Cost remains a critical factor in decision-making, influencing both consumer choices and business strategies. Understanding the hidden and explicit expenses can help optimize your budget and maximize value. Explore the rest of the article to uncover key insights about managing cost effectively.
Table of Comparison
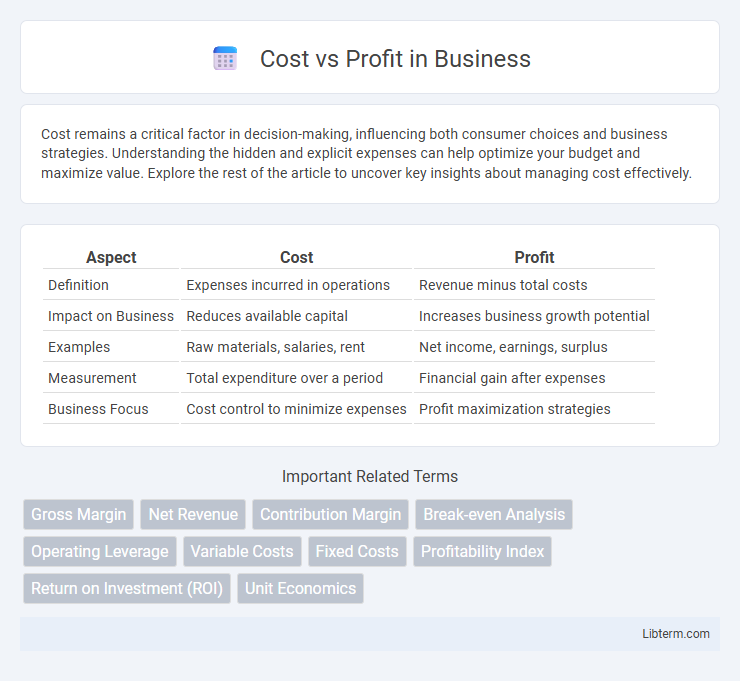
| Aspect | Cost | Profit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expenses incurred in operations | Revenue minus total costs |
| Impact on Business | Reduces available capital | Increases business growth potential |
| Examples | Raw materials, salaries, rent | Net income, earnings, surplus |
| Measurement | Total expenditure over a period | Financial gain after expenses |
| Business Focus | Cost control to minimize expenses | Profit maximization strategies |
Understanding Cost vs Profit: Key Concepts
Cost represents the total expenditure incurred in producing goods or services, including fixed and variable expenses, while profit is the financial gain achieved when revenue exceeds these costs. Understanding key concepts such as break-even point, gross profit margin, and net profit margin is essential for evaluating business performance and making informed financial decisions. Accurate cost analysis and profit calculation enable effective pricing strategies, resource allocation, and sustainable growth.
Types of Costs in Business Operations
Fixed costs such as rent, salaries, and insurance remain constant regardless of production levels, while variable costs like raw materials and direct labor fluctuate with output volume. Semi-variable or mixed costs contain both fixed and variable components, impacting overall profitability as operational activity changes. Understanding the distinction between these costs enables businesses to effectively manage expenses, optimize pricing strategies, and maximize profit margins.
How to Calculate Gross and Net Profit
Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue, highlighting the direct profitability of products or services. Net profit, also known as the bottom line, is derived by deducting all operating expenses, taxes, interest, and other costs from the gross profit. Understanding these calculations allows businesses to assess operational efficiency and overall financial health accurately.
The Impact of Cost Management on Profitability
Effective cost management directly enhances profitability by reducing unnecessary expenses and optimizing resource allocation. Identifying fixed and variable costs allows businesses to implement strategic budget controls, improving gross margins and net income. Companies that leverage advanced cost analysis tools gain a competitive advantage through increased operational efficiency and sustainable profit growth.
Fixed vs Variable Costs: Effects on Profit Margin
Fixed costs, such as rent and salaries, remain constant regardless of production volume, creating a baseline expense that impacts profit margins by limiting flexibility. Variable costs fluctuate with production levels, including materials and labor, directly affecting the cost per unit and overall profitability. Managing the balance between fixed and variable costs is crucial for optimizing profit margins and achieving sustainable financial performance.
Strategies to Reduce Costs and Increase Profits
Implementing lean manufacturing techniques significantly reduces production costs by minimizing waste and optimizing resource use. Strategic sourcing and negotiation with suppliers lower raw material expenses, enhancing profit margins. Leveraging technology for automation and data analytics improves operational efficiency, driving higher revenue while controlling costs effectively.
Case Studies: Cost vs Profit in Successful Businesses
Case studies of successful businesses illustrate how strategic cost management directly enhances profit margins, as seen in companies like Amazon, which optimized operational costs through technology and scale, resulting in increased profitability. Walmart's cost-saving supply chain innovations allowed for aggressive pricing strategies that boosted sales volumes and net profits. Lean manufacturing principles applied by Toyota demonstrate how reducing production costs while maintaining quality leads to sustained profit growth and competitive advantage.
Cost-Profit Analysis Tools and Techniques
Cost-profit analysis tools and techniques such as break-even analysis, marginal cost analysis, and activity-based costing provide crucial insights for businesses to optimize profitability. These methods enable precise allocation of expenses and identification of profit drivers by evaluating fixed and variable costs against revenue streams. Utilizing software like Excel models, cost accounting systems, and financial dashboards enhances decision-making by delivering real-time cost-profit data and scenario forecasting.
Common Mistakes in Balancing Cost and Profit
Common mistakes in balancing cost and profit include underestimating indirect expenses, which leads to inaccurate pricing and reduced profitability. Businesses often overlook variable costs, causing profit margins to shrink unexpectedly during sales fluctuations. Failing to regularly analyze cost structures and market trends results in missed opportunities for optimizing profit while controlling expenses.
Future Trends in Cost Optimization for Maximum Profit
Advanced cost optimization strategies leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning are revolutionizing profit maximization by enabling precise expense forecasting and dynamic resource allocation. The integration of predictive analytics with real-time financial monitoring tools allows organizations to identify cost-saving opportunities while maintaining operational efficiency. Sustainable practices and automation technologies are also driving future trends, reducing overhead while enhancing profitability in competitive markets.
Cost Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com