A value chain outlines every step a company takes to deliver a product or service, from raw materials to final distribution, enhancing efficiency and customer value. By analyzing each activity within the chain, businesses can identify cost-saving opportunities and improve competitive advantage. Discover how optimizing your value chain can elevate your business performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
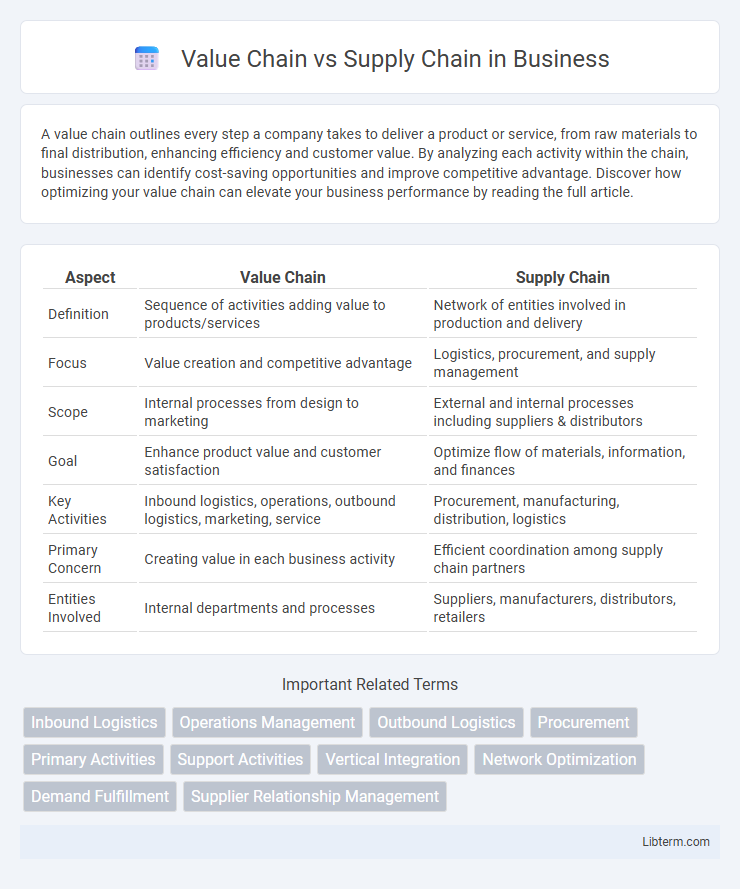
| Aspect | Value Chain | Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sequence of activities adding value to products/services | Network of entities involved in production and delivery |
| Focus | Value creation and competitive advantage | Logistics, procurement, and supply management |
| Scope | Internal processes from design to marketing | External and internal processes including suppliers & distributors |
| Goal | Enhance product value and customer satisfaction | Optimize flow of materials, information, and finances |
| Key Activities | Inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing, service | Procurement, manufacturing, distribution, logistics |
| Primary Concern | Creating value in each business activity | Efficient coordination among supply chain partners |
| Entities Involved | Internal departments and processes | Suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers |
Understanding the Concepts: Value Chain vs Supply Chain
The value chain encompasses all activities that create value for customers, from product design and production to marketing and after-sales service, emphasizing value addition at each step. The supply chain focuses on the efficient flow and logistics of materials, information, and finances from raw materials to end product delivery. Understanding the distinction helps businesses optimize operational efficiency (supply chain) while enhancing competitive advantage through value creation (value chain).
Key Differences Between Value Chain and Supply Chain
The value chain focuses on activities that add value to a product or service, encompassing everything from design to after-sales support, while the supply chain emphasizes the flow of goods and materials from suppliers to customers. Key differences include the value chain's emphasis on enhancing competitive advantage through value creation, compared to the supply chain's priority on efficient logistics and inventory management. Moreover, the value chain integrates internal processes with customer-centric strategies, whereas the supply chain primarily manages external partnerships and supplier relationships.
Core Components of a Value Chain
The core components of a value chain include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service, which collectively enhance product value and customer satisfaction. Each component focuses on adding value at different stages, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product. Understanding these elements clarifies the distinction from a supply chain, which primarily addresses the flow and management of goods and services.
Essential Elements of a Supply Chain
A supply chain encompasses the essential elements of sourcing raw materials, manufacturing processes, logistics, and distribution channels to efficiently deliver products to customers. Critical components include procurement, inventory management, transportation, and order fulfillment, all focused on minimizing costs and enhancing speed. Unlike the broader value chain, which emphasizes adding value at each stage, the supply chain prioritizes seamless coordination and operational efficiency across suppliers, manufacturers, and retailers.
Objectives: Value Creation vs Efficient Delivery
Value Chain focuses on value creation by enhancing product quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction through activities like design, production, and marketing. Supply Chain prioritizes efficient delivery by optimizing logistics, inventory management, and procurement processes to reduce costs and improve speed. Both aim to enhance business performance but differ in targeting value addition versus operational efficiency.
Stakeholders Involved in Each Chain
The value chain primarily involves internal stakeholders such as company management, product development teams, marketing, and sales departments working collaboratively to enhance product value and customer satisfaction. In contrast, the supply chain encompasses a broader range of external stakeholders including suppliers, manufacturers, logistics providers, distributors, and retailers, all coordinating to ensure the efficient flow of goods from production to end consumers. Understanding the distinct roles of these stakeholders clarifies how value creation and product delivery are managed differently within each chain.
Integration and Coordination Strategies
Value chain integration emphasizes aligning internal activities such as inbound logistics, operations, and marketing to maximize value creation and competitive advantage. Supply chain coordination focuses on synchronizing external partners, including suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors, to optimize inventory levels, reduce lead times, and enhance responsiveness. Effective strategies in both systems involve information sharing, collaborative planning, and technology adoption like ERP and SCM software to streamline processes and improve overall efficiency.
Impact of Technology on Both Chains
Technology enhances the efficiency of both value chains and supply chains by enabling real-time data analytics, automation, and improved communication across all stages. In value chains, digital tools optimize product development, customer engagement, and after-sales service, boosting overall value creation. Supply chains benefit from technologies such as IoT, blockchain, and AI-driven forecasting to reduce costs, increase transparency, and improve inventory management.
Measuring Performance: Metrics and KPIs
Measuring performance in value chains emphasizes KPIs such as value added per activity, customer satisfaction, and innovation rate, highlighting how each step contributes to overall value creation. Supply chain performance metrics focus on efficiency indicators like order fulfillment cycle time, inventory turnover, and supply chain cost as a percentage of sales, reflecting operational effectiveness. Integrating both sets of metrics provides a comprehensive view of organizational performance, balancing value enhancement with operational efficiency.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business
Selecting between a value chain and supply chain approach hinges on your business goals: value chain emphasizes creating competitive advantage through activities that add customer value, while supply chain prioritizes efficient flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. Businesses focused on innovation and differentiation benefit from analyzing value chain activities like design, marketing, and after-sale services. In contrast, companies aiming to reduce costs and improve delivery timelines should prioritize supply chain optimization strategies such as inventory management, logistics, and procurement.
Value Chain Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com