Variable cost refers to expenses that fluctuate directly with production volume, such as raw materials or labor. Understanding these costs is essential for managing Your business's profitability and pricing strategies. Explore the article to learn how variable costs impact financial planning and decision-making.
Table of Comparison
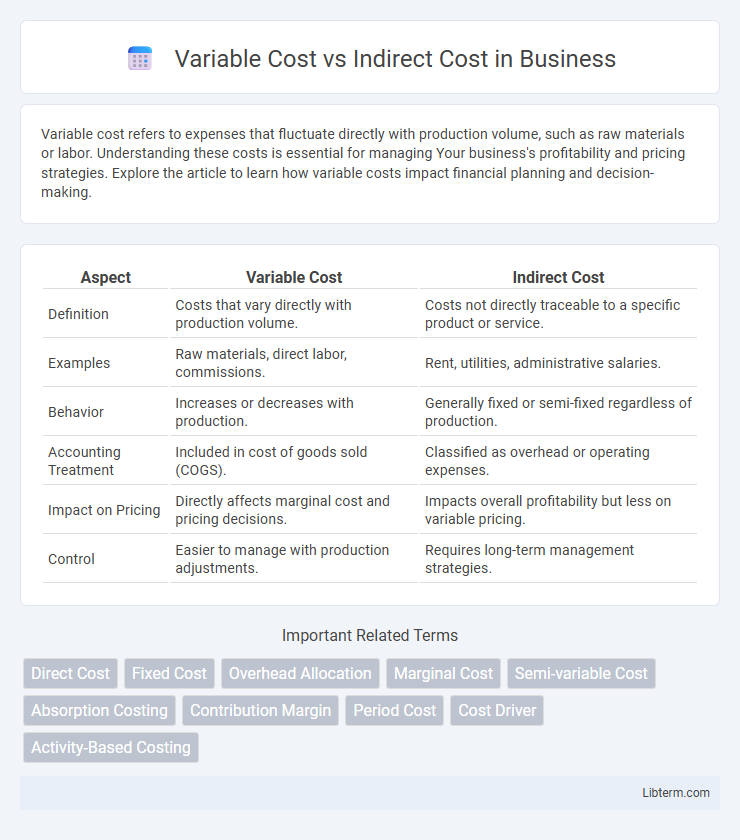
| Aspect | Variable Cost | Indirect Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Costs that vary directly with production volume. | Costs not directly traceable to a specific product or service. |
| Examples | Raw materials, direct labor, commissions. | Rent, utilities, administrative salaries. |
| Behavior | Increases or decreases with production. | Generally fixed or semi-fixed regardless of production. |
| Accounting Treatment | Included in cost of goods sold (COGS). | Classified as overhead or operating expenses. |
| Impact on Pricing | Directly affects marginal cost and pricing decisions. | Impacts overall profitability but less on variable pricing. |
| Control | Easier to manage with production adjustments. | Requires long-term management strategies. |
Understanding Variable Costs
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, encompassing expenses like raw materials, direct labor, and utilities tied to manufacturing processes. Understanding variable costs is crucial for accurate budgeting and forecasting, as they impact the cost of goods sold and overall profitability. Unlike indirect costs, which remain fixed regardless of output, variable costs provide insights into how production scale influences total expenses.
Defining Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are expenses not directly tied to a specific product or service but necessary for overall business operations, such as utilities, rent, and administrative salaries. These costs differ from variable costs, which fluctuate directly with production volume, whereas indirect costs typically remain fixed or only vary slightly regardless of output levels. Understanding indirect costs is essential for accurate product costing, budgeting, and financial analysis in any organization.
Key Differences Between Variable and Indirect Costs
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, such as raw materials and direct labor expenses, while indirect costs remain fixed regardless of output, including rent and administrative salaries. Variable costs are traceable to specific units of production, making them controllable in short-term operational decisions. Indirect costs support overall business functions and are allocated across departments, often requiring cost allocation methods for accurate financial reporting.
Examples of Variable Costs in Business
Variable costs in business include expenses that fluctuate directly with production volume, such as raw materials, direct labor, and utility costs tied to manufacturing processes. For example, a bakery's variable costs encompass flour, sugar, and wages for bakers paid per hour worked. These costs contrast with indirect costs like rent and administrative salaries, which remain constant regardless of output levels.
Common Types of Indirect Costs
Common types of indirect costs include utilities, rent, administrative salaries, depreciation, and office supplies, which cannot be directly traced to a specific product or service. Variable costs fluctuate with production volume, such as raw materials and direct labor, while indirect costs remain fixed or semi-variable regardless of output. Understanding the distinction aids accurate budgeting and cost allocation for businesses.
Cost Allocation Methods: Variable vs Indirect
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, making cost allocation straightforward by assigning expenses based on output levels. Indirect costs, such as overhead, are not directly traceable to specific products and require allocation methods like activity-based costing or predetermined overhead rates to distribute expenses accurately. Effective cost allocation distinguishes variable from indirect costs to ensure precise product costing and financial analysis.
Impact on Profit Margins and Pricing Strategies
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, impacting profit margins by increasing total expenses as output rises, which necessitates pricing strategies that cover these costs to maintain profitability. Indirect costs remain constant regardless of production levels, affecting overall fixed expenses and requiring pricing strategies that allocate these overhead costs appropriately to ensure sustainable profit margins. Understanding the balance between variable and indirect costs enables businesses to set prices that optimize profitability by accurately reflecting cost behavior and maintaining competitive advantage.
Variable and Indirect Costs in Financial Reporting
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, making them essential for accurate cost behavior analysis in financial reporting. Indirect costs, also known as overhead, cannot be directly traced to a single product but are allocated across multiple departments or products in the financial statements. Proper classification of variable and indirect costs ensures precise profit margin calculation and effective budgeting in managerial accounting.
Managing and Reducing Cost Structures
Variable costs fluctuate directly with production volume, making them a key target for cost management through process efficiency and resource optimization. Indirect costs, such as administrative expenses, require strategic allocation and continuous monitoring to identify waste and improve overhead control. Effective reduction of both cost types enhances overall cost structures, boosting profitability and operational agility.
Strategic Importance in Decision-Making
Variable costs directly fluctuate with production levels, making them crucial for pricing strategies and operational budgeting, while indirect costs remain fixed or semi-variable, influencing overhead allocation and long-term financial planning. Distinguishing between these cost types enhances cost control, profitability analysis, and resource allocation decisions, enabling managers to optimize efficiency and strategic investments. Accurate identification of variable and indirect costs supports break-even analysis and cost-volume-profit modeling, essential for informed decision-making and competitive advantage.
Variable Cost Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com