Franchise business models offer entrepreneurs a proven path to success by leveraging established brand recognition and support systems. Understanding the legal, financial, and operational aspects is crucial to maximize your return on investment. Explore the article to discover key insights that will guide you in choosing the right franchise opportunity.
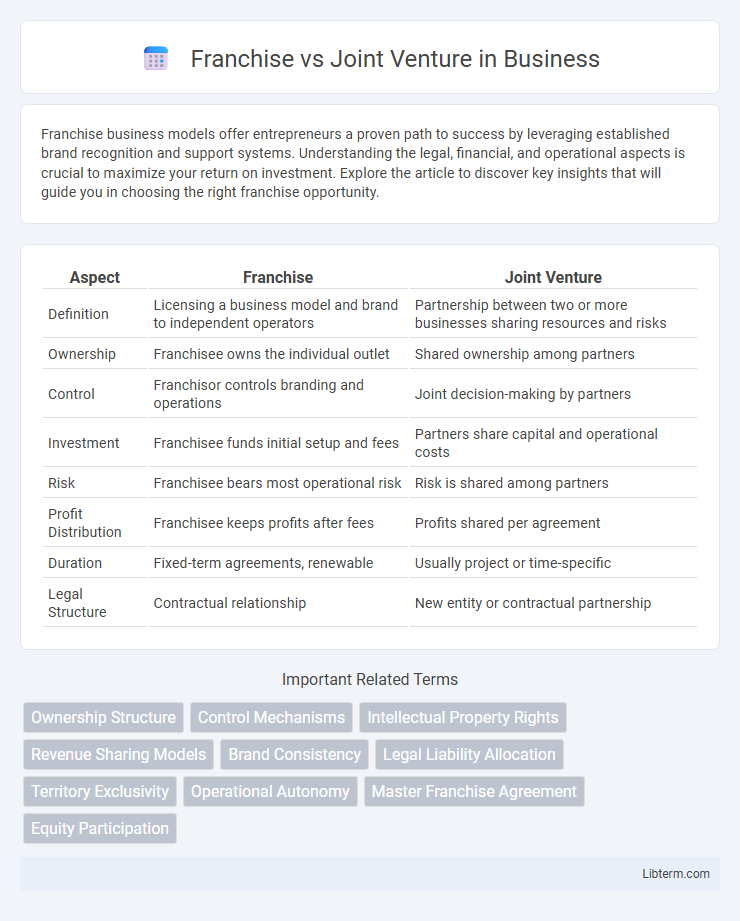
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Franchise | Joint Venture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Licensing a business model and brand to independent operators | Partnership between two or more businesses sharing resources and risks |
| Ownership | Franchisee owns the individual outlet | Shared ownership among partners |
| Control | Franchisor controls branding and operations | Joint decision-making by partners |
| Investment | Franchisee funds initial setup and fees | Partners share capital and operational costs |
| Risk | Franchisee bears most operational risk | Risk is shared among partners |
| Profit Distribution | Franchisee keeps profits after fees | Profits shared per agreement |
| Duration | Fixed-term agreements, renewable | Usually project or time-specific |
| Legal Structure | Contractual relationship | New entity or contractual partnership |
Understanding Franchise and Joint Venture Models
Franchise models involve a franchisor granting a franchisee the rights to operate a business using the franchisor's brand, products, and systems, ensuring consistent quality and brand recognition across locations. Joint ventures create a new, jointly owned entity where two or more parties share resources, risks, and profits while combining expertise to achieve specific business goals. Understanding these models helps businesses choose between brand-driven expansion with controlled operations (franchise) or collaborative partnerships with shared decision-making (joint venture).
Key Differences Between Franchise and Joint Venture
Franchises operate under a licensing model where the franchisee uses the franchisor's brand, business model, and support system in exchange for fees and royalties, while joint ventures involve two or more parties pooling resources to create a new business entity with shared ownership and risks. Franchisees maintain operational control within the franchisor's guidelines, whereas joint venture partners share decision-making authority and profits based on their investment. The franchise model emphasizes brand consistency and standardized operations, contrasting with joint ventures that prioritize collaboration and resource integration for mutual benefit.
Legal Structures: Franchise vs Joint Venture
Franchise legal structures involve a franchisor granting a franchisee the right to operate under its established brand and business model, typically governed by a franchise agreement outlining fees, territorial rights, and operational standards. Joint ventures, on the other hand, create a new legal entity owned jointly by two or more parties who share profits, losses, and management responsibilities according to a joint venture agreement. Franchise agreements emphasize brand consistency and control, while joint venture contracts focus on partnership terms, capital contribution, and shared governance.
Investment and Financial Commitments
Franchise models typically require lower initial investment and ongoing royalty fees, allowing franchisees to leverage established brand recognition while maintaining financial flexibility. Joint ventures demand higher capital contributions as partners share equity, risks, and profits, leading to deeper financial commitments and more complex investment structures. Understanding the scale of investment and financial obligations is crucial when choosing between franchising's lower-cost entry and joint ventures' shared ownership model.
Control and Decision-Making Authority
Franchise agreements grant the franchisor significant control over the brand standards, operational guidelines, and marketing strategies while allowing the franchisee limited autonomy in day-to-day management. In joint ventures, control and decision-making authority are typically shared or negotiated between partners, with both entities actively involved in operational and strategic decisions based on their equity stake or contractual terms. The level of control in joint ventures varies depending on the partnership structure, unlike franchising where the franchisor maintains primary authority.
Operational Responsibilities and Support
Franchise agreements typically delegate daily operational responsibilities to the franchisee, while the franchisor provides systematic support, including brand guidelines, training, and marketing resources to ensure consistency. In joint ventures, operational responsibilities are shared or divided based on the partnership agreement, requiring collaborative management and decision-making between partners. Franchise models emphasize standardized operations with individual ownership, whereas joint ventures involve collective control and resource sharing to achieve mutual business goals.
Brand Ownership and Intellectual Property
Franchise agreements grant the franchisee the right to operate using the franchisor's brand, trademarks, and intellectual property while ownership remains with the franchisor. In joint ventures, both parties typically share ownership and control over brand assets and intellectual property developed collaboratively. This fundamental difference impacts legal responsibilities, brand consistency, and the management of proprietary technologies or trade secrets.
Profit Sharing and Revenue Models
Franchise agreements typically involve royalty-based revenue models where the franchisor earns a percentage of the franchisee's sales, ensuring steady profit sharing aligned with performance. Joint ventures operate on shared investment and risk principles, with profits distributed based on predefined equity stakes, fostering collaborative revenue generation. The franchise model emphasizes ongoing fees and brand leverage, while joint ventures focus on mutual capital contribution and direct profit sharing from combined business activities.
Risk Assessment and Liability
Franchise agreements typically limit the franchisor's liability, placing most operational risks on the franchisee, who must adhere to strict guidelines but retains financial and legal responsibility. Joint ventures involve shared risks and liabilities between partners based on the equity and contractual terms, often resulting in higher exposure due to mutual obligations and joint decision-making. Risk assessment in franchises emphasizes brand protection and franchisee compliance, whereas joint ventures require detailed evaluation of partner reliability, financial commitments, and potential disputes.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a franchise and a joint venture requires evaluating control preferences, financial investment, and risk tolerance. Franchises offer a proven business model with brand consistency and lower capital risk, while joint ventures provide shared ownership, decision-making, and profit potential. Consider the desired level of operational control, market entry speed, and long-term growth objectives to select the best partnership structure.
Franchise Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com