Lean Startup methodology focuses on building a sustainable business by developing products iteratively, validating ideas through customer feedback, and minimizing waste. This approach encourages rapid experimentation and adaptability to meet market needs effectively. Discover how applying Lean Startup principles can transform your business strategy in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
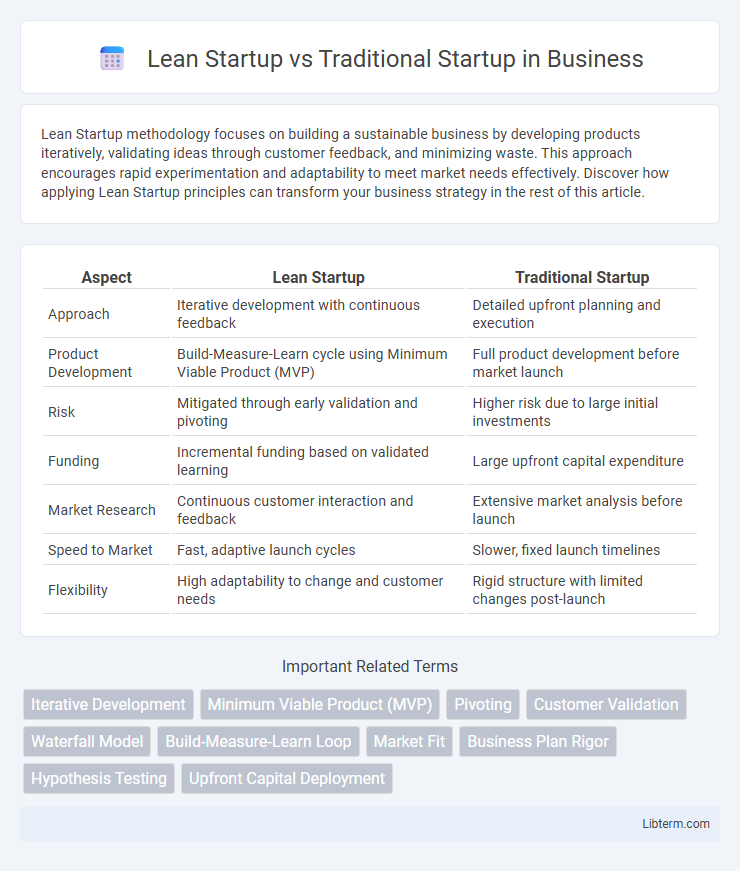
| Aspect | Lean Startup | Traditional Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Iterative development with continuous feedback | Detailed upfront planning and execution |
| Product Development | Build-Measure-Learn cycle using Minimum Viable Product (MVP) | Full product development before market launch |
| Risk | Mitigated through early validation and pivoting | Higher risk due to large initial investments |
| Funding | Incremental funding based on validated learning | Large upfront capital expenditure |
| Market Research | Continuous customer interaction and feedback | Extensive market analysis before launch |
| Speed to Market | Fast, adaptive launch cycles | Slower, fixed launch timelines |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to change and customer needs | Rigid structure with limited changes post-launch |
Introduction to Startup Methodologies
Lean Startup methodology emphasizes rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product releases to reduce market risks and avoid unnecessary expenditures. Traditional Startup approaches often rely on extensive upfront planning, large capital investment, and longer development cycles before product launch. Embracing Lean Startup techniques accelerates innovation, enhances customer feedback integration, and improves adaptability in dynamic market environments.
Defining Lean Startup
Lean Startup is a methodology centered on rapid experimentation, validated learning, and iterative product releases to reduce market risks and avoid unnecessary resource expenditure. It emphasizes building a minimum viable product (MVP) to test hypotheses with real customers and pivoting based on data-driven insights. Traditional Startup approaches often rely on extensive upfront planning and large initial investments, whereas Lean Startup prioritizes agility and customer feedback for scalable growth.
Defining Traditional Startup
Traditional startups typically rely on extensive upfront planning, large initial investments, and rigid business models that emphasize long-term product development before market testing. This approach often involves significant risk due to limited customer feedback during early stages, potentially leading to misaligned product-market fit. Traditional startups prioritize comprehensive market analysis and detailed business plans prior to launching their product or service.
Key Principles of Lean Startup
Lean Startup methodology emphasizes validated learning, rapid experimentation, and iterative product releases to reduce market risks and avoid costly failures. Key principles include building a minimum viable product (MVP), measuring real customer responses, and learning from feedback to pivot or persevere. This contrasts with traditional startups that often rely on extensive upfront planning and assumptions before product-market fit is tested.
Key Principles of Traditional Startup
Traditional startups emphasize comprehensive upfront planning, detailed business plans, and extensive market research before product development. These startups rely heavily on fixed budgets, hierarchical decision-making, and long product development cycles, aiming for a fully developed product launch. Risk management is often addressed through thorough forecasting and predefined milestones, contrasting with the iterative testing and customer feedback focus characteristic of Lean Startups.
Funding Approaches: Lean vs Traditional
Lean startups prioritize iterative funding methods such as seed funding and angel investments, leveraging minimal viable products (MVPs) to attract early-stage investors and validate market demand quickly. Traditional startups typically pursue substantial venture capital or bank loans upfront, relying on detailed business plans and projections to secure larger financial commitments. Lean funding reduces financial risk by aligning expenditures with validated learning cycles, whereas traditional funding depends on comprehensive market analysis and long-term capital allocation.
Product Development Cycles Compared
Lean Startup emphasizes rapid product development cycles through iterative testing, validated learning, and continuous customer feedback, minimizing waste and adapting quickly to market needs. Traditional startup methodologies often follow longer, linear development phases with extensive upfront planning and less frequent product iterations. This leads to slower time-to-market and higher risk of building products misaligned with customer demands.
Risk Management in Both Models
Lean Startup emphasizes iterative testing and customer feedback to minimize market risks by validating hypotheses early, reducing wasted resources and improving product-market fit. Traditional Startup models rely heavily on upfront planning and large capital investments, increasing financial risk if assumptions about the market or product prove incorrect. Lean methodology's focus on rapid prototyping and pivoting offers a dynamic approach to managing uncertainty compared to the static risk profiles inherent in traditional startup frameworks.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Lean Startup offers rapid validation of business ideas through continuous customer feedback, significantly reducing the risk of market failure. Traditional Startup relies on extensive planning and upfront investment, which can provide a clear roadmap but often leads to wasted resources if market assumptions are incorrect. Lean Startup's iterative approach enhances flexibility and responsiveness, while Traditional Startup may benefit from structured development but struggles with adaptability in dynamic markets.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Choosing the right approach for your business involves assessing flexibility, market conditions, and resource availability. Lean Startup emphasizes iterative product development, validated learning, and rapid customer feedback to minimize risk and optimize market fit. Traditional Startup relies on detailed planning, significant upfront investment, and established processes, which may suit industries requiring extensive initial research or capital.
Lean Startup Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com