Second mover advantage allows companies to learn from the mistakes of first movers and improve their products or services while entering the market with reduced risk. By leveraging market insights and consumer feedback, second movers can refine strategies and gain competitive positioning more efficiently. Discover how understanding the second mover strategy can enhance your business approach in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
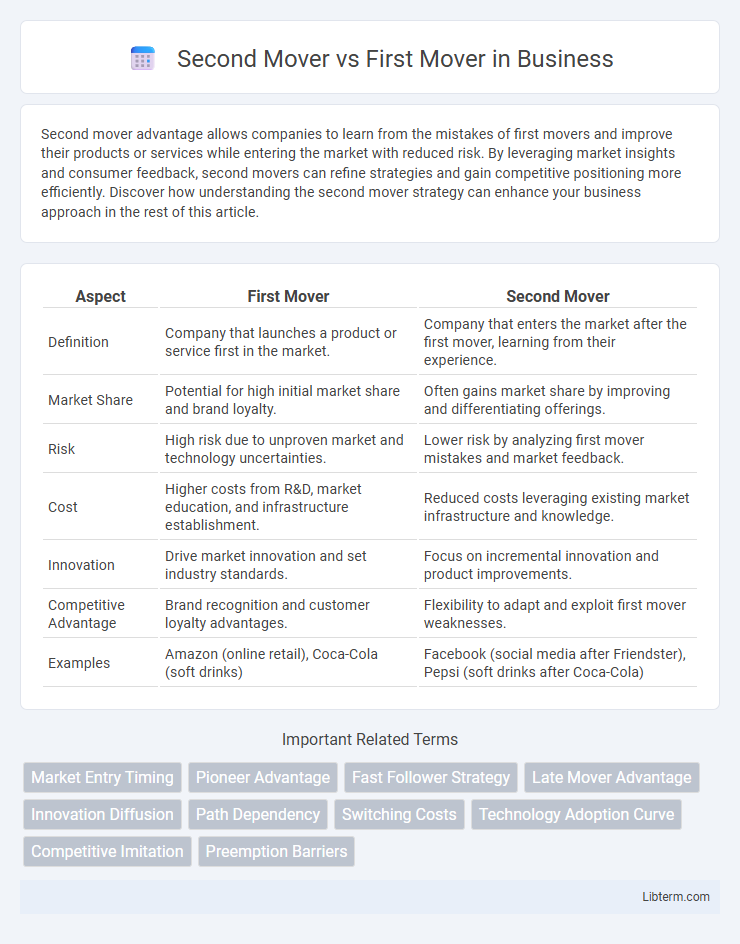
| Aspect | First Mover | Second Mover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Company that launches a product or service first in the market. | Company that enters the market after the first mover, learning from their experience. |
| Market Share | Potential for high initial market share and brand loyalty. | Often gains market share by improving and differentiating offerings. |
| Risk | High risk due to unproven market and technology uncertainties. | Lower risk by analyzing first mover mistakes and market feedback. |
| Cost | Higher costs from R&D, market education, and infrastructure establishment. | Reduced costs leveraging existing market infrastructure and knowledge. |
| Innovation | Drive market innovation and set industry standards. | Focus on incremental innovation and product improvements. |
| Competitive Advantage | Brand recognition and customer loyalty advantages. | Flexibility to adapt and exploit first mover weaknesses. |
| Examples | Amazon (online retail), Coca-Cola (soft drinks) | Facebook (social media after Friendster), Pepsi (soft drinks after Coca-Cola) |
Understanding First Mover Advantage
First mover advantage refers to the competitive edge gained by the initial entrant in a market, enabling brand recognition, customer loyalty, and control over scarce resources. Companies like Amazon and Apple exemplify how early entry can establish market dominance, technological leadership, and high switching costs for consumers. However, this advantage requires significant investment in innovation, market education, and risk management to maintain a sustainable lead over second movers.
Defining Second Mover Strategy
Second mover strategy leverages the advantages of observing and learning from the first mover's market entry, allowing companies to avoid early mistakes and optimize product offerings. By capitalizing on existing market demand and customer feedback, second movers can refine technology and improve cost efficiency, positioning themselves strategically for competitive gains. This approach focuses on agility and innovation to quickly adapt and capture market share while mitigating risks associated with pioneering new markets.
Key Benefits of Being a First Mover
First movers gain significant competitive advantages by establishing strong brand recognition and customer loyalty early in the market. They secure critical patents and control over scarce resources, creating high entry barriers for competitors. Early market entry also enables first movers to set industry standards and influence consumer preferences.
Advantages of the Second Mover Approach
The second mover approach leverages the ability to learn from the first mover's market mistakes, reducing risks and trial-and-error costs. Second movers benefit from improved technologies and refined business models, often capturing market share with enhanced products or services. Strategic timing allows second movers to capitalize on established customer needs while optimizing marketing and operational efficiency.
Common Risks Faced by First Movers
First movers often face substantial risks such as high research and development costs, market uncertainty, and the challenge of educating consumers on a new product. These pioneers must navigate untested technologies and regulatory environments that can delay market entry or increase expenses. Competitors, or second movers, may capitalize on the first mover's mistakes by improving product features and reducing costs, gaining a strategic advantage.
Challenges Encountered by Second Movers
Second movers face challenges including overcoming the market dominance established by first movers, which often benefits from brand recognition and customer loyalty. They must also invest significantly in research and development to improve upon or differentiate from the initial product while avoiding infringement issues. Second movers encounter higher switching costs among customers, making it difficult to capture market share despite potential technological advantages.
Case Studies: First Movers Who Succeeded
First movers such as Apple with the iPhone revolutionized the smartphone market by establishing strong brand loyalty and setting industry standards, securing a dominant market share. Amazon's early entry into e-commerce allowed it to build extensive distribution networks and customer data, creating significant barriers to entry for competitors. Tesla's pioneering efforts in electric vehicles resulted in groundbreaking innovations and a loyal customer base, making it a leader in the EV market despite later entrants.
Notable Successes of Second Movers
Second movers often capitalize on the pioneering efforts of first movers by improving product features, reducing costs, and exploiting market insights, leading to significant successes such as Facebook overtaking MySpace and Google surpassing Yahoo. These companies leverage the established market infrastructure and customer feedback to optimize their strategies and enhance user experience. The advantage of learning from early market entrants allows second movers to avoid initial pitfalls and innovate more efficiently, driving substantial competitive gains.
Factors Influencing Market Entry Timing
Market entry timing is influenced by factors such as technological innovation speed, market readiness, and competitive dynamics. First movers risk high costs and uncertainty but can capitalize on brand loyalty and market share dominance. Second movers benefit from observing first-mover mistakes, leveraging improved technologies, and adapting to established consumer preferences.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Business Growth
First movers secure early market dominance and brand loyalty but face high risks and significant costs of innovation. Second movers capitalize on the first movers' market insights, improving products and marketing strategies to capture market share effectively. Selecting the ideal strategy depends on competitive dynamics, resource availability, and the potential to leverage existing market knowledge for scalable growth.
Second Mover Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com