A tax audit meticulously examines your financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance with tax laws, helping to identify discrepancies that could lead to penalties. Understanding the audit process and knowing how to prepare can reduce stress and protect your financial standing. Explore the rest of this article to learn effective strategies for navigating a tax audit confidently.
Table of Comparison
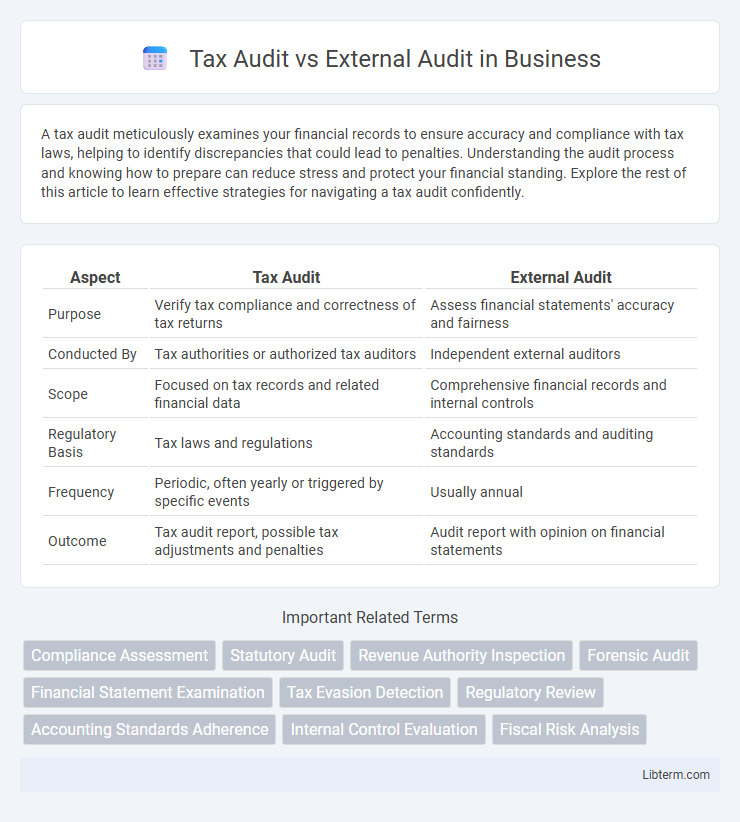
| Aspect | Tax Audit | External Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify tax compliance and correctness of tax returns | Assess financial statements' accuracy and fairness |
| Conducted By | Tax authorities or authorized tax auditors | Independent external auditors |
| Scope | Focused on tax records and related financial data | Comprehensive financial records and internal controls |
| Regulatory Basis | Tax laws and regulations | Accounting standards and auditing standards |
| Frequency | Periodic, often yearly or triggered by specific events | Usually annual |
| Outcome | Tax audit report, possible tax adjustments and penalties | Audit report with opinion on financial statements |
Introduction to Tax Audit vs External Audit
Tax audit involves a detailed examination of an entity's tax returns to ensure compliance with tax laws and accuracy in reporting taxable income. External audit refers to an independent evaluation of an organization's financial statements by a third-party auditor to provide assurance on their fairness and compliance with accounting standards. Both audits serve distinct purposes, with tax audit focusing on tax obligations and external audit emphasizing overall financial transparency.
Definitions: Tax Audit and External Audit
Tax audit refers to a detailed examination of an individual's or organization's tax returns and financial records to ensure compliance with tax laws and accuracy in reporting to tax authorities. External audit involves an independent professional review of an organization's financial statements and internal controls to provide an unbiased opinion on their fairness and adherence to accounting standards. Both audits serve regulatory and compliance purposes but differ in scope, authority, and reporting requirements.
Key Differences Between Tax Audit and External Audit
Tax audits primarily evaluate compliance with tax laws and accuracy of tax returns filed by businesses or individuals, focusing on identifying discrepancies that could lead to tax liabilities or penalties. External audits assess the overall financial statements' fairness and accuracy, following accounting standards to provide stakeholders with an independent opinion on an entity's financial health. Key differences include the scope, purpose, regulatory framework, and reporting requirements, with tax audits governed by tax authorities and external audits by professional accounting bodies.
Objectives of Tax Audits
Tax audits primarily aim to verify the accuracy of tax returns and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations, focusing on identifying discrepancies in income reporting, deductions, and tax liabilities. They help detect tax evasion or fraud by examining financial records related to taxable transactions and assessing the appropriate tax amounts owed to the government. Unlike external audits, which evaluate overall financial statements and internal controls for stakeholders, tax audits specifically target adherence to tax codes and accurate tax reporting.
Objectives of External Audits
External audits aim to provide an independent and objective evaluation of a company's financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. They help build stakeholder confidence by verifying the integrity of financial reporting and detecting any material misstatements or fraud. External audits also assess the effectiveness of internal controls and identify areas for operational improvements.
Legal Requirements for Each Audit Type
Tax audits are mandated by tax authorities to ensure compliance with tax laws, requiring businesses to provide detailed financial records and tax filings for verification. External audits are legally required under corporate governance regulations and financial reporting standards, focusing on the accuracy and fairness of an organization's financial statements. Both audits demand strict adherence to legal frameworks but differ in scope: tax audits center on tax law compliance, while external audits assess overall financial transparency and accountability.
Audit Processes: Step-by-Step Comparison
Tax audit involves a detailed examination of financial records to ensure compliance with tax laws, starting with preparing tax returns, followed by selecting audit targets, reviewing supporting documentation, and concluding with a formal audit report submitted to tax authorities. External audit focuses on verifying the accuracy and fairness of financial statements, beginning with planning and risk assessment, performing substantive testing and internal control evaluation, and ending with the issuance of an independent auditor's opinion. Both processes require thorough documentation review and evidence gathering, but tax audits emphasize tax law adherence, while external audits prioritize financial statement reliability.
Roles and Responsibilities of Auditors
Tax audit focuses on verifying compliance with tax laws and the accuracy of tax returns, ensuring that all financial records align with tax regulations enforced by tax authorities. External audit involves an independent evaluation of an organization's financial statements to provide assurance on their fairness and adherence to accounting standards, enhancing stakeholder confidence. Auditors in tax audits primarily review tax filings, deductions, and credits, while external auditors assess overall financial accuracy, internal controls, and risk management practices.
Impact of Tax Audit vs External Audit on Businesses
Tax audits primarily impact businesses by ensuring compliance with tax laws, minimizing the risk of penalties, and optimizing tax liabilities through detailed examination of financial records related to tax returns. External audits enhance overall financial transparency and credibility by providing independent verification of financial statements, which boosts stakeholder confidence and supports regulatory compliance. Both audits influence business operations, with tax audits focusing on fiscal accuracy and external audits promoting trust in financial reporting.
Choosing the Right Audit for Your Organization
Selecting the right audit hinges on your organization's primary compliance and financial transparency needs; a Tax Audit ensures adherence to tax laws and accurate tax liability reporting, crucial for minimizing risks with tax authorities. An External Audit provides a comprehensive evaluation of financial statements, enhancing stakeholder confidence through independent verification of financial health. Assess your organization's regulatory environment, reporting requirements, and stakeholder expectations to determine whether a Tax Audit or External Audit will best safeguard your financial integrity.
Tax Audit Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com