance due to dedicated development teams and comprehensive support infrastructure, ensuring it can handle large-scale enterprise demands efficiently. Open source technology offers flexible scalability driven by community contributions and customizable code, allowing organizations to tailor performance to specific requirements, though it may require more in-house expertise for optimization. Performance factors in commercial solutions typically benefit from stringent quality assurance and proprietary enhancements, while open source relies on rapid updates and collaborative problem-solving to achieve comparable efficiency.
User Experience and Interface Design
Commercial software often provides polished user experience (UX) and intuitive interface design backed by dedicated resources for usability testing and continuous improvements. Open source technology enables community-driven customization and flexibility, allowing users to tailor interfaces to specific needs but may lack consistent UX standards. The choice between the two depends on prioritizing turnkey ease-of-use versus adaptability and user-driven innovation in interface design.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Selecting between commercial software and open source technology depends on your business's specific needs, budget, and support requirements. Commercial software often provides robust customer support, regular updates, and extensive documentation, making it ideal for businesses seeking reliability and scalability. Open source technology offers flexibility, cost-efficiency, and customization potential, which suits businesses with in-house technical expertise aiming to adapt software to unique workflows.
Commercial Software Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com