Onshoring involves relocating business processes or manufacturing back to the company's home country to reduce costs and improve supply chain reliability. This strategic move enhances quality control and supports local economies while minimizing risks associated with global disruptions. Discover how onshoring can transform Your operations by exploring the detailed benefits and challenges in the full article.
Table of Comparison
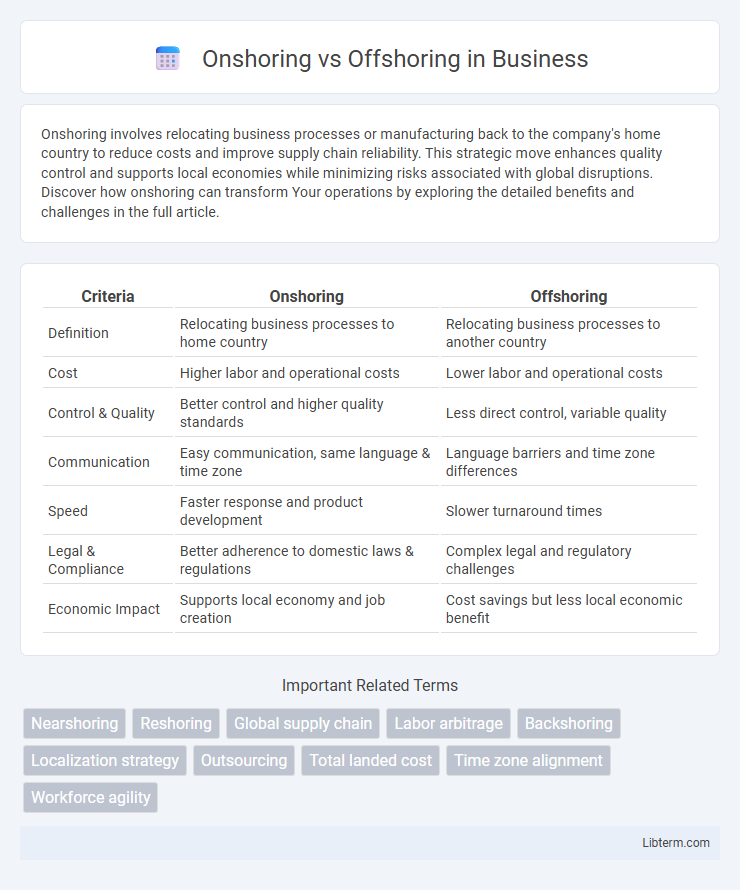
| Criteria | Onshoring | Offshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating business processes to home country | Relocating business processes to another country |
| Cost | Higher labor and operational costs | Lower labor and operational costs |
| Control & Quality | Better control and higher quality standards | Less direct control, variable quality |
| Communication | Easy communication, same language & time zone | Language barriers and time zone differences |
| Speed | Faster response and product development | Slower turnaround times |
| Legal & Compliance | Better adherence to domestic laws & regulations | Complex legal and regulatory challenges |
| Economic Impact | Supports local economy and job creation | Cost savings but less local economic benefit |
Introduction to Onshoring and Offshoring
Onshoring involves relocating business processes or manufacturing back to the company's home country, enhancing control, reducing shipping costs, and improving supply chain resilience. Offshoring refers to transferring operations to foreign countries to capitalize on lower labor costs, tax advantages, and access to emerging markets. Businesses evaluate onshoring and offshoring strategies based on factors such as cost efficiency, quality control, and geopolitical stability to optimize global operations.
Defining Onshoring and Offshoring
Onshoring refers to relocating business operations or services back to the company's home country to improve control, quality, and responsiveness. Offshoring involves transferring business processes or manufacturing to foreign countries to leverage cost advantages and access specialized skills. Both strategies impact supply chain efficiency, labor costs, and regulatory compliance.
Key Differences Between Onshoring and Offshoring
Onshoring refers to relocating business operations within the company's home country, while offshoring involves moving processes to a foreign country to leverage cost advantages. Key differences include labor cost variations, with offshoring often offering lower wages, and communication challenges, as onshoring benefits from closer cultural and time zone alignment. Risk factors such as geopolitical stability and quality control generally favor onshoring, whereas offshoring prioritizes economic efficiency and scalability.
Advantages of Onshoring
Onshoring offers significant advantages such as enhanced communication and collaboration due to geographic proximity, which reduces language barriers and cultural misunderstandings. It boosts local economies by creating jobs and supporting domestic suppliers, while also improving supply chain reliability and reducing shipping costs and delays. Companies benefit from better quality control and faster response times, enabling more agile and flexible production processes.
Benefits of Offshoring
Offshoring offers significant cost savings by leveraging lower labor and operational expenses in foreign markets, enhancing overall profitability. It provides access to a diverse talent pool with specialized skills, enabling companies to scale operations efficiently. Moreover, offshoring supports 24/7 productivity through time zone advantages, accelerating project timelines and improving market responsiveness.
Challenges in Onshoring
Onshoring presents challenges such as higher labor costs compared to offshore locations, limited access to specialized skills, and potential supply chain disruptions due to local regulations or infrastructure constraints. Companies may also face increased expenses related to compliance with domestic labor laws and environmental standards. These factors can complicate efforts to achieve cost efficiency and operational scalability in onshore manufacturing or service delivery.
Drawbacks of Offshoring
Offshoring often leads to challenges such as communication barriers, cultural differences, and time zone mismatches that can delay project timelines and reduce efficiency. Companies may face higher hidden costs due to quality control issues, intellectual property risks, and increased management oversight. Dependence on offshore suppliers also introduces political and economic instability risks that can disrupt supply chains and impact overall business continuity.
Cost Comparison: Onshoring vs Offshoring
Onshoring typically involves higher labor costs due to domestic wage standards, but it reduces expenses related to shipping, tariffs, and long supply chains. Offshoring can offer significant cost savings through lower labor rates and operational expenses in countries with cheaper manufacturing environments. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including quality control, lead times, and potential geopolitical risks, is essential for an accurate cost comparison.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Choosing between onshoring and offshoring requires evaluating factors such as cost efficiency, supply chain reliability, and market proximity. Businesses prioritizing quality control and local compliance often favor onshoring, while those aiming to reduce operational expenses may opt for offshoring. Analyzing industry-specific demands and long-term scalability ensures the chosen strategy aligns with organizational goals and competitive advantage.
Future Trends in Onshoring and Offshoring
Future trends in onshoring emphasize increased automation and the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies to boost local production efficiency. Offshoring is expected to evolve with the rise of digital platforms and artificial intelligence, enabling more streamlined global supply chain management and remote collaboration. Sustainability concerns and geopolitical shifts will drive companies to adopt hybrid strategies combining onshoring and offshoring for resilience and risk mitigation.
Onshoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com