Dogs provide loyal companionship and improve your physical and mental well-being through regular exercise and social interaction. Different breeds offer unique traits, so understanding their personalities helps you choose the perfect dog for your lifestyle. Explore the rest of this article to learn everything you need to know about caring for your furry friend.
Table of Comparison
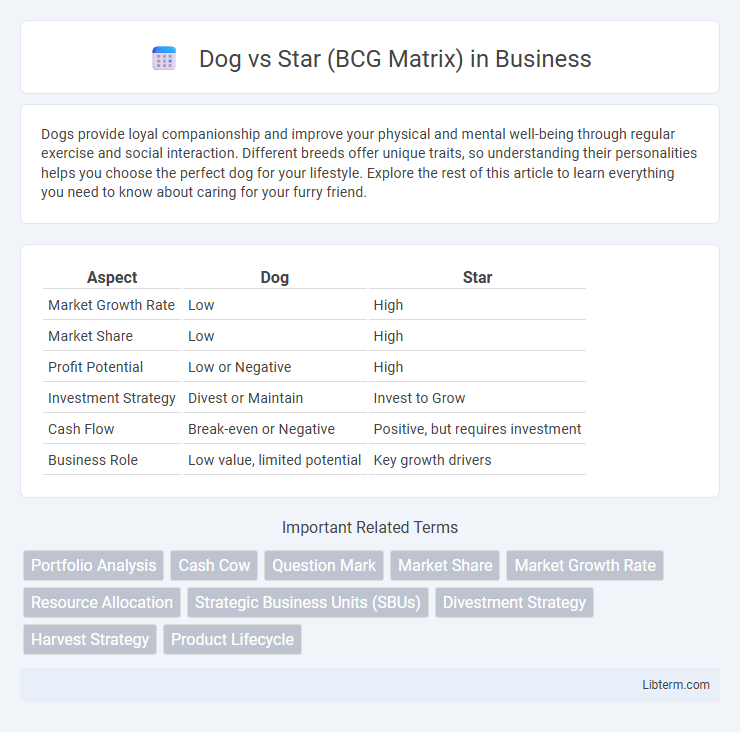
| Aspect | Dog | Star |
|---|---|---|
| Market Growth Rate | Low | High |
| Market Share | Low | High |
| Profit Potential | Low or Negative | High |
| Investment Strategy | Divest or Maintain | Invest to Grow |
| Cash Flow | Break-even or Negative | Positive, but requires investment |
| Business Role | Low value, limited potential | Key growth drivers |
Introduction to the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix, developed by the Boston Consulting Group, categorizes business units into four quadrants: Stars, Cash Cows, Dogs, and Question Marks based on market growth rate and relative market share. "Stars" are units with high market growth and strong market share, often requiring investment for expansion, while "Dogs" have low market share in low-growth markets, typically generating limited profit or losses. This matrix helps companies prioritize resource allocation by identifying which units to invest in, maintain, or divest.
Understanding “Dog” and “Star” Categories
In the BCG Matrix, the "Star" category represents high-growth business units with a dominant market share, requiring substantial investment to maintain their position and capitalize on market opportunities. The "Dog" category consists of products or divisions with low market share in a mature, slow-growing industry, often generating minimal profits or even losses. Understanding these categories helps businesses allocate resources strategically, promoting Stars for growth while deciding whether to divest or rejuvenate Dogs.
Key Characteristics of Dog Businesses
Dog businesses in the BCG Matrix are characterized by low market share and operate within low-growth industries, often generating minimal profits or losses. These units typically lack the resources and competitive advantage to improve their position, leading to limited potential for growth or return on investment. Organizations usually consider divestment, restructuring, or selective investment when managing dog businesses to optimize overall portfolio performance.
Defining Traits of Star Businesses
Star businesses in the BCG Matrix exhibit high market growth rates coupled with a large relative market share, positioning them as leaders in rapidly expanding industries. These entities generate substantial revenue and demand significant investment to sustain growth and capitalize on emerging market opportunities. Their strategic focus centers on innovation, competitive advantage, and market penetration to transition into Cash Cows as market growth stabilizes.
Market Share and Growth in the BCG Matrix
In the BCG Matrix, Dog represents business units with low market share in a low-growth market, indicating limited potential for expansion or profitability. Star denotes units with high market share in a rapidly growing market, suggesting strong competitive positioning and significant growth opportunities. Prioritizing resource allocation to Stars can drive growth, while Dogs may require strategic reevaluation or divestment.
Strategic Implications for Dogs
Dogs in the BCG Matrix represent business units with low market share and low market growth, indicating limited potential for profitability and growth. Strategic implications for Dogs often involve divestment, cost reduction, or repositioning to minimize resource drain and improve operational efficiency. Companies may choose to liquidate Dogs, harvest them for short-term cash flow, or selectively invest if niche opportunities exist.
Strategic Approaches for Stars
Stars in the BCG Matrix demonstrate high market growth and high market share, indicating strong competitive positions and significant potential for revenue generation. Strategic approaches focus on heavy investment to sustain rapid growth, including innovation, aggressive marketing, and capacity expansion to defend market dominance. Firms should prioritize resource allocation to Stars to capitalize on their growth trajectory and eventually transition them into Cash Cows.
Real-World Examples: Dogs vs Stars
In the BCG Matrix, real-world examples of Stars include Apple's iPhone, which operates in a high-growth market with a dominant market share, driving substantial revenue and investment. Conversely, Dogs are represented by products such as Kodak's traditional film cameras, which faced low market growth and declining market share, leading to reduced profitability and eventual obsolescence. Companies often divest Dogs to focus resources on Stars, aiming to maximize market opportunities and sustain competitive advantage.
Transitioning Between Quadrants
Transitioning a product from the Dog quadrant to a Star in the BCG Matrix requires strategic investment and innovation to boost market growth and share. Companies must enhance competitive advantages through marketing, product development, or market expansion to increase growth rates and market dominance. Careful resource allocation during this transition can transform low-performing products into high-growth market leaders, driving long-term profitability.
Conclusion: Making Effective Portfolio Decisions
In the BCG Matrix, Dog units represent businesses with low market share in low-growth markets, often yielding minimal returns and limited potential for growth. Effective portfolio decisions require evaluating whether to divest, harvest, or strategically reposition these Dogs based on resource allocation priorities and long-term objectives. Prioritizing investment in Stars or Cash Cows while managing Dogs carefully helps optimize overall portfolio performance and maximize shareholder value.
Dog Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com