Venture capital is a form of private equity financing that provides startups and early-stage companies with the essential funds needed to scale and innovate. Investors take on significant risk in exchange for equity, aiming for high returns through the company's growth and eventual exit events like IPOs or acquisitions. Discover how venture capital can transform your business and the key factors to consider by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
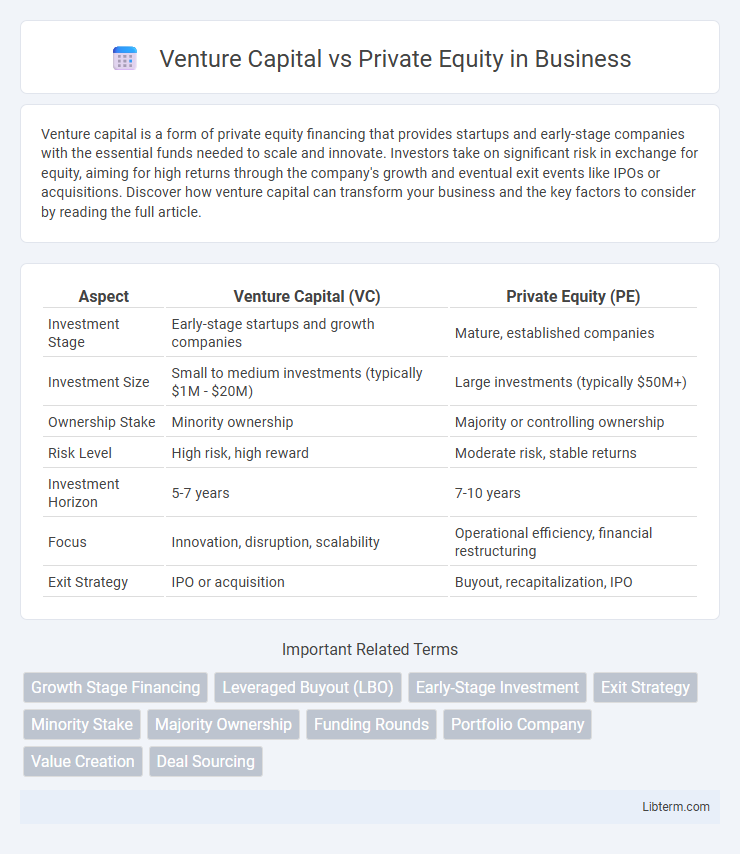
| Aspect | Venture Capital (VC) | Private Equity (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Investment Stage | Early-stage startups and growth companies | Mature, established companies |
| Investment Size | Small to medium investments (typically $1M - $20M) | Large investments (typically $50M+) |
| Ownership Stake | Minority ownership | Majority or controlling ownership |
| Risk Level | High risk, high reward | Moderate risk, stable returns |
| Investment Horizon | 5-7 years | 7-10 years |
| Focus | Innovation, disruption, scalability | Operational efficiency, financial restructuring |
| Exit Strategy | IPO or acquisition | Buyout, recapitalization, IPO |
Introduction to Venture Capital and Private Equity
Venture capital involves early-stage investments in startups and high-growth companies, providing capital in exchange for equity to fuel innovation and expansion. Private equity focuses on acquiring or investing in mature companies through buyouts, aiming to improve operations and increase value before eventual exit. Both asset classes offer distinct risk-reward profiles, with venture capital targeting high growth and private equity emphasizing operational improvements and stable returns.
Key Differences Between Venture Capital and Private Equity
Venture capital focuses on early-stage startups with high growth potential, investing in innovative companies to fuel expansion and product development. Private equity targets mature companies, often acquiring significant or controlling stakes to improve operations, restructure, or drive efficiency for long-term value creation. The investment horizon differs, with venture capital typically embracing higher risk and shorter timeframes, while private equity involves larger capital commitments and longer holding periods aimed at stable returns.
Investment Stages: VC vs PE
Venture capital (VC) typically invests in early-stage startups and emerging companies with high growth potential, providing seed or Series A funding to fuel innovation and expansion. Private equity (PE) focuses on more mature businesses, often acquiring majority stakes in established companies to restructure, optimize operations, and generate long-term value. VC investments carry higher risk but offer substantial upside, while PE investments prioritize stability and consistent returns through strategic management.
Fund Structures and Capital Sourcing
Venture capital funds typically operate as limited partnerships with a focus on early-stage investments, sourcing capital primarily from institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and family offices seeking high-growth potential startups. Private equity funds also use limited partnership structures but concentrate on later-stage companies, leveraging larger commitments from pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, and endowments to execute buyouts and restructuring strategies. Fundraising for venture capital emphasizes multiple smaller rounds aligned with startup growth phases, whereas private equity capital sourcing involves large, infrequent capital calls optimized for long-term asset management.
Target Companies: Startups vs Mature Businesses
Venture capital primarily targets early-stage startups with high growth potential, often in technology or innovative sectors seeking initial funding rounds. Private equity focuses on mature businesses with established cash flows, aiming to improve operations and increase profitability through buyouts or restructuring. These investment approaches differ significantly in risk profile, investment horizon, and involvement level with the target companies.
Risk Profiles and Return Expectations
Venture capital investments typically carry higher risk profiles due to their focus on early-stage startups with uncertain market potential, but they offer the possibility of outsized returns through exponential growth. Private equity targets more mature companies with established cash flows, presenting lower risk but generally delivering steadier, moderate returns through operational improvements and financial restructuring. Investors in venture capital accept significant volatility for the chance of substantial equity appreciation, whereas private equity investors prioritize capital preservation alongside consistent value creation.
Involvement in Portfolio Companies
Venture capital firms actively engage in the growth and development of early-stage startups, providing strategic guidance, operational support, and networking opportunities to accelerate innovation and market entry. Private equity firms typically take a more hands-on approach with mature companies, implementing financial restructuring, cost optimization, and governance improvements to maximize value and drive long-term profitability. Both types of investors play crucial roles in enhancing portfolio company performance, but venture capital emphasizes scaling potential, while private equity focuses on operational efficiency and exit strategies.
Exit Strategies: VC vs PE
Venture Capital exit strategies typically involve Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) or acquisitions by larger corporations, aiming for high-growth startups with scalable business models. Private Equity exits often rely on leveraged buyouts (LBOs), secondary sales, or recapitalizations, focusing on mature companies with stable cash flows. The timing and approach differ, as VCs seek rapid growth exits while PEs prioritize value extraction through operational improvements.
Pros and Cons for Entrepreneurs and Investors
Venture capital offers entrepreneurs rapid access to funding and strategic guidance but often requires sacrificing significant equity and control, posing risks of dilution and investor influence. Private equity provides investors opportunities to acquire substantial ownership stakes and implement operational improvements, though it involves high capital commitment and longer investment horizons with potential liquidity constraints. Entrepreneurs face trade-offs between growth acceleration with venture capital and stability with private equity, while investors must balance risk profiles, exit strategies, and return expectations in both asset classes.
Choosing Between Venture Capital and Private Equity
Choosing between venture capital and private equity depends on the stage and growth potential of the business seeking investment. Venture capital targets early-stage startups with high growth potential and innovation in technology or disruptive markets, while private equity firms typically invest in more mature companies requiring restructuring or capital for expansion. Evaluating the company's risk tolerance, growth objectives, and need for strategic guidance is critical in determining the best fit between venture capital and private equity funding sources.
Venture Capital Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com