Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) optimizes the entire lifecycle of a product from inception through design, manufacturing, and service to disposal. Integrating data, processes, and business systems, PLM enables your organization to enhance collaboration, improve product quality, and accelerate time to market. Explore the rest of the article to discover how implementing PLM can transform your product development strategy.
Table of Comparison
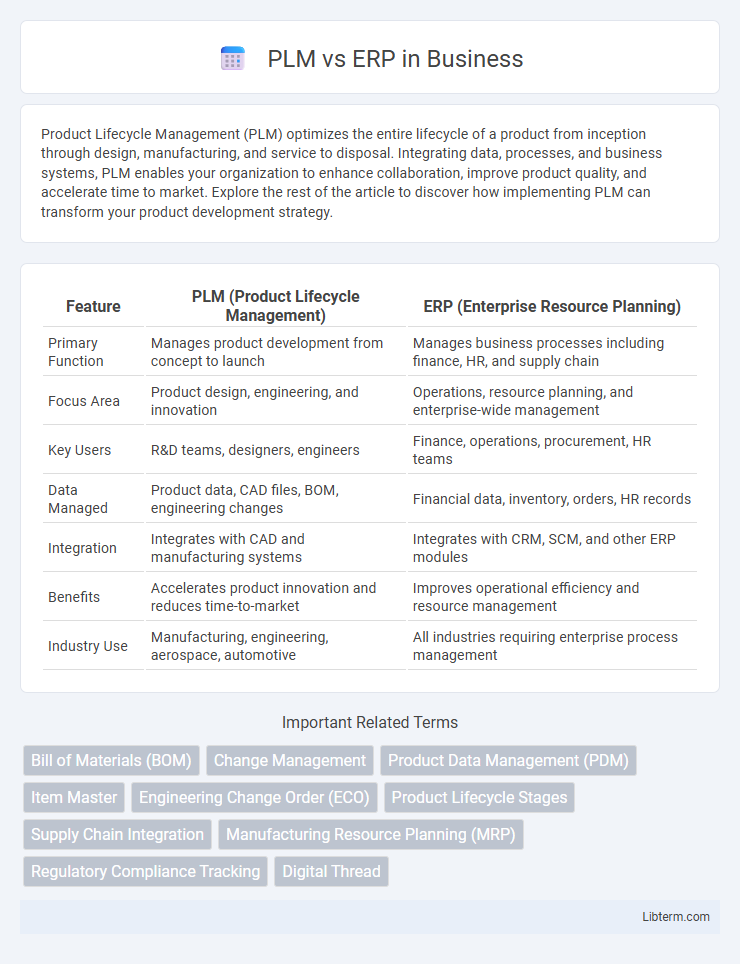
| Feature | PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) | ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages product development from concept to launch | Manages business processes including finance, HR, and supply chain |
| Focus Area | Product design, engineering, and innovation | Operations, resource planning, and enterprise-wide management |
| Key Users | R&D teams, designers, engineers | Finance, operations, procurement, HR teams |
| Data Managed | Product data, CAD files, BOM, engineering changes | Financial data, inventory, orders, HR records |
| Integration | Integrates with CAD and manufacturing systems | Integrates with CRM, SCM, and other ERP modules |
| Benefits | Accelerates product innovation and reduces time-to-market | Improves operational efficiency and resource management |
| Industry Use | Manufacturing, engineering, aerospace, automotive | All industries requiring enterprise process management |
Introduction to PLM and ERP
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems streamline the entire lifecycle of a product from conception, design, and manufacturing to service and disposal, emphasizing collaboration and innovation management. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems centralize core business processes such as finance, supply chain, human resources, and inventory management, providing real-time data for operational efficiency. Both PLM and ERP integrate critical enterprise functions but target different stages and aspects of product and business management to enhance overall organizational performance.
Defining PLM: Purpose and Core Functions
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is designed to manage the entire lifecycle of a product from inception, engineering design, and manufacturing to service and disposal. Core functions of PLM include product data management, collaboration across departments, change management, and compliance tracking, enabling efficient innovation and quality control. Unlike ERP systems that focus on resource planning and business operations, PLM centers on product development and engineering processes.
Understanding ERP: Objectives and Key Features
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are designed to integrate and manage core business processes such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and inventory management within a single unified platform. The primary objective of ERP is to streamline operations, improve data accuracy, and facilitate real-time decision-making by providing centralized access to critical organizational data. Key features of ERP include modular architecture, scalability, workflow automation, and comprehensive reporting capabilities that support cross-functional collaboration and operational efficiency.
Core Differences Between PLM and ERP
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) focuses on managing product data, design processes, and development workflows from concept to retirement, emphasizing innovation and collaboration. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) centers on integrating business processes such as finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and inventory management to optimize operational efficiency. Core differences include PLM's role in product ideation and version control versus ERP's function in resource planning, order processing, and enterprise-wide data consolidation.
How PLM and ERP Interact in Business Processes
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems interact by integrating product design and development data with manufacturing, supply chain, and financial operations, streamlining workflows from concept to production. PLM manages product-related information such as design specs, CAD files, and change management, while ERP handles inventory, procurement, order fulfillment, and accounting. This interaction ensures seamless data flow and alignment across departments, improving product quality, reducing time-to-market, and optimizing operational efficiency.
Benefits of Implementing PLM
Implementing Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) enhances collaboration across design, engineering, and manufacturing teams by centralizing product data and streamlining workflows. PLM reduces time-to-market and improves product quality through version control and real-time updates, which are often not as finely detailed in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. Unlike ERP, which focuses on resource planning and financial management, PLM provides specialized tools for innovation management and regulatory compliance, directly impacting product development efficiency.
Advantages of ERP Systems
ERP systems provide comprehensive integration of business processes, enabling real-time data visibility and enhanced decision-making across finance, supply chain, and human resources. They improve operational efficiency by automating routine tasks, reducing errors, and streamlining workflows within manufacturing and service industries. ERP solutions support scalability and regulatory compliance, making them essential for organizations seeking unified control and growth management.
When to Use PLM vs ERP
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) is ideal for managing product development, design iterations, and engineering processes, ensuring innovation and collaboration across the product lifecycle. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) excels in handling business operations such as inventory management, procurement, finance, and supply chain logistics, optimizing resource allocation and process efficiency. Use PLM when product data control and R&D collaboration are critical, while ERP is essential for operational execution and financial management.
Integration Challenges and Best Practices
Integration challenges between PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) often stem from data silos, differing data models, and inconsistent workflows, which can lead to errors and inefficiencies. Best practices for overcoming these issues include adopting standardized data exchange formats like XML or JSON, implementing middleware to synchronize data in real-time, and fostering cross-functional collaboration to align processes. Ensuring seamless integration enhances product development speed, improves data accuracy, and enables more informed decision-making across the enterprise.
Future Trends in PLM and ERP Solutions
Future trends in PLM focus on integrating AI-driven analytics to enhance product lifecycle visibility and predictive maintenance, while ERP solutions increasingly incorporate cloud-based platforms to improve scalability and real-time enterprise resource management. Advanced IoT integration in PLM drives smarter product development cycles by leveraging sensor data, whereas ERP systems evolve with blockchain technology to ensure data security and transparency across supply chains. The convergence of PLM and ERP through unified digital threads enables seamless collaboration and faster innovation cycles, transforming manufacturing and business operations for Industry 4.0.
PLM Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com