Direct Market Access (DMA) enables traders to interact with financial markets directly, bypassing traditional brokers for faster and more transparent trade execution. This approach offers enhanced control over order placement, increased market transparency, and reduced transaction costs, making it ideal for high-frequency and institutional traders. Explore the rest of this article to discover how DMA can optimize your trading strategy and execution.
Table of Comparison
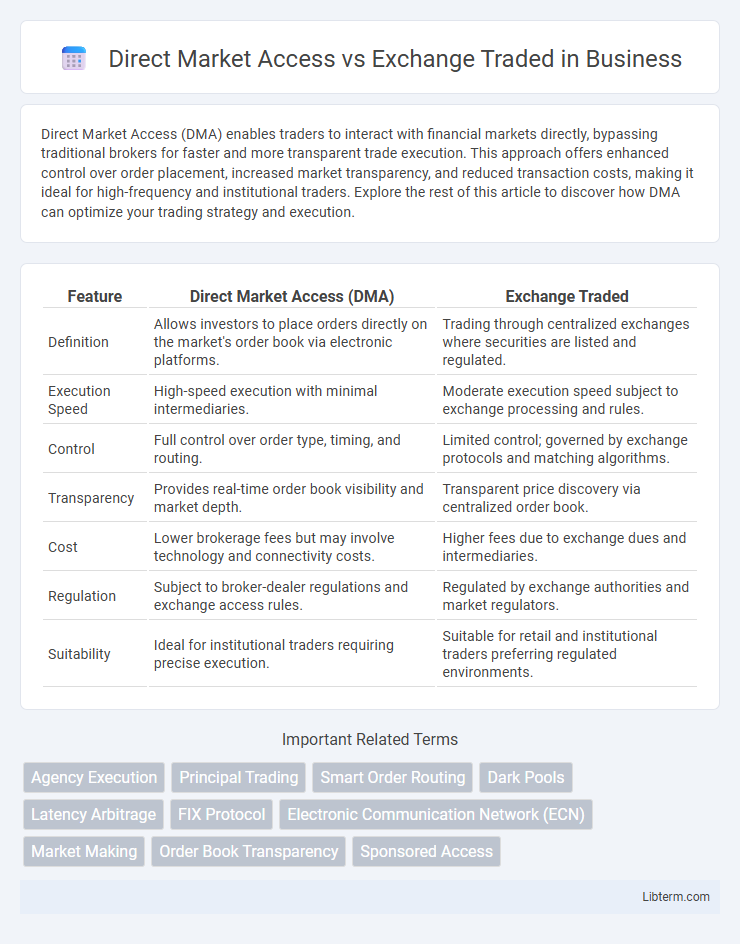
| Feature | Direct Market Access (DMA) | Exchange Traded |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allows investors to place orders directly on the market's order book via electronic platforms. | Trading through centralized exchanges where securities are listed and regulated. |
| Execution Speed | High-speed execution with minimal intermediaries. | Moderate execution speed subject to exchange processing and rules. |
| Control | Full control over order type, timing, and routing. | Limited control; governed by exchange protocols and matching algorithms. |
| Transparency | Provides real-time order book visibility and market depth. | Transparent price discovery via centralized order book. |
| Cost | Lower brokerage fees but may involve technology and connectivity costs. | Higher fees due to exchange dues and intermediaries. |
| Regulation | Subject to broker-dealer regulations and exchange access rules. | Regulated by exchange authorities and market regulators. |
| Suitability | Ideal for institutional traders requiring precise execution. | Suitable for retail and institutional traders preferring regulated environments. |
Introduction to Direct Market Access (DMA) and Exchange-Traded Platforms
Direct Market Access (DMA) enables traders to interact directly with market order books, bypassing traditional broker routes and significantly reducing latency for high-frequency and algorithmic trading. Exchange-traded platforms, by contrast, facilitate centralized trading through regulated exchanges where orders are matched within an organized order book, ensuring transparency and standardized processes. DMA provides enhanced control and faster execution, whereas exchange-traded platforms prioritize market integrity and regulatory compliance.
Key Features of Direct Market Access
Direct Market Access (DMA) enables traders to place orders directly into the exchange order book, offering greater speed, transparency, and control compared to Exchange Traded methods where brokers route orders. Key features of DMA include real-time market data access, customizable order types, and reduced latency, facilitating faster execution and improved price discovery. This direct connection also enhances execution quality by minimizing intermediaries and allowing sophisticated algorithmic trading strategies.
Essential Characteristics of Exchange-Traded Markets
Exchange-traded markets possess essential characteristics such as centralized order books, transparent pricing, and regulated environments that ensure market integrity and investor protection. These markets facilitate standardized contracts and rigorous settlement procedures, promoting liquidity and reducing counterparty risk. Unlike direct market access, exchange-traded markets benefit from consolidated price discovery and mandatory reporting, enhancing transparency and regulatory oversight.
Speed and Execution: DMA vs Exchange-Traded
Direct Market Access (DMA) offers traders ultra-fast order execution by connecting directly to liquidity providers and exchanges, bypassing intermediaries, which reduces latency significantly compared to traditional exchange-traded methods. Exchange-traded orders typically pass through brokers, introducing additional layers and processing time, potentially slowing execution speed and increasing slippage risk. High-frequency traders and institutional investors often prefer DMA for its superior speed and precise order execution, enabling improved trade agility and reduced cost impact.
Transparency and Market Visibility
Direct Market Access (DMA) provides traders with enhanced transparency by allowing real-time order book visibility and direct interaction with exchange liquidity, reducing latency and improving execution quality. Exchange Traded platforms offer standardized transparency through centralized order matching and public trade reporting, ensuring all participants have equal market visibility. DMA's access to detailed market depth and order flow data often surpasses traditional exchange-traded transparency, empowering sophisticated trading strategies.
Cost Considerations and Fee Structures
Direct Market Access (DMA) typically involves lower transaction fees by allowing traders to place orders directly on the exchange order book, bypassing intermediaries, which reduces commission and markup costs. Exchange-traded execution often incurs higher fees due to broker commissions, exchange charges, and clearing fees embedded in the trade process. Cost considerations favor DMA for high-frequency and institutional traders seeking cost efficiency, while retail traders may benefit from bundled fee structures offered by traditional exchange-traded platforms.
Accessibility and User Requirements
Direct Market Access (DMA) offers traders direct entry to the order books of exchanges, requiring advanced technical infrastructure, low-latency connectivity, and sophisticated order management systems. Exchange-traded platforms provide broader accessibility with standardized interfaces, requiring less technical expertise and offering regulatory oversight that simplifies compliance for retail investors. DMA is typically favored by institutional traders seeking high-speed execution and customization, whereas exchange-traded access serves a wider user base with more straightforward access and user-friendly requirements.
Liquidity and Price Discovery
Direct Market Access (DMA) provides traders with immediate execution on exchange order books, enhancing liquidity by allowing faster order placement and greater market transparency. Exchange-traded platforms centralize trades through a regulated marketplace, which traditionally ensures more consistent price discovery due to aggregated order flow and standardized rules. DMA can improve price discovery efficiency by enabling access to multiple liquidity pools, but exchange-traded venues maintain deeper order books and tighter spreads, supporting more reliable market valuations.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
Direct Market Access (DMA) allows institutional investors to place orders directly into the exchange's order book, requiring strict adherence to regulatory frameworks such as MiFID II in Europe and Reg NMS in the United States, which emphasize transparency and best execution standards. Exchange-traded transactions operate under comprehensive exchange regulations, mandating compliance with market surveillance, reporting obligations, and centralized clearing to mitigate systemic risk. Both trading methods demand rigorous compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) rules, ensuring market integrity and investor protection within their respective regulatory environments.
Choosing the Right Platform: Factors to Consider
Evaluating direct market access (DMA) versus exchange-traded platforms requires careful consideration of execution speed, cost efficiency, and control over order types. DMA offers traders ultra-fast trade execution and granular control with lower latency, ideal for high-frequency trading or professional investors seeking better price discovery. Exchange-traded platforms prioritize transparency, regulatory oversight, and liquidity, suiting investors who value standardized processes and robust market safeguards.
Direct Market Access Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com