Dividends represent a portion of a company's earnings distributed to shareholders, providing a steady income stream and reflecting the company's financial health. Understanding how dividends work can help you make informed investment decisions and maximize your returns. Explore the rest of the article to learn how dividends impact your portfolio and strategies to benefit from them.
Table of Comparison
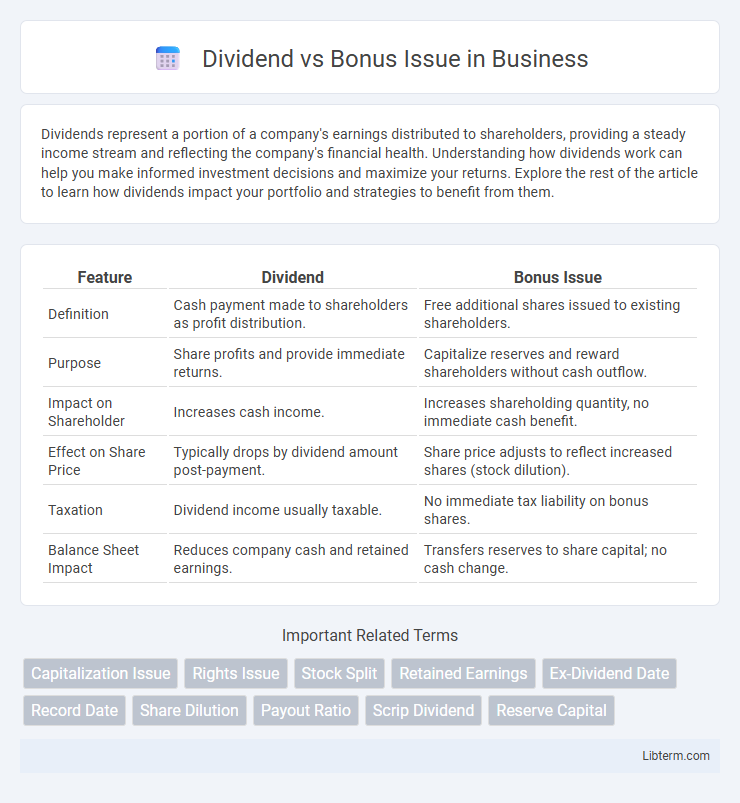
| Feature | Dividend | Bonus Issue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cash payment made to shareholders as profit distribution. | Free additional shares issued to existing shareholders. |
| Purpose | Share profits and provide immediate returns. | Capitalize reserves and reward shareholders without cash outflow. |
| Impact on Shareholder | Increases cash income. | Increases shareholding quantity, no immediate cash benefit. |
| Effect on Share Price | Typically drops by dividend amount post-payment. | Share price adjusts to reflect increased shares (stock dilution). |
| Taxation | Dividend income usually taxable. | No immediate tax liability on bonus shares. |
| Balance Sheet Impact | Reduces company cash and retained earnings. | Transfers reserves to share capital; no cash change. |
Understanding Dividend vs Bonus Issue: Key Differences
Dividends are cash payments made to shareholders from a company's profits, providing immediate income, whereas bonus issues involve distributing additional shares to existing shareholders, increasing share capital without cash outflow. Dividend payments affect a company's cash reserves and signal profitability, while bonus issues dilute earnings per share but maintain shareholder equity value. Understanding these key differences helps investors evaluate a company's financial strategy and potential returns.
Definition of Dividend in Corporate Finance
A dividend in corporate finance refers to the distribution of a portion of a company's earnings to its shareholders, typically in the form of cash or additional shares. It represents a return on investment and signals the company's profitability and financial health. Unlike bonus issues, dividends provide immediate income rather than increasing the number of shares held.
What is a Bonus Issue?
A bonus issue, also known as a scrip issue or capitalisation issue, is a corporate action where a company issues additional shares to existing shareholders without any extra cost, based on the number of shares they already hold. Unlike dividends, which distribute cash or other assets, bonus shares are issued by converting a company's reserves into equity, increasing the total shareholding without affecting the overall market capitalization. This approach rewards shareholders while conserving the company's cash reserves, often signaling confidence in future profitability.
Objectives: Why Companies Offer Dividends and Bonus Shares
Companies offer dividends to provide shareholders with a tangible return on their investment, reflecting profitability and rewarding shareholder loyalty. Bonus shares are issued to capitalize on retained earnings by converting them into additional equity, enhancing shareholder value without reducing cash reserves. Both dividends and bonus issues aim to strengthen investor confidence and improve market perception of the company's financial health.
Impact on Shareholders’ Wealth
Dividend distribution directly increases shareholders' immediate cash income, enhancing their liquidity without altering the company's market capitalization, while bonus issues increase the number of shares held, diluting the share price but maintaining overall investment value. Dividends signal company profitability and can attract income-focused investors, whereas bonus shares boost shareholding at no extra cost, often perceived as a positive growth indicator. The impact on shareholders' wealth depends on market perception, with dividends providing tangible returns and bonus issues potentially offering long-term capital gains through increased share volume.
Effects on Company’s Share Capital
A dividend payout reduces a company's retained earnings and distributes profits to shareholders without changing the share capital, thereby impacting cash reserves but not the number of outstanding shares. A bonus issue reallocates reserves to share capital by issuing additional shares to existing shareholders, increasing the total number of shares while keeping the overall equity value unchanged. This process dilutes earnings per share but strengthens the company's capital base without affecting cash flow.
Tax Implications for Investors
Dividend payments are typically subject to income tax at the investor's applicable rate, leading to immediate tax liability upon receipt. Bonus issues, which involve the issuance of additional shares to existing shareholders without any cash payout, generally do not trigger immediate tax obligations, as they are considered a capital adjustment rather than income. However, investors may face capital gains tax upon selling bonus shares, calculated based on their adjusted cost basis.
Market Perception and Stock Price Movement
Dividend issuance often signals strong company profitability and can lead to immediate positive market perception, typically resulting in a modest stock price increase reflecting direct shareholder returns. Bonus issues, by contrast, do not provide immediate cash value but are perceived as a sign of confidence in future growth, causing stock price adjustment proportional to the increased share count without actual market value gain. Market perception favors dividends for tangible returns, while bonus issues boost investor sentiment and liquidity, influencing stock price through psychological and quantitative adjustments.
Which is Better: Dividend or Bonus Issue?
Dividends provide immediate cash returns to shareholders, enhancing income stability, while bonus issues increase the number of shares held, potentially boosting market liquidity without affecting cash flow. Investors seeking regular income prefer dividends, whereas long-term holders often favor bonus issues for capital appreciation and improved share liquidity. The choice depends on individual investment goals, tax implications, and the company's financial strategy.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Dividend and Bonus Issue
Choosing between a dividend and a bonus issue depends on a company's cash flow status and shareholder expectations. Dividends provide immediate cash returns, appealing to investors seeking regular income, while bonus issues increase shareholding without affecting cash reserves, often signaling confidence in future growth. Companies aiming to reward shareholders without straining liquidity typically prefer bonus issues, whereas firms generating steady profits may opt for dividends to enhance shareholder value.
Dividend Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com