Income investing focuses on generating steady cash flow through dividends, interest, or other regular payouts from investments like bonds and dividend-paying stocks. This strategy prioritizes preserving capital while providing reliable income, making it ideal for retirees and conservative investors. Explore the rest of the article to discover how income investing can enhance your financial stability.
Table of Comparison
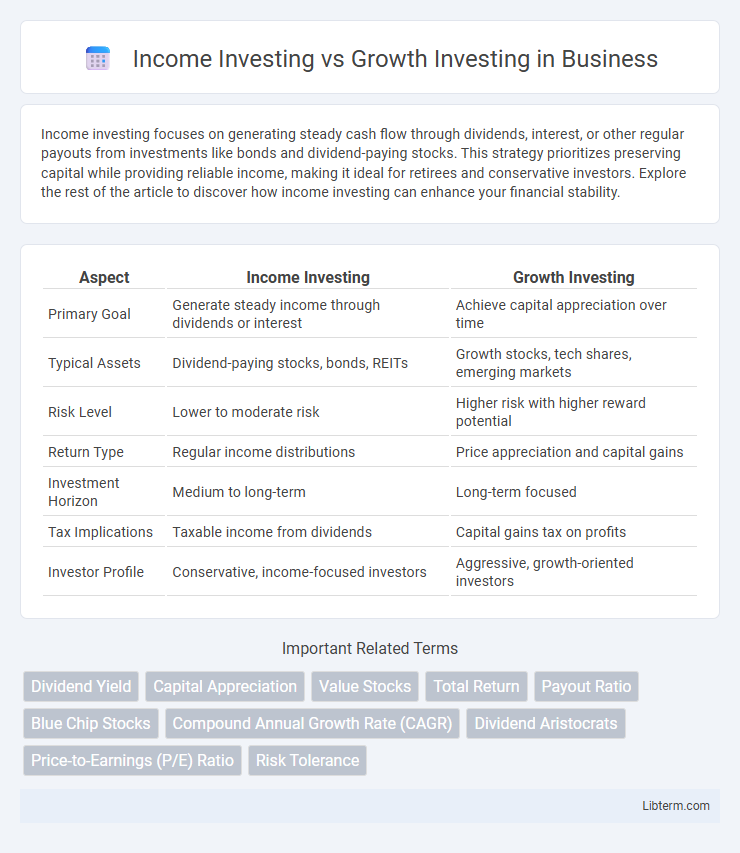
| Aspect | Income Investing | Growth Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Generate steady income through dividends or interest | Achieve capital appreciation over time |
| Typical Assets | Dividend-paying stocks, bonds, REITs | Growth stocks, tech shares, emerging markets |
| Risk Level | Lower to moderate risk | Higher risk with higher reward potential |
| Return Type | Regular income distributions | Price appreciation and capital gains |
| Investment Horizon | Medium to long-term | Long-term focused |
| Tax Implications | Taxable income from dividends | Capital gains tax on profits |
| Investor Profile | Conservative, income-focused investors | Aggressive, growth-oriented investors |
Introduction to Income Investing and Growth Investing
Income investing focuses on generating steady cash flow through dividends and interest from stocks, bonds, or real estate investment trusts (REITs). Growth investing targets capital appreciation by investing in companies with strong potential for revenue and earnings expansion, often characterized by higher risk and volatility. Investors seeking consistent income typically prefer income stocks, while growth stocks attract those aiming for long-term portfolio value increase.
Key Concepts: Income vs. Capital Appreciation
Income investing focuses on generating a steady cash flow through dividends or interest payments from securities like dividend-paying stocks, bonds, or real estate investment trusts (REITs). Growth investing targets capital appreciation by investing in companies expected to increase in value, often reinvesting earnings rather than paying dividends. The key difference lies in income investing prioritizing regular income streams, while growth investing emphasizes long-term asset value growth.
Typical Asset Classes in Income Investing
Income investing primarily targets asset classes that generate consistent cash flow, including dividend-paying stocks, bonds, real estate investment trusts (REITs), and preferred shares. Fixed-income securities like government and corporate bonds provide reliable interest payments, while REITs offer rental income along with potential capital appreciation. Dividend-paying blue-chip stocks also serve as a core asset class, delivering steady income through periodic dividend distributions.
Common Investments for Growth-Oriented Portfolios
Growth-oriented portfolios typically emphasize investments in high-growth stocks, including technology companies, biotechnology firms, and emerging market equities known for above-average revenue and earnings expansion. These portfolios often include smaller-cap stocks and innovative industry leaders with strong potential for capital appreciation, reflecting a focus on future earnings and reinvestment over dividends. Common investments also encompass sector-specific exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and mutual funds designed to capture market trends and capitalize on rapid growth opportunities.
Risk Profiles: Income Investing vs Growth Investing
Income investing typically involves lower risk by focusing on stable, dividend-paying stocks and bonds that provide regular cash flow, appealing to conservative investors seeking steady returns. Growth investing carries higher risk as it targets companies with potential for significant capital appreciation but often lacks dividend income and can experience greater market volatility. Understanding individual risk tolerance and investment goals is crucial when choosing between income investing and growth-oriented strategies.
Dividend Yields vs Capital Gains Potential
Income investing targets steady dividend yields, providing regular cash flow through investments in established companies with consistent profit distributions. Growth investing prioritizes capital gains potential by focusing on companies with high earnings growth rates and reinvestment strategies, often resulting in lower or no dividends. Investors seeking predictable income may prefer dividend-focused stocks, while those aiming for long-term wealth accumulation often opt for growth stocks with significant appreciation possibilities.
Time Horizon and Investment Objectives
Income investing targets steady cash flow through dividends or interest, appealing to investors seeking regular income and lower risk over shorter to medium time horizons. Growth investing prioritizes capital appreciation by reinvesting earnings into high-potential companies, suited for investors with longer time horizons willing to accept higher volatility for substantial wealth accumulation. Time horizon directly influences the choice between income and growth strategies, aligning investment objectives with risk tolerance and financial goals.
Tax Implications of Income and Growth Strategies
Income investing often generates regular dividend income, which may be taxed at higher ordinary income tax rates depending on the investor's jurisdiction, reducing after-tax returns. Growth investing focuses on capital appreciation, with taxes typically deferred until the sale of assets, potentially benefiting from lower long-term capital gains tax rates. Understanding these distinct tax implications helps investors optimize portfolio strategies based on their income needs and tax situations.
Blending Income and Growth Approaches
Blending income and growth investing strategies allows investors to achieve a balanced portfolio with steady cash flow and potential capital appreciation. By incorporating dividend-paying stocks alongside growth-oriented equities, investors can benefit from regular income while capturing market value increases. This hybrid approach enhances diversification, mitigates risk, and supports long-term financial goals through a combination of yield and expansion.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Financial Goals
Income investing focuses on generating steady cash flow through dividends or interest, making it ideal for investors seeking regular income or retirement stability. Growth investing targets capital appreciation by investing in companies with strong potential for revenue and earnings expansion, suitable for investors aiming for long-term wealth accumulation. Choosing the right approach depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon, with some investors combining both strategies for balanced portfolio diversification.
Income Investing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com