Income serves as the foundation for financial stability, influencing your ability to save, invest, and cover essential expenses. Understanding different income sources helps optimize tax planning and maximize earnings potential. Dive into the article to explore strategies that can enhance your income and secure your financial future.
Table of Comparison
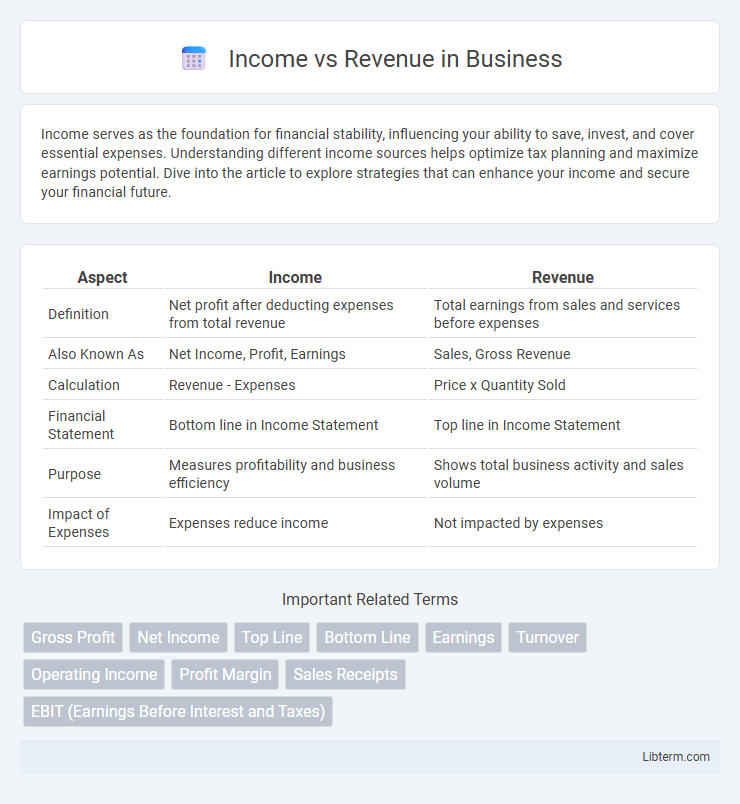
| Aspect | Income | Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Net profit after deducting expenses from total revenue | Total earnings from sales and services before expenses |
| Also Known As | Net Income, Profit, Earnings | Sales, Gross Revenue |
| Calculation | Revenue - Expenses | Price x Quantity Sold |
| Financial Statement | Bottom line in Income Statement | Top line in Income Statement |
| Purpose | Measures profitability and business efficiency | Shows total business activity and sales volume |
| Impact of Expenses | Expenses reduce income | Not impacted by expenses |
Introduction to Income vs Revenue
Income represents the net earnings of a business after deducting expenses, taxes, and costs, whereas revenue is the total amount generated from sales or services before any deductions. Understanding the distinction between income and revenue is crucial for analyzing a company's financial health and profitability. Revenue reflects the inflow of cash or receivables, while income indicates the actual profit retained by the business.
Defining Revenue: What It Means
Revenue represents the total amount of money generated by a company from its core business activities, such as sales of goods or services, before any expenses are deducted. It serves as a key indicator of business performance and market demand, reflecting the company's ability to generate income through its operations. Understanding revenue is essential for analyzing financial health and guiding strategic decisions within an organization.
Understanding Income: Key Concepts
Income represents the net profit remaining after all expenses, taxes, and costs are deducted from total revenue, reflecting a company's true profitability. It includes various forms such as gross income, operating income, and net income, each providing insight into different aspects of financial performance. Understanding income is crucial for evaluating a business's financial health, investor returns, and sustainable growth potential.
Income vs Revenue: Core Differences
Income represents the net profit remaining after deducting all expenses, taxes, and costs from total revenue, reflecting a company's true profitability. Revenue, also known as sales or turnover, signifies the total amount of money generated from goods sold or services provided before any expenses are subtracted. The core difference lies in revenue being the gross inflow, while income indicates the net earnings that determine financial health and operational efficiency.
How Businesses Calculate Revenue
Businesses calculate revenue by totaling all sales from goods or services before any expenses are deducted, reflecting the gross income generated within a specific period. This figure includes income from core operations such as product sales, service fees, and recurring subscriptions, excluding returns, allowances, and discounts for accuracy. Accurate revenue calculation is essential for evaluating business performance, forecasting growth, and preparing financial statements like the income statement.
Types of Income Explained
Income encompasses various types, including earned income from wages, rental income from properties, and passive income derived from investments such as dividends or royalties. Each type contributes differently to an individual's or business's total financial inflow, with earned income subject to payroll taxes while passive income often enjoys favorable tax treatment. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize tax strategies and financial planning by categorizing income into operating, non-operating, and comprehensive segments for accurate reporting and analysis.
The Role of Expenses in Income
Income represents the net profit remaining after all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, and interest, are deducted from total revenue. Revenue reflects the total earnings generated from sales or services before any expenses are applied. The critical role of expenses lies in transforming gross revenue into meaningful income, highlighting operational efficiency and financial health.
Why Revenue Doesn’t Equal Profit
Revenue represents the total amount of money generated from sales before any expenses are deducted, while income, often referred to as net profit, is the remaining amount after all costs such as operating expenses, taxes, and interest are subtracted. Businesses may have high revenue but low or negative income if their expenses exceed their revenues, highlighting that revenue alone does not indicate profitability. Understanding the distinction between revenue and income is critical for accurate financial analysis and decision-making.
Real-World Examples: Income vs Revenue
Revenue represents the total amount a company earns from sales before any expenses, as seen with Walmart reporting $572 billion in revenue in 2023. Income, often referred to as net income or profit, is the amount left after deducting all costs, such as Apple's net income of $99.8 billion in the same period. These distinctions highlight how Amazon's $524 billion revenue contrasts with its $33 billion net income, emphasizing the difference between gross earnings and actual profitability.
Impact on Financial Decision-Making
Income reflects the net profit after all expenses, directly influencing a company's capacity to reinvest, distribute dividends, and sustain operations. Revenue, as the total sales generated before costs, serves as a key indicator of market demand and business scalability. Understanding the distinction between income and revenue enables more accurate budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning in financial decision-making.
Income Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com