CRM and ERP systems integrate business processes to enhance customer relationship management and operational efficiency. By streamlining data across sales, finance, and inventory, they provide actionable insights that boost productivity and decision-making. Discover how aligning CRM and ERP solutions can transform Your business by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
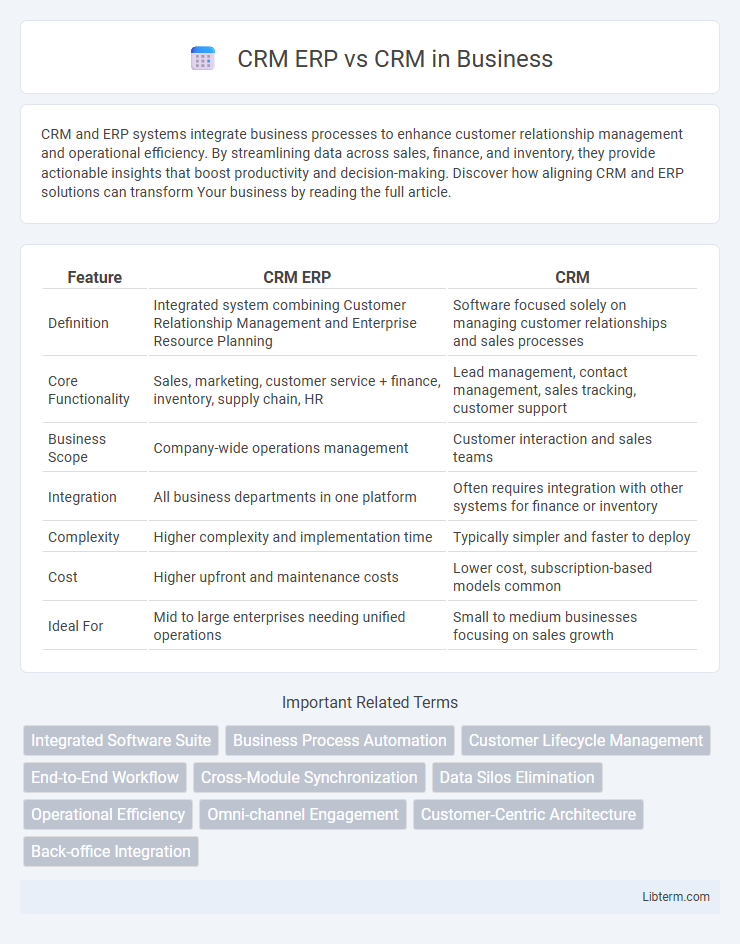
| Feature | CRM ERP | CRM |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated system combining Customer Relationship Management and Enterprise Resource Planning | Software focused solely on managing customer relationships and sales processes |
| Core Functionality | Sales, marketing, customer service + finance, inventory, supply chain, HR | Lead management, contact management, sales tracking, customer support |
| Business Scope | Company-wide operations management | Customer interaction and sales teams |
| Integration | All business departments in one platform | Often requires integration with other systems for finance or inventory |
| Complexity | Higher complexity and implementation time | Typically simpler and faster to deploy |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance costs | Lower cost, subscription-based models common |
| Ideal For | Mid to large enterprises needing unified operations | Small to medium businesses focusing on sales growth |
Introduction to CRM ERP vs CRM
CRM ERP combines Customer Relationship Management (CRM) with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) to unify customer data and business processes into a single platform. While CRM focuses primarily on managing sales, marketing, and customer service interactions, CRM ERP integrates these functions with inventory, finance, and supply chain management for a holistic view of operations. This integration enhances data accuracy, streamlines workflows, and improves decision-making across departments.
Key Differences Between CRM ERP and CRM
CRM ERP integrates customer relationship management with enterprise resource planning, offering a unified system for sales, finance, inventory, and customer service. CRM systems focus exclusively on managing customer interactions, sales pipeline, and marketing efforts without handling back-end operations. The key difference lies in CRM ERP's expanded scope, combining front-office customer data with back-office processes to enhance overall business efficiency.
Core Functions of CRM Systems
CRM systems primarily focus on managing customer relationships by organizing sales, marketing, and customer service activities to enhance customer satisfaction and retention. Core functions include contact management, lead tracking, sales automation, and customer support, enabling businesses to streamline interactions and personalize communication. In contrast, CRM ERP systems integrate these CRM capabilities with broader enterprise resource planning functions like inventory management, accounting, and supply chain operations for comprehensive business management.
Core Features of CRM ERP Solutions
CRM ERP solutions integrate core features such as customer relationship management, sales automation, and marketing tools with enterprise resource planning capabilities like inventory management, financial accounting, and supply chain operations. These unified systems enhance data visibility, improve workflow efficiency, and enable comprehensive analytics across departments. By combining CRM's customer-centric functions with ERP's operational modules, businesses achieve streamlined processes and better resource allocation.
Integration Capabilities: CRM ERP vs CRM
CRM ERP systems offer enhanced integration capabilities by combining customer relationship management with enterprise resource planning, enabling seamless data flow across sales, inventory, finance, and customer service departments. CRM standalone solutions focus primarily on managing customer interactions and sales pipelines but often require third-party integrations to connect with other business functions. The unified database in CRM ERP reduces data silos, improves real-time analytics, and supports comprehensive business process automation.
Benefits of Implementing CRM ERP
Implementing CRM ERP integrates customer relationship management with enterprise resource planning, enhancing data accuracy and streamlining business processes. This unified system improves customer insights, automates workflows, and fosters collaboration across departments, leading to increased operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Companies experience better inventory management, sales forecasting, and financial tracking, which collectively drive revenue growth and reduce costs.
Advantages of Standalone CRM Systems
Standalone CRM systems offer specialized features tailored to customer relationship management, providing enhanced usability and faster deployment compared to integrated CRM ERP solutions. These systems excel in sales automation, lead tracking, and customer interaction analytics without the complexity of ERP modules. Businesses benefit from reduced costs, simpler customization, and focused support, making standalone CRM ideal for organizations prioritizing dedicated customer management.
Choosing Between CRM ERP and CRM: Factors to Consider
Choosing between CRM ERP and standalone CRM systems depends on your business size, integration needs, and budget constraints. CRM ERP systems offer comprehensive data management by integrating customer relationship management with enterprise resource planning, ideal for companies seeking unified workflows and real-time data across departments. Standalone CRM is more suitable for small to mid-sized businesses prioritizing customer interaction and sales management without the complexity or cost of full ERP integration.
Common Use Cases for CRM ERP and CRM
CRM ERP systems integrate customer relationship management with enterprise resource planning, streamlining operations such as sales forecasting, inventory management, and financial tracking for improved business efficiency. CRM platforms primarily focus on customer-focused activities like lead management, customer support, and marketing automation to enhance customer engagement and retention. Common use cases for CRM ERP include end-to-end order processing and supply chain optimization, while CRM is extensively used for managing sales pipelines and personalized customer communication.
Final Verdict: CRM ERP or CRM for Your Business?
Choosing between CRM ERP and standalone CRM depends on your business needs: CRM ERP integrates customer relationship management with enterprise resource planning, offering a comprehensive solution for companies seeking unified data across sales, finance, inventory, and customer service. Standalone CRM systems specialize in managing customer interactions, sales pipelines, and marketing automation, making them ideal for businesses focused solely on enhancing customer engagement without the complexity of ERP functionalities. For businesses aiming for streamlined operations and a single source of truth, CRM ERP is the optimal choice, whereas businesses prioritizing customer-focused tools with flexibility may benefit more from standalone CRM solutions.
CRM ERP Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com