Transactional revenue is generated from individual sales or one-time purchases, reflecting direct income from customers without recurring commitments. This model is common in retail, e-commerce, and service industries where each interaction results in immediate payment. Explore the rest of the article to understand how leveraging transactional revenue can optimize Your business growth and profitability.
Table of Comparison
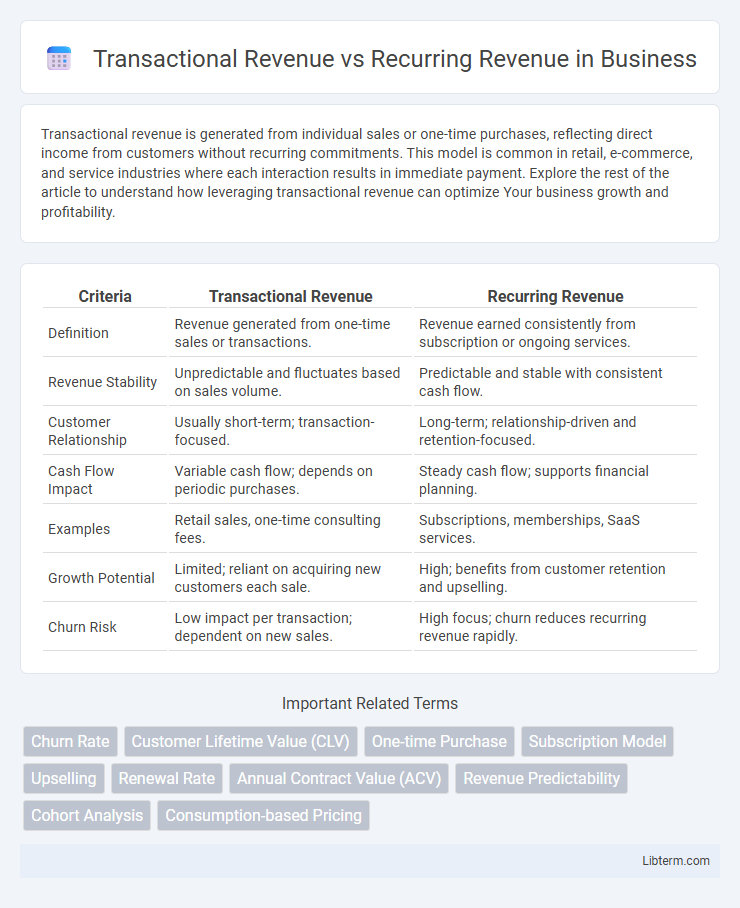
| Criteria | Transactional Revenue | Recurring Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Revenue generated from one-time sales or transactions. | Revenue earned consistently from subscription or ongoing services. |
| Revenue Stability | Unpredictable and fluctuates based on sales volume. | Predictable and stable with consistent cash flow. |
| Customer Relationship | Usually short-term; transaction-focused. | Long-term; relationship-driven and retention-focused. |
| Cash Flow Impact | Variable cash flow; depends on periodic purchases. | Steady cash flow; supports financial planning. |
| Examples | Retail sales, one-time consulting fees. | Subscriptions, memberships, SaaS services. |
| Growth Potential | Limited; reliant on acquiring new customers each sale. | High; benefits from customer retention and upselling. |
| Churn Risk | Low impact per transaction; dependent on new sales. | High focus; churn reduces recurring revenue rapidly. |
Understanding Transactional Revenue
Transactional revenue refers to income generated from one-time sales or individual customer purchases, typically involving a single exchange of goods or services. This revenue model is characterized by its unpredictability and lack of ongoing commitment, making it challenging to forecast long-term financial stability. Business examples include retail purchases, one-off consulting fees, and freelance projects, where revenue spikes correspond directly to sales volume.
What is Recurring Revenue?
Recurring revenue is the consistent, predictable income generated from ongoing customer subscriptions or contracts, such as SaaS services, membership fees, or maintenance plans. This revenue model ensures stability by providing businesses with a continuous cash flow over time, reducing dependence on one-time sales. Companies leveraging recurring revenue often experience higher customer retention rates and improved financial forecasting compared to transactional revenue models.
Key Differences Between Transactional and Recurring Revenue
Transactional revenue arises from one-time sales tied to specific products or services, generating revenue based on individual customer purchases. Recurring revenue, on the other hand, stems from ongoing subscriptions, memberships, or contracts, providing predictable and steady income over a period. Key differences include revenue predictability, customer retention focus, and cash flow stability, with recurring revenue typically offering greater financial sustainability and growth potential.
Advantages of Transactional Revenue
Transactional revenue offers immediate cash flow by generating income from one-time sales, enabling businesses to quickly capitalize on market demand. This model provides greater flexibility and scalability since companies are not bound by long-term commitments, allowing easier adaptation to shifting consumer preferences. High upfront payments from transactional revenue can boost short-term liquidity, supporting rapid investment and operational growth.
Benefits of Recurring Revenue Models
Recurring revenue models provide predictable cash flow, enhancing financial stability and enabling better business planning. They foster stronger customer relationships through ongoing engagement, increasing customer lifetime value and reducing churn rates. This consistent income stream supports scalable growth and improves valuation for investors compared to one-time transactional revenue.
Challenges Associated with Transactional Revenue
Transactional revenue faces significant challenges due to its unpredictable cash flow and dependence on one-time sales, which complicates financial forecasting and budgeting. This revenue model often requires continuous customer acquisition efforts, increasing marketing and sales expenses while risking revenue volatility. Companies relying heavily on transactional revenue may struggle with customer retention, limiting growth potential compared to the stability offered by recurring revenue streams.
Obstacles in Implementing Recurring Revenue
Transitioning from transactional revenue to recurring revenue often faces obstacles such as customer resistance to subscription models, requiring a shift in marketing and sales strategies to emphasize ongoing value. Businesses encounter challenges in restructuring their pricing models and ensuring seamless billing and subscription management systems to maintain consistent cash flow. Integrating customer success initiatives becomes critical to reduce churn and sustain long-term subscriptions amid evolving market expectations.
Business Examples: Transactional vs Recurring Revenue
E-commerce platforms like Amazon primarily generate transactional revenue by earning fees on individual sales, while subscription services such as Netflix rely on recurring revenue through monthly membership fees. Software companies like Microsoft have shifted from one-time purchase models to recurring revenue by offering cloud-based subscriptions via Microsoft 365. Gyms and fitness centers exemplify recurring revenue by charging monthly memberships, contrasting with personal trainers who often depend on one-time session fees reflecting transactional revenue.
Impact on Business Growth and Stability
Transactional revenue provides immediate cash flow by generating income from one-time sales, which can boost short-term business growth but often lacks predictability. Recurring revenue creates a consistent and reliable income stream through subscriptions or ongoing services, enhancing financial stability and enabling long-term strategic planning. Businesses leveraging recurring revenue models tend to experience higher customer lifetime value and smoother cash flow management, leading to sustained growth and market resilience.
Choosing the Best Revenue Model for Your Business
Transactional revenue generates income through one-time purchases, ideal for businesses with varied product sales or project-based services. Recurring revenue ensures consistent cash flow via subscriptions or memberships, providing stability and easier financial forecasting. Selecting the best revenue model depends on your industry, customer behavior, and long-term growth goals, balancing immediate gains with predictable income streams.
Transactional Revenue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com