The Executive Board plays a crucial role in steering company strategy and making high-level decisions to ensure sustainable growth. Its members possess diverse expertise, enabling effective governance and oversight of operations that align with organizational goals. Discover how your involvement with the Executive Board can drive success by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
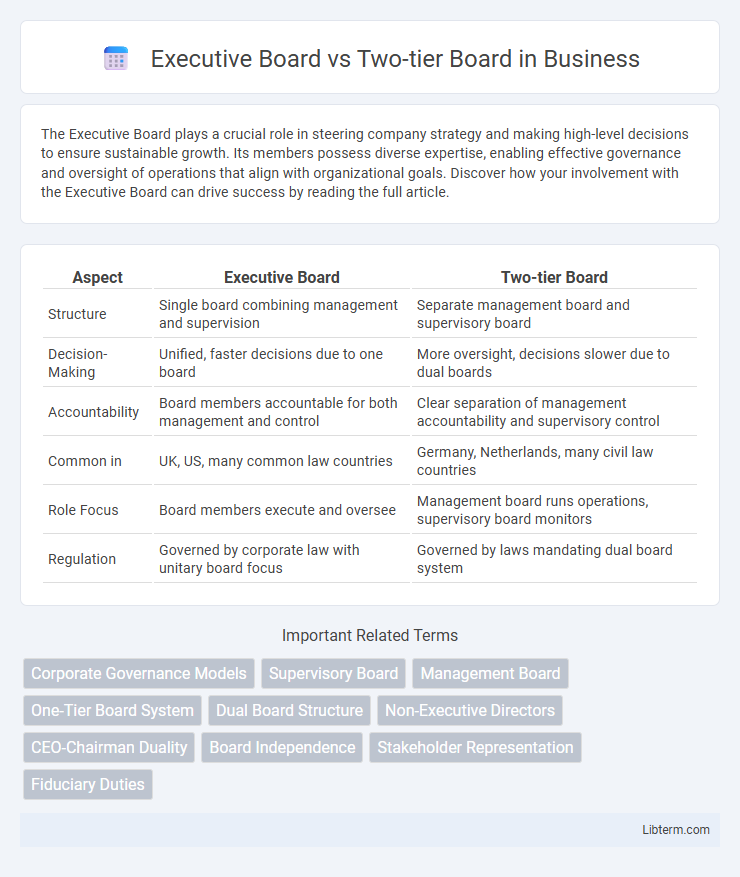
| Aspect | Executive Board | Two-tier Board |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single board combining management and supervision | Separate management board and supervisory board |
| Decision-Making | Unified, faster decisions due to one board | More oversight, decisions slower due to dual boards |
| Accountability | Board members accountable for both management and control | Clear separation of management accountability and supervisory control |
| Common in | UK, US, many common law countries | Germany, Netherlands, many civil law countries |
| Role Focus | Board members execute and oversee | Management board runs operations, supervisory board monitors |
| Regulation | Governed by corporate law with unitary board focus | Governed by laws mandating dual board system |
Introduction to Corporate Governance Structures
Corporate governance structures prominently feature Executive Boards and Two-tier Boards, each defining distinct roles and responsibilities in company management. Executive Boards integrate executive and supervisory functions within a single body, enhancing streamlined decision-making and operational control. Two-tier Boards separate these duties into a Management Board responsible for day-to-day operations and a Supervisory Board overseeing and monitoring the management, promoting checks and balances and accountability.
Defining the Executive Board Model
The Executive Board model consolidates management and oversight functions into a single board, combining executive directors responsible for daily operations with non-executive directors who provide supervision. This structure enhances decision-making efficiency by enabling faster communication and unified governance within the company. Predominantly used in Anglo-American corporate governance systems, the Executive Board model contrasts with the Two-tier Board by integrating roles rather than separating management from supervisory responsibilities.
Understanding the Two-Tier Board System
The two-tier board system separates management and supervisory functions into two distinct entities: the Management Board handles daily operations, while the Supervisory Board oversees and monitors management activities. This structure enhances corporate governance by providing independent oversight and reducing conflicts of interest between executives and shareholders. Common in countries like Germany and the Netherlands, the two-tier system contrasts with the executive board model, which combines both roles into a single board.
Key Differences Between Executive and Two-Tier Boards
Executive boards combine executive and non-executive directors into a single management body responsible for day-to-day decisions and strategic oversight. Two-tier boards separate supervisory and management functions, with a management board handling operations and a supervisory board overseeing compliance and long-term strategy. This structural distinction influences governance transparency, decision-making speed, and accountability mechanisms across corporate environments.
Roles and Responsibilities: Executive vs. Supervisory Functions
An Executive Board combines both management and oversight roles, where executives hold decision-making authority and are responsible for daily operations and strategic planning. In contrast, a Two-tier Board separates roles into an Executive Board handling management tasks and a Supervisory Board focused exclusively on monitoring, oversight, and ensuring compliance without engaging in day-to-day operations. This clear division in a Two-tier Board enhances accountability by distinctly separating executive functions from supervisory responsibilities.
Advantages of the Executive Board Structure
The Executive Board structure centralizes decision-making authority, enabling faster and more cohesive strategic actions by integrating management and oversight roles within a single board. This streamlined governance model enhances accountability and facilitates clearer communication between executives and directors. Companies benefit from reduced complexity and improved alignment of business objectives with operational execution under the Executive Board system.
Benefits and Drawbacks of the Two-Tier Board
The two-tier board system separates supervisory and management functions, enhancing oversight by allowing the supervisory board to focus solely on monitoring executive decisions. This structure can improve accountability and reduce conflicts of interest but may slow decision-making due to increased bureaucracy and coordination needs between the two boards. Companies may face challenges with communication inefficiencies and potential power struggles between supervisory and management boards, limiting agility in dynamic markets.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks Across Jurisdictions
Legal and regulatory frameworks governing Executive Boards and Two-tier Boards vary significantly across jurisdictions, with Executive Boards commonly found in Anglo-American systems under a unitary structure emphasizing centralized decision-making and fiduciary duties codified in corporate law. Two-tier Boards, prevalent in Germanic and some European civil law countries, enforce strict separation between management and supervisory functions, mandated by regulations such as Germany's Aktiengesetz and similar statutes ensuring employee representation and enhanced oversight. Compliance requirements under both structures impact governance transparency, liability allocation, and stakeholder engagement differently, reflecting contrasting statutory mandates and cultural norms.
Factors Influencing Board Structure Selection
Company size, regulatory environment, and corporate governance culture significantly influence the choice between an Executive Board and a Two-tier Board. Large corporations and firms in countries with stringent governance regulations often prefer Two-tier Boards for enhanced oversight through separate supervisory and management bodies. In contrast, smaller companies or those in jurisdictions with flexible governance codes tend to adopt Executive Boards for streamlined decision-making and direct management involvement.
Trends and Future Prospects in Board Governance
The trend towards executive boards emphasizes streamlined decision-making with combined supervisory and management functions, promoting agility in fast-changing markets. Two-tier boards, prevalent in European corporate governance, enhance oversight through clear separation between supervisory and management roles, catering to stakeholder accountability and long-term sustainability. Future prospects suggest hybrid models integrating executive agility with independent oversight are gaining traction, supported by regulatory shifts favoring transparency and stakeholder-inclusive governance.
Executive Board Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com