HRMS, or Human Resource Management System, streamlines employee data management, payroll processing, and recruitment tasks, enhancing overall organizational efficiency. Integrating HRMS into your company allows for automated workflows and real-time analytics, reducing errors and saving valuable time. Discover how implementing a robust HRMS can transform your Human Resources operations in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
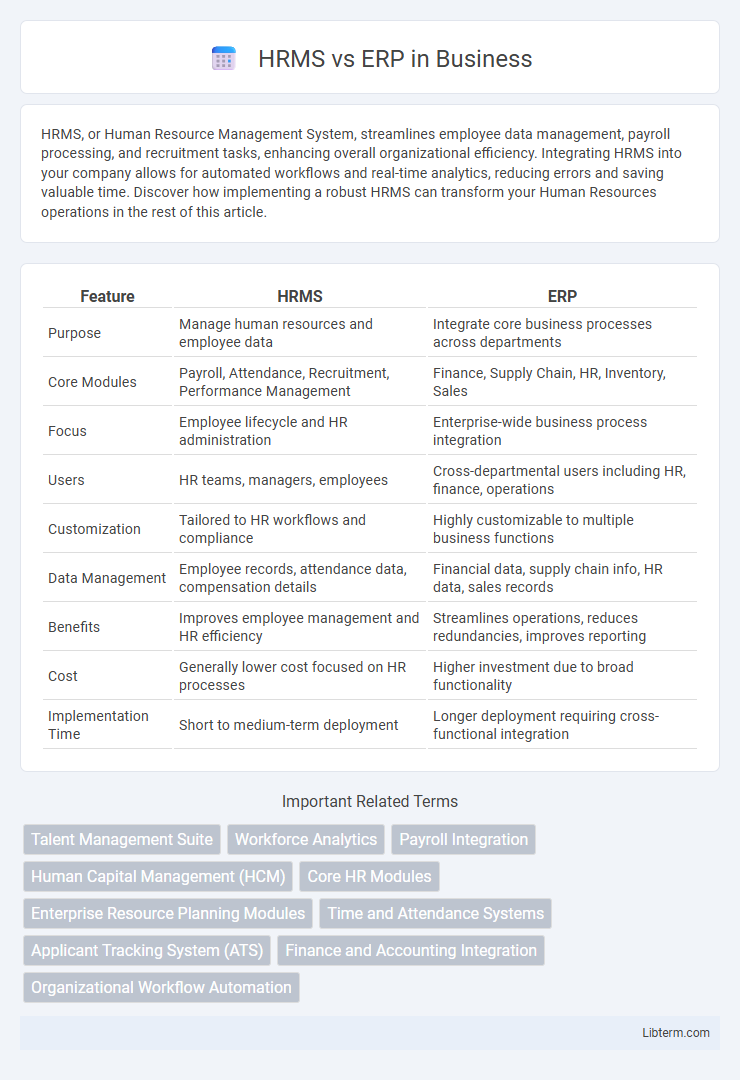
| Feature | HRMS | ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manage human resources and employee data | Integrate core business processes across departments |
| Core Modules | Payroll, Attendance, Recruitment, Performance Management | Finance, Supply Chain, HR, Inventory, Sales |
| Focus | Employee lifecycle and HR administration | Enterprise-wide business process integration |
| Users | HR teams, managers, employees | Cross-departmental users including HR, finance, operations |
| Customization | Tailored to HR workflows and compliance | Highly customizable to multiple business functions |
| Data Management | Employee records, attendance data, compensation details | Financial data, supply chain info, HR data, sales records |
| Benefits | Improves employee management and HR efficiency | Streamlines operations, reduces redundancies, improves reporting |
| Cost | Generally lower cost focused on HR processes | Higher investment due to broad functionality |
| Implementation Time | Short to medium-term deployment | Longer deployment requiring cross-functional integration |
Introduction to HRMS and ERP
HRMS (Human Resource Management System) is designed to streamline and automate HR functions such as payroll, recruitment, performance management, and employee data management. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) integrates core business processes including finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and HRMS into a unified system to enhance organizational efficiency. Both HRMS and ERP are essential software solutions that optimize business operations, with HRMS focusing specifically on human resources and ERP covering a broader range of enterprise activities.
Definition and Core Functions of HRMS
HRMS (Human Resource Management System) is specialized software designed to automate and streamline HR processes such as payroll, recruitment, employee attendance, performance evaluation, and benefits administration. Unlike ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), which integrates various business functions like finance, supply chain, and manufacturing, HRMS focuses exclusively on managing an organization's human capital efficiently. Core functions of HRMS include employee data management, talent acquisition, training and development, compliance tracking, and workforce analytics.
Overview and Key Features of ERP
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems integrate core business processes across finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and human resources into a unified platform, enabling real-time data visibility and process automation. Key features include financial management, inventory control, order processing, procurement, and reporting analytics, which streamline operations and improve decision-making. Unlike HRMS, which focuses primarily on workforce management functions such as payroll and talent acquisition, ERP systems offer broader organizational resource planning capabilities beyond human capital.
HRMS vs ERP: Primary Differences
HRMS (Human Resource Management System) focuses specifically on managing employee-related processes such as recruitment, payroll, attendance, and performance management, while ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) provides an integrated platform covering various business functions including finance, supply chain, and HR. HRMS is a specialized module that enhances human capital management, whereas ERP offers a broader scope encompassing multiple departments for streamlined organizational operations. The primary difference lies in HRMS's dedicated HR functionalities compared to ERP's comprehensive enterprise-wide resource integration.
Integration Capabilities: HRMS vs ERP
HRMS (Human Resource Management System) specializes in managing employee data, payroll, recruitment, and performance, offering integration primarily with payroll systems and time tracking tools. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) provides a comprehensive integration framework connecting HR functions with finance, supply chain, and customer relationship management modules, enabling seamless data flow across departments. The broader integration capabilities of ERP systems support end-to-end business process automation beyond HR-specific tasks, making them suitable for organizations seeking unified enterprise-wide solutions.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
HRMS offers higher scalability by allowing organizations to add or modify human resource functions independently, making it adaptable to changing workforce sizes and needs. ERP systems provide integrated scalability across various business functions but may require more complex customization to flex with specific HR demands. Flexibility in HRMS is enhanced through specialized modules tailored for recruiting, payroll, and performance management, while ERP flexibility depends on the extent of module integration and the vendor's configuration capabilities.
Cost Considerations: HRMS vs ERP
HRMS solutions typically incur lower implementation and maintenance costs compared to comprehensive ERP systems due to their specialized focus on human resource management functions. ERP systems involve higher upfront investment and ongoing expenses due to their extensive modules covering finance, supply chain, and operations alongside HR, demanding greater customization and integration efforts. Organizations should analyze total cost of ownership (TCO) including licensing fees, training, and scalability when deciding between HRMS and ERP for workforce management.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
HRMS implementation challenges often include data integration complexities, resistance to change, and customization difficulties, while ERP systems face hurdles such as high costs, extensive training requirements, and scalability issues. Effective solutions involve thorough planning, stakeholder engagement, and phased deployment to minimize disruptions. Leveraging cloud-based platforms and vendor support can enhance flexibility and streamline the integration process for both HRMS and ERP implementations.
Industry Use Cases for HRMS and ERP
HRMS (Human Resource Management System) is extensively used in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and retail to streamline employee management, payroll processing, and talent acquisition, improving workforce efficiency and compliance. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) integrates core business processes across finance, supply chain, inventory, and human resources, and is vital in sectors such as automotive, construction, and pharmaceuticals for enhancing operational visibility and resource planning. Companies leverage HRMS for specialized human capital management while ERP provides a comprehensive platform for enterprise-wide process automation and data centralization.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Choosing the right solution between HRMS and ERP depends on your business needs: HRMS specializes in optimizing human resources functions like payroll, recruitment, and employee management, while ERP integrates various business processes including finance, supply chain, and inventory. Businesses focused primarily on human capital management benefit from HRMS, which offers tailored features and automation for workforce productivity. Enterprises requiring comprehensive operational oversight with interconnected modules should opt for ERP to streamline processes and enhance data-driven decision-making.
HRMS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com