Sales volume measures the total quantity of products or services sold within a specific period, reflecting market demand and business performance. Tracking sales volume helps you identify trends, optimize inventory, and enhance revenue strategies effectively. Explore the full article to learn how to leverage sales volume data for your business growth.
Table of Comparison
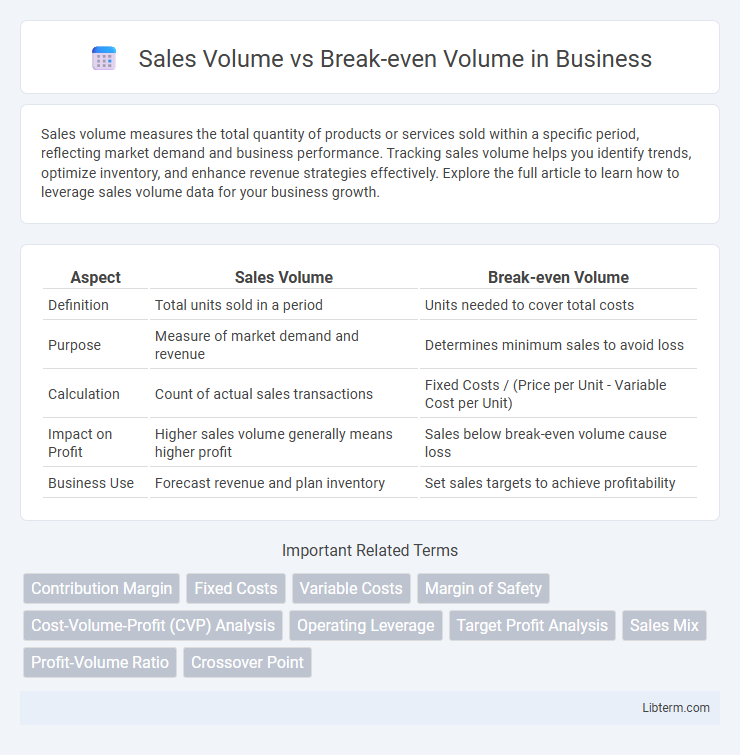
| Aspect | Sales Volume | Break-even Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total units sold in a period | Units needed to cover total costs |
| Purpose | Measure of market demand and revenue | Determines minimum sales to avoid loss |
| Calculation | Count of actual sales transactions | Fixed Costs / (Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit) |
| Impact on Profit | Higher sales volume generally means higher profit | Sales below break-even volume cause loss |
| Business Use | Forecast revenue and plan inventory | Set sales targets to achieve profitability |
Introduction to Sales Volume and Break-even Volume
Sales volume represents the total number of units sold by a business within a specific period, crucial for measuring market demand and revenue generation. Break-even volume is the number of units that must be sold to cover all fixed and variable costs, marking the point where total revenue equals total expenses. Understanding both metrics enables companies to set realistic sales targets and evaluate profitability thresholds effectively.
Defining Sales Volume
Sales volume refers to the total quantity of units sold by a business within a specific period, serving as a key metric to measure market demand and revenue generation. It directly impacts the company's profitability, as higher sales volume can lead to economies of scale and reduced per-unit costs. Understanding sales volume is essential for comparing against break-even volume, which is the minimum sales quantity required to cover all fixed and variable costs without incurring a loss.
Understanding Break-even Volume
Break-even volume represents the number of units that must be sold to cover all fixed and variable costs, ensuring no profit or loss. Understanding break-even volume helps businesses set sales targets and make informed pricing and production decisions. Accurately calculating this volume involves analyzing fixed costs, variable costs per unit, and the selling price per unit.
Importance of Analyzing Sales Volume
Analyzing sales volume is crucial for understanding a company's revenue generation and market demand, providing insights into how many units are sold within a specific period. This analysis helps businesses identify trends, optimize inventory, and set realistic sales targets that align with break-even volume--the minimum sales needed to cover fixed and variable costs. Accurate sales volume assessment enables strategic decision-making to enhance profitability and ensure sustainable growth beyond the break-even point.
The Break-even Point: What Does It Mean?
The break-even point is the sales volume at which total revenue equals total costs, resulting in zero profit or loss. It represents the minimum sales quantity a business must achieve to cover fixed and variable expenses, ensuring financial stability. Understanding the break-even volume helps companies set sales targets and pricing strategies to avoid losses and begin generating profit.
Key Differences: Sales Volume vs Break-even Volume
Sales volume refers to the total quantity of products or services sold within a specific period, indicating actual market demand and revenue generation. Break-even volume represents the minimum sales units required to cover all fixed and variable costs, marking the point where profit equals zero. Key differences include sales volume reflecting real performance, while break-even volume serves as a financial threshold for business viability and profitability analysis.
Factors Affecting Sales and Break-even Volumes
Sales volume and break-even volume are influenced by various factors including pricing strategies, production costs, and market demand. Changes in fixed and variable costs directly impact the break-even volume, while consumer preferences and competitive actions affect sales volume fluctuations. Accurate analysis of cost structures and market trends helps businesses optimize both sales performance and break-even points.
Calculating Break-even Volume: Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating break-even volume involves dividing fixed costs by the difference between unit selling price and variable cost per unit, which determines the minimum sales units needed to avoid losses. Start by accurately identifying all fixed costs, such as rent and salaries, and calculating variable costs per unit including materials and labor. This systematic approach enables businesses to set precise sales targets and effectively plan for profitability.
Impact of Sales Volume on Business Profitability
Sales volume directly influences business profitability by determining whether revenue covers fixed and variable costs, with break-even volume marking the threshold where total sales revenue equals total expenses. When sales volume exceeds the break-even volume, profit margins increase proportionally, enhancing financial stability and growth potential. Conversely, sales volumes below the break-even point result in losses, underscoring the critical need for businesses to monitor and optimize sales performance to sustain profitability.
Strategies to Increase Sales Volume Beyond Break-even
Increasing sales volume beyond the break-even point requires targeted marketing strategies such as enhancing product visibility through digital advertising and expanding distribution channels to reach a broader customer base. Implementing dynamic pricing models and offering promotional discounts can stimulate customer demand and encourage higher purchase frequency. Leveraging customer feedback to improve product quality and investing in brand loyalty programs also drive sustained sales growth beyond the break-even volume.
Sales Volume Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com