A Service Level Agreement (SLA) defines the expected level of service between a provider and a client, ensuring clear accountability and performance standards. It usually includes key metrics such as response time, resolution time, and uptime guarantees to measure service effectiveness. Discover more about how an SLA can protect Your interests and enhance service quality by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
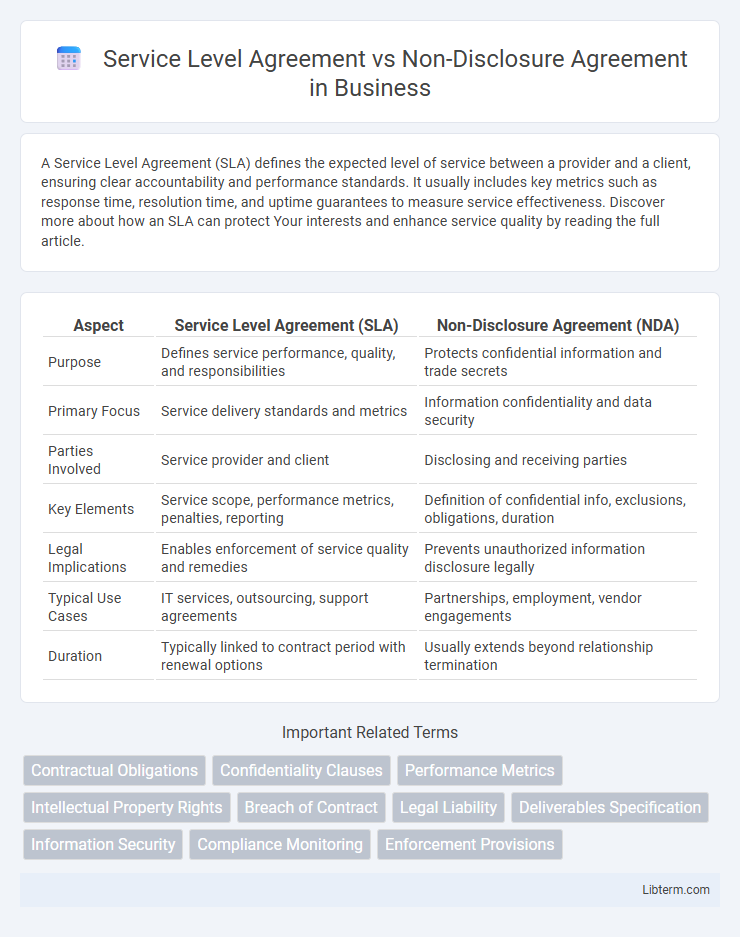
| Aspect | Service Level Agreement (SLA) | Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Defines service performance, quality, and responsibilities | Protects confidential information and trade secrets |
| Primary Focus | Service delivery standards and metrics | Information confidentiality and data security |
| Parties Involved | Service provider and client | Disclosing and receiving parties |
| Key Elements | Service scope, performance metrics, penalties, reporting | Definition of confidential info, exclusions, obligations, duration |
| Legal Implications | Enables enforcement of service quality and remedies | Prevents unauthorized information disclosure legally |
| Typical Use Cases | IT services, outsourcing, support agreements | Partnerships, employment, vendor engagements |
| Duration | Typically linked to contract period with renewal options | Usually extends beyond relationship termination |
Introduction to Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs)
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) define the expected performance standards and responsibilities between service providers and clients, ensuring measurable quality and accountability. Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) legally bind parties to confidentiality, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure during business transactions or collaborations. Both SLAs and NDAs are essential contractual tools that establish clear expectations and safeguard intellectual property in professional relationships.
Defining Service Level Agreements: Purpose and Scope
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) establish clear expectations by defining the scope, quality, and responsibilities of service delivery between providers and clients. These contracts specify measurable performance metrics, such as uptime, response times, and resolution targets, ensuring accountability and transparency. Unlike Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), which focus on confidentiality obligations, SLAs emphasize operational standards and service commitments critical to maintaining business continuity.
Understanding Non-Disclosure Agreements: Key Elements
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) are legal contracts designed to protect confidential information shared between parties, specifying what information must remain private. Key elements include the definition of confidential information, obligations of receiving parties, duration of confidentiality, and exclusions such as publicly known information. Understanding these components ensures both parties safeguard sensitive data while clarifying rights and responsibilities compared to a Service Level Agreement, which primarily defines service expectations and performance metrics.
Key Differences Between SLAs and NDAs
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) define specific performance metrics and responsibilities between service providers and clients, focusing on the quality, availability, and reliability of services. Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) emphasize confidentiality obligations, ensuring that sensitive information shared between parties remains protected and undisclosed. While SLAs govern service delivery expectations, NDAs primarily safeguard proprietary or confidential information without addressing service performance.
Legal Implications: SLA vs NDA
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) differ significantly in legal implications; SLAs define the specific performance standards and remedies for breaches related to service delivery, while NDAs focus on protecting confidential information and imposing legal obligations to prevent unauthorized disclosure. Breach of an SLA can lead to financial penalties, service credits, or contract termination, whereas violating an NDA typically results in injunctions, damages for losses, and potential criminal liability depending on jurisdiction. Both agreements require precise drafting to clearly outline parties' responsibilities and legal consequences to ensure enforceability in courts.
When to Use a Service Level Agreement
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are essential when defining measurable performance standards for service delivery between providers and clients, ensuring accountability through specific metrics like uptime, response times, and support levels. SLAs are used in IT services, cloud computing, telecommunications, and outsourcing contracts where continuous service quality must be guaranteed and tracked. Unlike Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), which protect confidential information, SLAs focus solely on operational expectations and performance benchmarks.
When to Use a Non-Disclosure Agreement
A Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is crucial when sharing confidential information with clients, partners, or employees to protect trade secrets and proprietary data. Unlike Service Level Agreements (SLAs), which define performance standards and service expectations, NDAs are employed at the outset of a business relationship to ensure sensitive information remains private. Use an NDA whenever you need legal assurance that shared intellectual property or business insights will not be disclosed or misused.
Common Clauses in SLAs vs NDAs
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) commonly include clauses related to performance metrics, uptime guarantees, incident response times, and penalties for service failures. Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) focus on confidentiality obligations, definitions of confidential information, duration of the agreement, and exclusions from confidentiality. While SLAs emphasize service quality and accountability, NDAs prioritize protecting sensitive information and restricting unauthorized disclosures.
Benefits and Risks of SLAs Compared to NDAs
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) clearly define performance standards, response times, and responsibilities, ensuring measurable accountability and operational efficiency, whereas Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs) primarily protect confidential information without specifying service quality. SLAs benefit organizations by mitigating risks related to service failures or delays, while NDAs mainly shield proprietary data but do not address service delivery or penalties for non-performance. The risk of SLAs includes potential disputes over unmet service criteria, whereas NDAs carry risks related to insufficient protection or enforcement of confidentiality terms.
Choosing the Right Agreement for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right agreement depends on your business priorities: a Service Level Agreement (SLA) ensures clear performance standards and accountability between service providers and clients, while a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) protects sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure. Evaluate whether your primary concern is operational reliability or safeguarding proprietary data to determine the appropriate legal framework. Businesses often require both agreements to balance service quality with confidentiality in collaborative partnerships.
Service Level Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com