Effective sales strategies drive business growth by focusing on understanding customer needs and building strong relationships. Tailoring your approach to highlight the unique value of your product or service can significantly boost conversion rates and customer loyalty. Discover proven techniques to enhance your sales performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
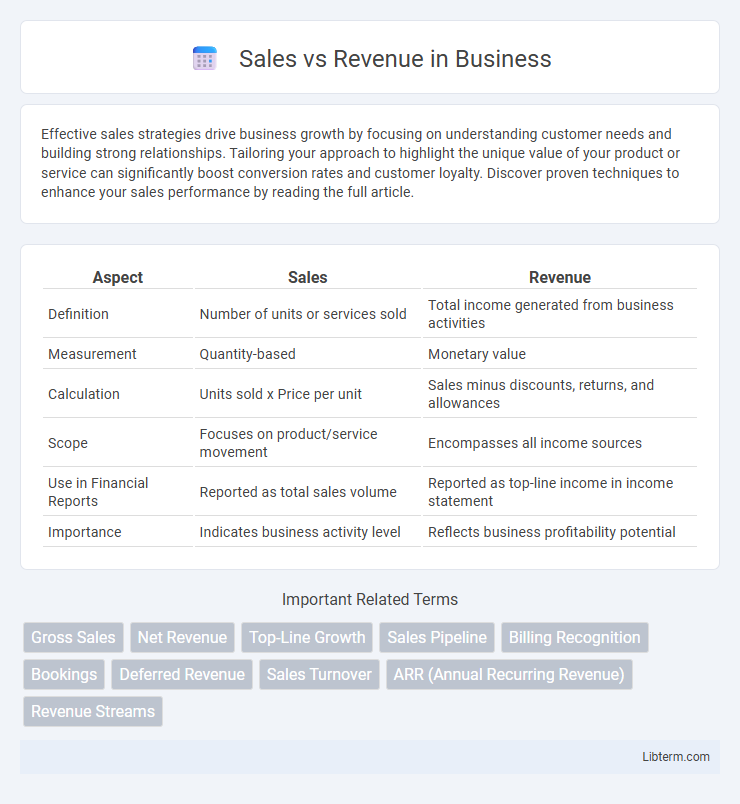
| Aspect | Sales | Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Number of units or services sold | Total income generated from business activities |
| Measurement | Quantity-based | Monetary value |
| Calculation | Units sold x Price per unit | Sales minus discounts, returns, and allowances |
| Scope | Focuses on product/service movement | Encompasses all income sources |
| Use in Financial Reports | Reported as total sales volume | Reported as top-line income in income statement |
| Importance | Indicates business activity level | Reflects business profitability potential |
Understanding Sales and Revenue: Key Definitions
Sales refer to the total value of goods or services sold by a company within a specific period, representing the primary source of income. Revenue encompasses all income generated from business activities, including sales, service fees, and other financial gains. Understanding the distinction helps businesses analyze financial performance accurately and optimize growth strategies.
Sales vs Revenue: What’s the Main Difference?
Sales represent the total amount earned from selling goods or services before any deductions, while revenue encompasses all income streams, including sales, interest, and other business activities. The main difference lies in scope; sales are a subset of revenue, specifically tied to core business operations. Understanding this distinction helps in analyzing financial statements and assessing overall business performance.
How Sales Drive Revenue Growth
Sales directly contribute to revenue growth by converting customer demand into monetary transactions, increasing the company's top-line income. Effective sales strategies boost product or service uptake, enhancing cash flow and market share simultaneously. High-performing sales teams identify new opportunities and upsell existing clients, propelling sustained revenue expansion.
Common Sources of Revenue Beyond Sales
Sales generate revenue through the direct exchange of goods or services for payment, but revenue also includes income from sources such as interest, royalties, licensing fees, and rental income. Businesses often diversify their revenue streams by investing in assets, earning dividends, or monetizing intellectual property to supplement sales income. Understanding these common sources of revenue beyond sales helps companies optimize financial performance and maintain cash flow stability.
Key Metrics: Measuring Sales Performance
Sales performance is measured using key metrics such as total sales volume, average transaction value, and sales growth rate, which provide insights into the effectiveness of sales strategies. Revenue, often calculated as the product of sales volume and price, reflects the total income generated from business operations and is crucial for assessing profitability. Monitoring metrics like conversion rate, customer acquisition cost, and sales cycle length helps optimize sales efforts and enhance revenue generation.
Revenue Streams: Types and Examples
Revenue streams represent the diverse sources from which a business earns income, including product sales, subscription fees, licensing, and advertising. Sales revenue is just one component, primarily derived from direct transactions exchanging goods or services for money. Examples of other revenue streams include rental income from property, commission from third-party sales, and royalties from intellectual property usage.
Impact of Discounts and Returns on Sales vs Revenue
Discounts and returns significantly reduce reported sales figures, directly lowering the total transaction value recorded during a period. Revenue, however, accounts for net income after deducting these factors, providing a more accurate measure of actual earnings. Understanding the distinction between gross sales and net revenue is essential for assessing a company's financial health and profitability.
Sales Strategies to Increase Revenue
Effective sales strategies such as personalized outreach, value-based selling, and leveraging data analytics significantly boost revenue by converting leads into paying customers. Emphasizing customer relationship management (CRM) systems enhances sales pipeline visibility and optimizes follow-up processes, driving higher conversion rates. Implementing dynamic pricing and upselling techniques further maximizes average transaction value, directly increasing overall revenue.
Financial Reporting: Sales and Revenue on Income Statements
Sales represent the total amount generated from goods sold or services provided, while revenue encompasses all income streams, including sales, interest, and other operating income. On income statements, sales appear as the top line, reflecting core business activity, whereas revenue provides a broader measure of overall financial performance. Accurate differentiation between sales and revenue is crucial for stakeholders analyzing profitability, growth, and operational efficiency.
Sales and Revenue: Implications for Business Success
Sales represent the total transactions completed by a company, directly affecting cash flow and market presence, while revenue encompasses all income, including non-sales sources such as interest or investments. Understanding the distinction between sales and revenue is critical for evaluating business performance, financial health, and growth potential. Accurate analysis of sales patterns and comprehensive revenue reporting drives strategic decisions, optimizes resource allocation, and enhances long-term profitability.
Sales Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com