Solvency measures a company's ability to meet its long-term financial obligations, reflecting overall financial health and stability. Key indicators include the debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio, and cash flow analysis, which help assess the risk of bankruptcy or financial distress. Discover how understanding solvency can protect your investments and guide smarter financial decisions in the full article.
Table of Comparison
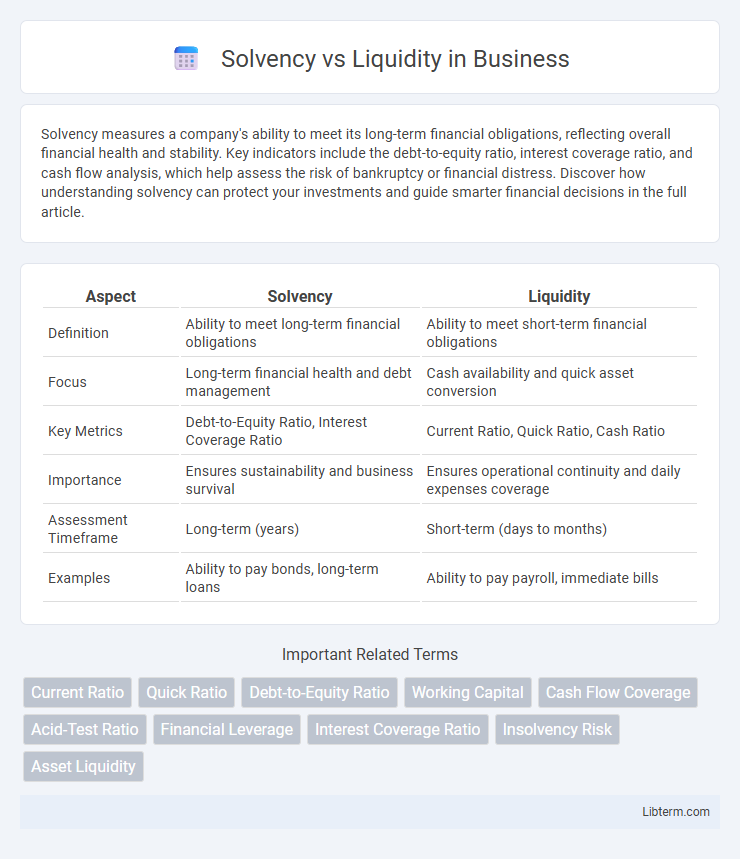
| Aspect | Solvency | Liquidity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to meet long-term financial obligations | Ability to meet short-term financial obligations |
| Focus | Long-term financial health and debt management | Cash availability and quick asset conversion |
| Key Metrics | Debt-to-Equity Ratio, Interest Coverage Ratio | Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, Cash Ratio |
| Importance | Ensures sustainability and business survival | Ensures operational continuity and daily expenses coverage |
| Assessment Timeframe | Long-term (years) | Short-term (days to months) |
| Examples | Ability to pay bonds, long-term loans | Ability to pay payroll, immediate bills |
Understanding Solvency and Liquidity
Solvency measures a company's ability to meet long-term debts and financial obligations, reflecting overall financial stability through assets exceeding liabilities. Liquidity assesses the ease with which a company can quickly convert assets to cash to cover short-term liabilities, crucial for day-to-day operational funding. Key financial ratios like the debt-to-equity ratio indicate solvency, while the current ratio and quick ratio directly evaluate liquidity status.
Key Differences Between Solvency and Liquidity
Solvency measures a company's ability to meet long-term obligations by comparing total assets to total liabilities, indicating financial health over time, while liquidity assesses short-term cash flow availability to cover immediate expenses and debts. Key differences include the focus on time frames, as solvency addresses long-term financial stability, whereas liquidity emphasizes the ability to quickly convert assets into cash. Solvency ratios like debt-to-equity and liquidity ratios such as current ratio or quick ratio provide distinct insights into financial performance and risk management.
Importance of Solvency in Financial Health
Solvency measures a company's ability to meet its long-term obligations and sustain operations over time, making it crucial for assessing financial stability and risk. High solvency ratios, such as debt-to-equity and interest coverage, indicate strong financial health and lower default risk, attracting investors and creditors. Insolvent businesses face bankruptcy and operational challenges, emphasizing solvency's role in ensuring business longevity and stakeholder confidence.
The Role of Liquidity in Business Operations
Liquidity plays a crucial role in business operations by ensuring that a company can meet its short-term financial obligations and maintain smooth day-to-day functions. High liquidity allows businesses to quickly convert assets into cash, facilitating payment of expenses such as payroll, suppliers, and debt servicing without disruption. Maintaining adequate liquidity safeguards against operational risks and supports sustained business continuity during periods of market volatility.
Common Ratios to Measure Solvency
Solvency indicates a company's ability to meet long-term obligations, often evaluated through ratios like the Debt-to-Equity Ratio, Debt Ratio, and Interest Coverage Ratio. The Debt-to-Equity Ratio compares total liabilities to shareholders' equity, highlighting financial leverage, while the Debt Ratio measures the proportion of total assets financed by debt. The Interest Coverage Ratio assesses how comfortably earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) can cover interest expenses, providing insight into debt service capability.
Key Metrics for Assessing Liquidity
Key metrics for assessing liquidity include the current ratio, quick ratio, and cash ratio, which measure a company's ability to meet short-term obligations. The current ratio compares current assets to current liabilities, indicating overall short-term financial health. The quick ratio excludes inventory from assets, providing a more stringent test of liquidity, while the cash ratio focuses solely on cash and cash equivalents against current liabilities.
Impact of Solvency on Long-Term Stability
Solvency directly impacts a company's long-term stability by ensuring its ability to meet long-term obligations and sustain operations through financial resilience. High solvency ratios indicate strong asset-to-debt balance, reducing bankruptcy risk and enabling strategic investments and growth. Poor solvency can lead to diminished credit ratings and increased borrowing costs, undermining investor confidence and operational continuity.
How Liquidity Affects Short-Term Obligations
Liquidity directly impacts a company's ability to meet short-term obligations by providing readily available cash or assets that can be quickly converted to cash. High liquidity ensures timely payment of bills, salaries, and other immediate expenses, preventing operational disruptions. Insufficient liquidity increases the risk of default, damaging creditworthiness and potentially leading to insolvency despite overall solvency.
Solvency vs Liquidity: Real-World Examples
Solvency and liquidity are critical financial metrics that assess a company's ability to meet long-term and short-term obligations respectively. For example, General Motors demonstrated strong solvency through steady asset growth and low debt ratios, while Tesla exhibited exceptional liquidity by maintaining high current ratios and cash reserves to cover immediate expenses. Companies like Sears faced solvency issues due to excessive long-term debt despite having moderate liquidity, highlighting the importance of balancing both financial health measures.
Strategies to Improve Solvency and Liquidity
Improving solvency involves strategies such as reducing debt levels, increasing equity financing, and optimizing asset management to ensure long-term financial stability. Enhancing liquidity can be achieved through better cash flow management, accelerating receivables, and maintaining a sufficient level of liquid assets or cash reserves. Companies often implement working capital optimization and debt refinancing to strengthen both solvency and liquidity positions simultaneously.
Solvency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com