A term sheet outlines the key terms and conditions of a business agreement, serving as a blueprint for negotiation and final contracts. It covers essential points like valuation, investment amount, equity stake, and shareholder rights to ensure clarity between involved parties. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a well-crafted term sheet can protect your interests and streamline your transaction.
Table of Comparison
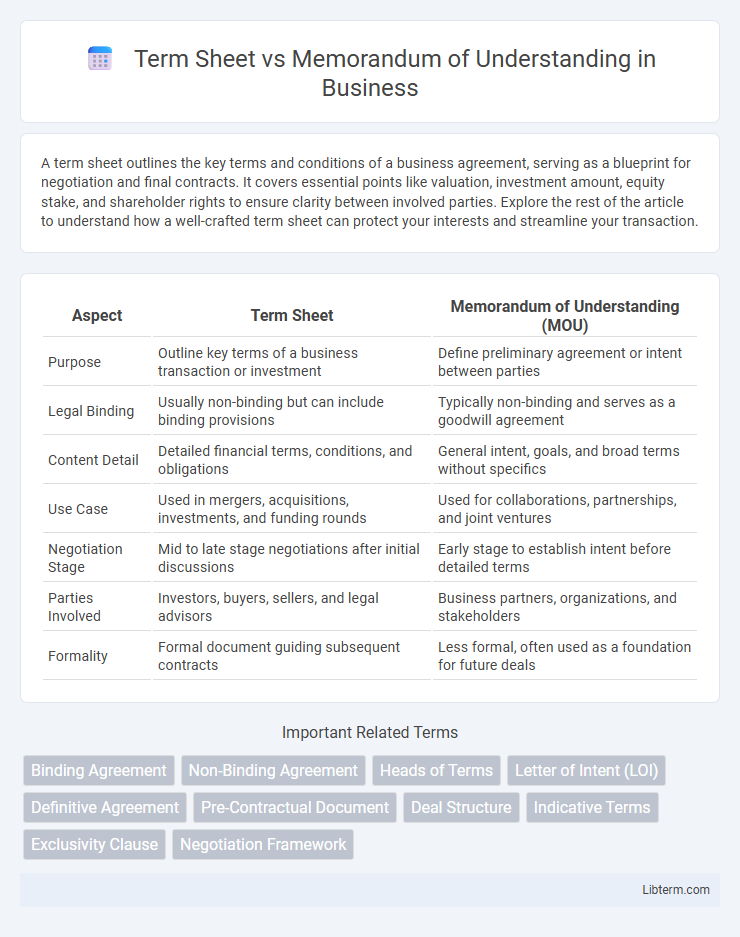
| Aspect | Term Sheet | Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Outline key terms of a business transaction or investment | Define preliminary agreement or intent between parties |
| Legal Binding | Usually non-binding but can include binding provisions | Typically non-binding and serves as a goodwill agreement |
| Content Detail | Detailed financial terms, conditions, and obligations | General intent, goals, and broad terms without specifics |
| Use Case | Used in mergers, acquisitions, investments, and funding rounds | Used for collaborations, partnerships, and joint ventures |
| Negotiation Stage | Mid to late stage negotiations after initial discussions | Early stage to establish intent before detailed terms |
| Parties Involved | Investors, buyers, sellers, and legal advisors | Business partners, organizations, and stakeholders |
| Formality | Formal document guiding subsequent contracts | Less formal, often used as a foundation for future deals |
Introduction to Term Sheet and Memorandum of Understanding
A Term Sheet outlines the key terms and conditions of a potential business agreement, serving as a non-binding agreement that guides further negotiations. A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is a formal document that expresses mutual intentions between parties, often used to establish preliminary commitments before a detailed contract is drafted. Both documents play crucial roles in the early stages of deal-making by clearly defining expectations and responsibilities without imposing legally binding obligations.
Definition of Term Sheet
A Term Sheet is a non-binding document outlining the key terms and conditions of a proposed agreement between parties, serving as a foundation for detailed contracts. It typically includes essential elements such as valuation, investment amount, equity ownership, and governance rights, providing clarity before formal negotiations commence. In contrast, a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) often represents a broader agreement expressing mutual intentions without detailed contractual obligations.
Definition of Memorandum of Understanding (MOU)
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is a formal but non-binding agreement between two or more parties outlining the terms and details of an understanding or partnership. MOUs define the roles, responsibilities, and expectations of each party without creating legally enforceable obligations, serving as a foundation for further negotiation. Unlike a Term Sheet, which is often used specifically in financial or investment contexts, an MOU covers broader collaborative agreements across various industries.
Purpose and Use Cases of Term Sheet
A Term Sheet outlines the key financial and legal terms of an investment or transaction, serving as a non-binding agreement that guides further negotiation and due diligence. It is primarily used in venture capital, mergers and acquisitions, and fundraising to establish clear expectations between parties before drafting definitive contracts. Unlike a Memorandum of Understanding, which broadly captures mutual intentions, a Term Sheet focuses on specific deal points such as valuation, equity stakes, and governance rights.
Key Elements in a Term Sheet
A Term Sheet outlines the key elements of a proposed business agreement, including valuation, investment amount, equity percentage, governance rights, and exit provisions. Unlike a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), which is often non-binding and focuses on general intentions, a Term Sheet is more detailed and serves as a basis for drafting definitive agreements. Key elements in a Term Sheet also include confidentiality clauses, closing conditions, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Key Components of a Memorandum of Understanding
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) typically includes key components such as the purpose of the agreement, detailed roles and responsibilities of each party, and the duration or term of the understanding. It outlines the scope of collaboration, confidentiality clauses, and dispute resolution mechanisms to ensure clarity and prevent conflicts. Unlike Term Sheets, MoUs emphasize mutual intentions and non-binding commitments without focusing extensively on financial terms or conditions.
Legal Enforceability: Term Sheet vs MOU
Term sheets generally outline preliminary terms and are often non-binding, intending to guide future contract negotiations without creating enforceable obligations. Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs) can be either non-binding or binding depending on the language used, with some MOUs explicitly establishing legal commitments between parties. The key distinction in legal enforceability lies in the specificity and intent embedded within each document, where term sheets tend to emphasize negotiation terms, while MOUs may formalize agreed-upon responsibilities.
Pros and Cons of Term Sheet
A Term Sheet outlines the key financial and legal terms of a potential deal, providing clarity on valuation, equity stakes, and investor rights, which helps streamline negotiations and set clear expectations. However, its non-binding nature can lead to uncertainty if parties change their positions, and the detailed focus may increase legal costs and prolong the deal process. Compared to a Memorandum of Understanding, a Term Sheet offers more specificity but requires careful drafting to avoid misunderstandings and ensure alignment on critical deal points.
Pros and Cons of Memorandum of Understanding
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) clearly outlines the intentions and preliminary agreements between parties, offering flexibility without legal enforceability, which helps in establishing trust early in negotiations. However, the lack of binding commitment can lead to uncertainties and reduced accountability compared to a Term Sheet. MoUs are cost-effective and quick to draft, but their non-binding nature may result in difficulties resolving disputes or ensuring follow-through on agreed actions.
Choosing Between a Term Sheet and MOU: Which is Right for You?
Choosing between a Term Sheet and a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) depends on the level of detail and legal commitment required; Term Sheets provide clear, binding agreements on key deal points, ideal for complex transactions involving investment or acquisition. MOUs offer a more flexible, non-binding outline of mutual intentions, suitable for preliminary collaborations or partnerships where parties seek to establish common goals without immediate legal obligations. Assess your project's scope, urgency for legal enforceability, and negotiation stage to determine whether a Term Sheet's precision or an MOU's adaptability best supports your strategic objectives.
Term Sheet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com