Conducting a pilot test is essential for identifying potential issues and refining processes before full-scale implementation. It allows you to gather valuable feedback, minimize risks, and ensure your project meets its objectives effectively. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to design and execute a successful pilot test.
Table of Comparison
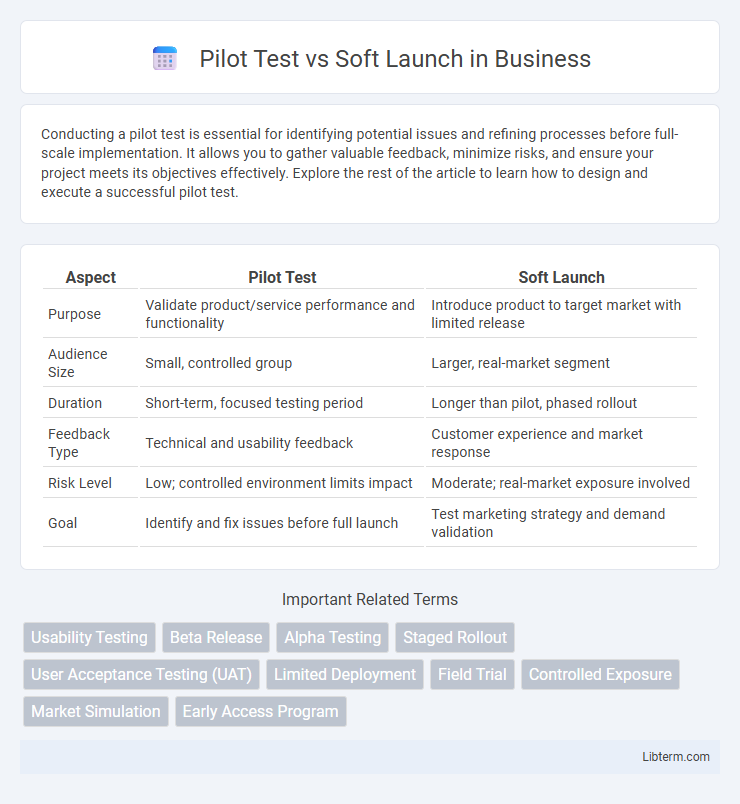
| Aspect | Pilot Test | Soft Launch |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Validate product/service performance and functionality | Introduce product to target market with limited release |
| Audience Size | Small, controlled group | Larger, real-market segment |
| Duration | Short-term, focused testing period | Longer than pilot, phased rollout |
| Feedback Type | Technical and usability feedback | Customer experience and market response |
| Risk Level | Low; controlled environment limits impact | Moderate; real-market exposure involved |
| Goal | Identify and fix issues before full launch | Test marketing strategy and demand validation |
Introduction to Pilot Test and Soft Launch
A Pilot Test is a small-scale trial of a product or service conducted to identify potential issues and gather user feedback before a full market release. A Soft Launch involves releasing the product to a limited audience or specific region to assess performance, user engagement, and operational readiness under real-world conditions. Both approaches aim to reduce risks and improve final product quality through controlled exposure and iterative improvements.
Key Differences Between Pilot Test and Soft Launch
Pilot tests evaluate product functionality and user interactions on a limited scale, primarily aiming to identify technical issues and gather detailed feedback before full release. Soft launches focus on market response and user adoption in a controlled environment to refine marketing strategies and product positioning with minimal risk. Key differences include pilot tests emphasizing technical validation, while soft launches prioritize market testing and user engagement metrics.
Purpose and Objectives of Pilot Testing
Pilot testing aims to validate the functionality, usability, and performance of a product or service in a controlled environment before full-scale deployment, minimizing risks and identifying potential issues. The primary objectives include gathering user feedback, assessing technical feasibility, and ensuring alignment with business goals to facilitate informed decision-making. Soft launch, by contrast, focuses on introducing the product to a limited audience to test market response and operational readiness without the comprehensive technical validation emphasis of pilot testing.
Purpose and Objectives of Soft Launch
A soft launch serves to validate product functionality, user experience, and market fit by releasing to a limited audience before full-scale launch. It aims to identify technical issues, gather user feedback, and assess demand without the risks associated with a broad rollout. The purpose of a soft launch is to optimize the product and marketing strategy based on real-world data, ensuring higher chances of success during the official launch.
When to Use a Pilot Test
Use a pilot test when introducing a new product, service, or process that requires controlled evaluation to identify potential issues before a full-scale launch. Pilot tests are ideal for gathering detailed user feedback, measuring performance metrics, and validating operational functionality in a limited, real-world environment. This approach minimizes risk by allowing adjustments based on real data and user response before committing extensive resources.
When to Opt for a Soft Launch
Opt for a soft launch when you need to gather user feedback in a real-world setting without the pressure of a full-scale release, allowing for iterative improvements and risk mitigation. This approach is ideal for refining product features, identifying unforeseen issues, and validating market demand with a limited audience before broader exposure. Soft launches are particularly useful in dynamic markets where user preferences can shift rapidly, providing crucial insights that a pilot test's controlled environment might miss.
Benefits of Running a Pilot Test
Running a pilot test offers valuable benefits, including identifying potential issues and gathering user feedback before a full-scale launch, which reduces the risk of costly failures. It allows companies to refine product features, optimize user experience, and validate assumptions with real-world data, leading to more informed decision-making. Pilot tests also facilitate smoother transitions by preparing teams and processes for broader implementation, ensuring higher success rates in subsequent phases.
Advantages of Conducting a Soft Launch
A soft launch allows businesses to gather real user feedback and identify potential issues in a controlled environment, minimizing the risk of widespread failure during a full-scale release. It enables gradual market entry, helping to build initial customer relationships and generate early buzz without the pressure of complete exposure. This approach also provides valuable insights for refining product features and marketing strategies before broader deployment.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Pilot Tests and Soft Launches
Common mistakes to avoid in pilot tests and soft launches include neglecting clear success metrics, which can result in ambiguous performance evaluation and misguided decision-making. Failing to select a representative sample or target audience skews feedback and limits the scalability of insights gathered during these early-stage rollouts. Overlooking effective communication with stakeholders often leads to misaligned expectations and insufficient data integration, hindering iterative improvements before the full launch.
Choosing the Right Approach: Pilot Test vs Soft Launch
Choosing the right approach between a pilot test and a soft launch depends on the product's complexity and target market size, with pilot tests ideal for smaller, controlled environments to gather in-depth user feedback and identify critical flaws. Soft launches work better for broader market exposure, enabling teams to assess product performance, user engagement, and operational scalability before a full-scale release. Evaluating factors like risk tolerance, budget, and desired feedback granularity ensures selecting the approach that maximizes product success and market readiness.
Pilot Test Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com