A joint venture combines the strengths and resources of two or more businesses to achieve a shared goal, often leading to increased market reach and innovation. By pooling expertise and capital, companies can tackle larger projects and reduce risks. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your business can benefit from forming a joint venture.
Table of Comparison
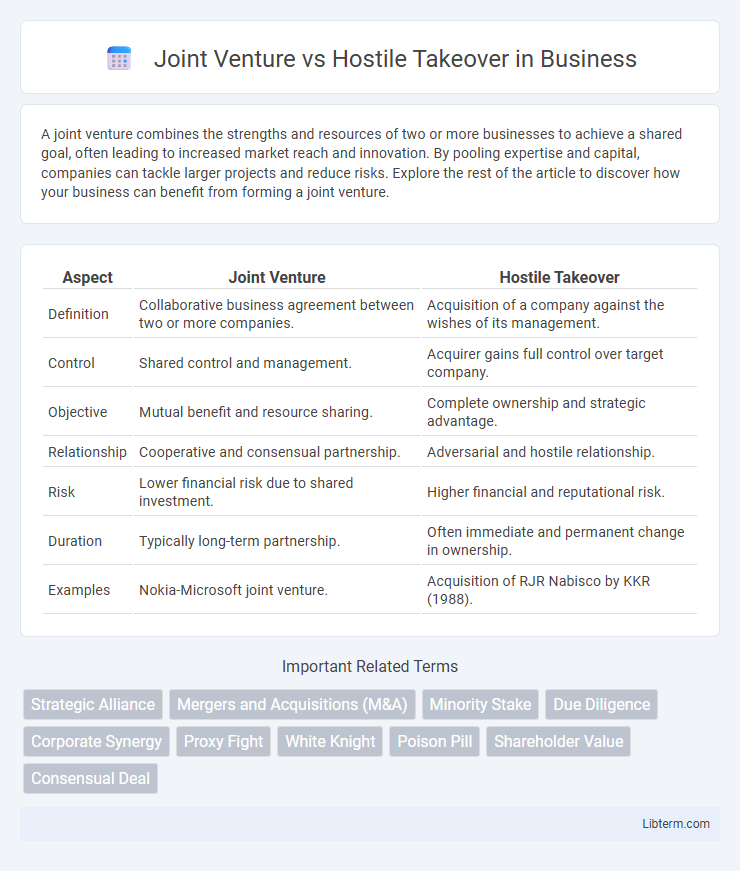
| Aspect | Joint Venture | Hostile Takeover |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative business agreement between two or more companies. | Acquisition of a company against the wishes of its management. |
| Control | Shared control and management. | Acquirer gains full control over target company. |
| Objective | Mutual benefit and resource sharing. | Complete ownership and strategic advantage. |
| Relationship | Cooperative and consensual partnership. | Adversarial and hostile relationship. |
| Risk | Lower financial risk due to shared investment. | Higher financial and reputational risk. |
| Duration | Typically long-term partnership. | Often immediate and permanent change in ownership. |
| Examples | Nokia-Microsoft joint venture. | Acquisition of RJR Nabisco by KKR (1988). |
Introduction: Defining Joint Ventures and Hostile Takeovers
Joint ventures involve two or more companies collaboratively pooling resources to achieve shared business objectives, fostering mutual growth and risk-sharing. In contrast, hostile takeovers occur when one company attempts to acquire another without the approval of the target's management, often through aggressive financial or legal tactics. Understanding these fundamental definitions highlights the cooperative nature of joint ventures versus the adversarial approach of hostile takeovers in corporate strategy.
Key Differences Between Joint Ventures and Hostile Takeovers
Joint ventures involve mutually agreed partnerships where two or more companies collaborate to achieve shared goals, typically involving shared ownership, profits, and risks. Hostile takeovers occur when one company attempts to acquire another without the consent of the target's management, often through a direct purchase of stock to gain control. Key differences include cooperation versus aggression, shared management in joint ventures versus unilateral control in hostile takeovers, and strategic alliance versus forced acquisition dynamics.
Strategic Objectives: Collaboration vs. Acquisition
Joint ventures prioritize collaboration by combining resources and expertise from both parties to achieve shared strategic objectives and drive mutual growth. Hostile takeovers focus on acquisition, where one company seeks to gain control of another, often against the target's will, to rapidly expand market share or eliminate competition. The collaborative nature of joint ventures contrasts sharply with the aggressive, control-seeking motives behind hostile takeovers.
Legal Frameworks Governing Joint Ventures and Hostile Takeovers
Legal frameworks governing joint ventures emphasize contract law, regulatory approvals, and antitrust compliance to ensure collaborative agreements between entities are transparent and equitable. Hostile takeovers are primarily regulated under securities law, takeover bid regulations, and shareholder rights protections to prevent coercive acquisitions. Both mechanisms operate within distinct legal parameters designed to safeguard stakeholder interests and maintain market integrity.
Risks and Rewards: Assessing Both Strategies
Joint ventures offer shared risks and combined expertise, enhancing market entry while limiting individual financial exposure; however, they require strong partnership alignment and can lead to conflicts over management decisions. Hostile takeovers allow rapid acquisition of control and potential for high returns by restructuring the target company but carry significant risks including legal battles, cultural clashes, and integration challenges. Evaluating these strategies involves balancing the collaborative growth and stability of joint ventures against the aggressive expansion and volatility associated with hostile takeovers.
Impact on Company Culture and Management
Joint ventures foster collaboration by blending organizational cultures and encouraging shared management practices, which can enhance innovation and employee morale. In contrast, hostile takeovers often disrupt company culture due to abrupt leadership changes and conflicting management styles, leading to employee uncertainty and decreased productivity. The long-term impact on company culture depends on the integration strategy post-takeover or joint venture formation, influencing retention and operational efficiency.
Financial Implications and Shareholder Value
Joint ventures typically involve shared financial risk and pooled resources, promoting stable shareholder value through cooperative growth and profit sharing. Hostile takeovers often lead to significant upfront costs, including premiums paid for acquiring control, potentially disrupting existing operations and causing volatility in shareholder value. While joint ventures aim for long-term financial gains by leveraging complementary strengths, hostile takeovers prioritize rapid market expansion, which can result in short-term financial strain and uncertain impacts on shareholder wealth.
Due Diligence and Negotiation Processes
Due diligence in joint ventures emphasizes collaborative assessment of synergies, financials, and regulatory compliance to ensure mutual benefits and aligned objectives, whereas hostile takeovers involve aggressive scrutiny of target company vulnerabilities and potential legal risks without consent. Negotiation in joint ventures centers on cooperative dialogue to establish governance structures and profit-sharing mechanisms, contrasting with hostile takeover tactics that often bypass negotiation, relying on tender offers or proxy battles to gain control. Understanding these distinct due diligence and negotiation approaches is critical for strategic decision-making in mergers and acquisitions.
Case Studies: Successful Joint Ventures vs. Notable Hostile Takeovers
The Tata Starbucks partnership exemplifies a successful joint venture, combining Tata's local market expertise with Starbucks' global brand, resulting in rapid expansion across India. In contrast, Oracle's hostile takeover of PeopleSoft in 2004, despite significant legal battles, ultimately expanded Oracle's software portfolio but highlighted high risks and resistance associated with hostile acquisitions. These case studies underscore that joint ventures often facilitate synergistic growth, whereas hostile takeovers can enable swift market dominance but entail greater conflict and uncertainty.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors Influencing Strategic Decisions
Choosing between a joint venture and a hostile takeover hinges on factors such as risk tolerance, control preferences, and long-term strategic goals. Joint ventures offer shared resources and market access with mitigated risks, ideal for collaboration and mutual growth. In contrast, hostile takeovers provide rapid market expansion and consolidated control but involve higher financial risk and potential cultural clashes.
Joint Venture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com