Business-to-Consumer (B2C) refers to transactions where businesses sell products or services directly to individual customers, focusing on delivering personalized experiences that meet consumer needs. Effective B2C strategies leverage digital marketing, user-friendly websites, and customer engagement to drive sales and brand loyalty. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your business can thrive in the competitive B2C landscape.
Table of Comparison
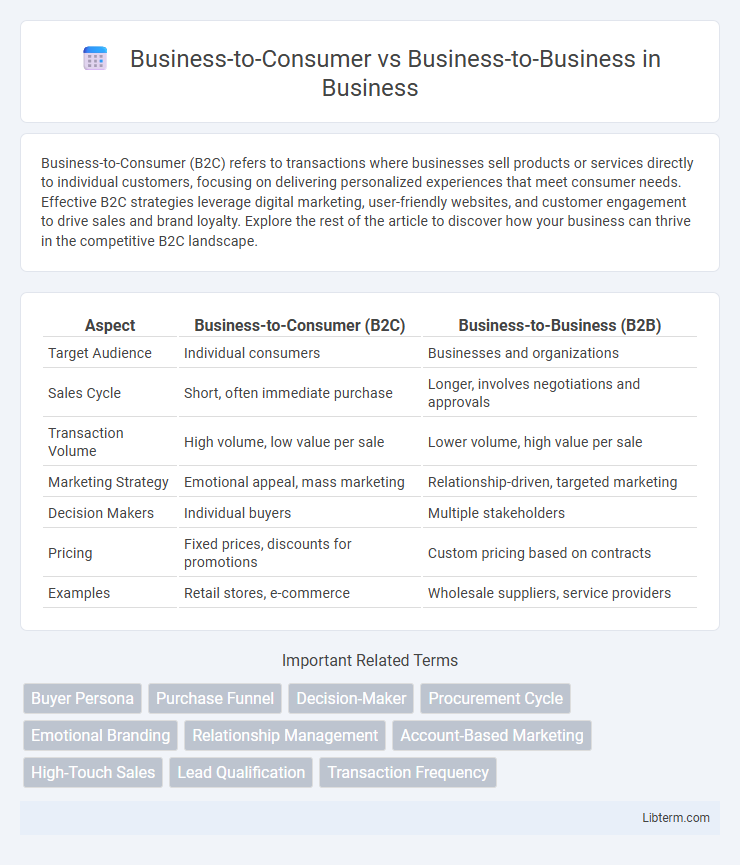
| Aspect | Business-to-Consumer (B2C) | Business-to-Business (B2B) |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Individual consumers | Businesses and organizations |
| Sales Cycle | Short, often immediate purchase | Longer, involves negotiations and approvals |
| Transaction Volume | High volume, low value per sale | Lower volume, high value per sale |
| Marketing Strategy | Emotional appeal, mass marketing | Relationship-driven, targeted marketing |
| Decision Makers | Individual buyers | Multiple stakeholders |
| Pricing | Fixed prices, discounts for promotions | Custom pricing based on contracts |
| Examples | Retail stores, e-commerce | Wholesale suppliers, service providers |
Understanding Business-to-Consumer (B2C) and Business-to-Business (B2B) Models
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) models focus on selling products or services directly to individual consumers, emphasizing user experience, brand engagement, and quick purchasing decisions. Business-to-Business (B2B) models involve transactions between companies where buying decisions are driven by efficiency, long-term relationships, and product customization. Understanding the distinct sales cycles, marketing strategies, and customer needs is essential for optimizing each model's performance and achieving targeted growth.
Key Differences Between B2C and B2B Markets
B2C markets target individual consumers with shorter sales cycles and emotion-driven purchasing decisions, emphasizing brand loyalty and user experience. B2B markets focus on organizational buyers with longer decision-making processes, detailed product specifications, and relationship-based sales strategies. Pricing structures in B2B often involve bulk orders and negotiated contracts, while B2C pricing is fixed and aimed at high-volume, low-value transactions.
Target Audience and Customer Relationships
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) targets individual consumers, emphasizing emotional appeal and personalized experiences to build customer loyalty. Business-to-Business (B2B) focuses on organizational clients, prioritizing long-term relationships, trust, and value-driven communication to support complex purchasing decisions. Understanding the distinct needs and decision-making processes of these target audiences is crucial for tailoring marketing strategies and customer relationship management.
Product Offerings and Customization
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) product offerings typically emphasize mass-produced, standardized goods designed for quick purchase and immediate use. In contrast, Business-to-Business (B2B) product offerings prioritize customization, scalability, and integration to meet specific organizational needs and industry requirements. B2B transactions often involve tailored solutions, such as bespoke software or adjustable machinery, ensuring alignment with client workflows and operational goals.
Sales Cycles and Purchasing Processes
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) sales cycles are typically shorter, often driven by individual emotions and immediate needs, with purchasing decisions made quickly and transactions completed via direct channels. In contrast, Business-to-Business (B2B) sales cycles are longer and more complex, involving multiple stakeholders, detailed evaluations, and formal approval processes before finalizing purchases. B2B procurement relies heavily on relationship building, contract negotiations, and customized solutions, while B2C focuses on streamlined online or retail experiences optimizing convenience and speed.
Marketing Strategies for B2C vs B2B
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) marketing strategies prioritize emotional engagement, broad outreach through social media channels, and personalized content to drive quick purchasing decisions. Business-to-Business (B2B) marketing focuses on relationship building, detailed product information, and longer sales cycles, leveraging content marketing, email campaigns, and industry-specific events. Data-driven targeting and customer journey mapping are essential in both B2C and B2B to optimize marketing ROI and conversion rates.
Pricing Structures and Negotiations
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) pricing structures are typically fixed and transparent, with standardized prices set to appeal to a broad customer base and facilitate quick purchasing decisions. In contrast, Business-to-Business (B2B) pricing often involves customized quotes, volume discounts, and negotiated terms based on long-term relationships and purchase commitments. B2B negotiations focus on contract flexibility, payment terms, and value-added services, while B2C transactions emphasize simplicity and immediate value.
Technology and Digital Transformation
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) leverages digital transformation primarily through personalized marketing, mobile commerce, and user-friendly interfaces, enhancing customer experience and engagement. Business-to-Business (B2B) emphasizes technology integration such as ERP systems, supply chain automation, and data analytics to streamline operations and improve collaboration. Both models rely on cloud computing, AI, and cybersecurity innovations to optimize efficiency and drive scalable growth in the digital economy.
Challenges Faced by B2C and B2B Businesses
B2C businesses face challenges such as high customer acquisition costs, rapidly changing consumer preferences, and intense competition in digital marketing channels. B2B companies struggle with longer sales cycles, complex decision-making processes, and maintaining strong relationships with fewer but larger clients. Both models require tailored strategies to address distinct operational and market demands effectively.
Future Trends in B2C and B2B Commerce
Future trends in B2C commerce emphasize personalization through AI-driven customer insights and seamless omnichannel experiences that integrate mobile, social media, and augmented reality shopping. B2B commerce is evolving with the adoption of advanced digital platforms, automation in supply chain management, and increased use of data analytics to optimize procurement and sales processes. Both sectors are moving towards greater sustainability and ethical sourcing, driven by consumer demand and regulatory pressures.
Business-to-Consumer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com